@1234567890
2016-10-12T11:59:06.000000Z
字数 10608
阅读 2435
concurrent包详解
java
第一部分 Atomic数据类型
这部分都被放在java.util.concurrent.atomic这个包里面,实现了原子化操作的数据类型,包括 Boolean, Integer, Long, 和Referrence这四种类型以及这四种类型的数组类型。
public class AtomicDemo {private static int count =1000;private static AtomicInteger result= new AtomicInteger(0);static class Work implements Runnable{private CountDownLatch latch;Work(CountDownLatch latch){this.latch = latch;}public void run() {try {for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {result.incrementAndGet();}}finally {latch.countDown();}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {CountDownLatch l = new CountDownLatch(2);Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Work(l));Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Work(l));thread1.start();thread2.start();l.await();System.out.println(result);}}
第二部分 锁
这部分都被放在java.util.concurrent.lock这个包里面,实现了并发操作中的几种类型的锁
public interface Lock {void lock();void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException;boolean tryLock();boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;void unlock();Condition newCondition();}
Lock接口中每个方法的使用,lock()、tryLock()、tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit)和lockInterruptibly()是用来获取锁的。unLock()方法是用来释放锁的。
锁的几个方法介绍
- lock()
就是用来获取锁。如果锁已被其他线程获取,则进行等待。必须主动去释放锁,并且在发生异常时,不会自动释放锁。因此一般来说,使用Lock必须在try{}catch{}块中进行,并且将释放锁的操作放在finally块中进行,以保证锁一定被被释放,防止死锁的发生
Lock lock = ...;lock.lock();try{//处理任务}catch(Exception ex){}finally{lock.unlock(); //释放锁}
- tryLock()
用来尝试获取锁,如果获取成功,则返回true,如果获取失败(即锁已被其他线程获取),则返回false,也就说这个方法无论如何都会立即返回。在拿不到锁时不会一直在那等待。
tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit)方法和tryLock()方法是类似的,只不过区别在于这个方法在拿不到锁时会等待一定的时间,在时间期限之内如果还拿不到锁,就返回false。如果如果一开始拿到锁或者在等待期间内拿到了锁,则返回true。
Lock lock = ...;if(lock.tryLock()) {try{//处理任务}catch(Exception ex){}finally{lock.unlock(); //释放锁}}else {//如果不能获取锁,则直接做其他事情}
- lockInterruptibly()
当通过这个方法去获取锁时,如果线程正在等待获取锁,则这个线程能够响应中断,即中断线程的等待状态。也就使说,当两个线程同时通过lock.lockInterruptibly()想获取某个锁时,假若此时线程A获取到了锁,而线程B只有在等待,那么对线程B调用threadB.interrupt()方法能够中断线程B的等待过程。
由于lockInterruptibly()的声明中抛出了异常,所以lock.lockInterruptibly()必须放在try块中或者在调用lockInterruptibly()的方法外声明抛出InterruptedException。
public void method() throws InterruptedException {lock.lockInterruptibly();try {//.....}finally {lock.unlock();}}
public class Test {private ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>();private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //注意这个地方public static void main(String[] args) {final Test test = new Test();new Thread(){public void run() {test.insert(Thread.currentThread());};}.start();new Thread(){public void run() {test.insert(Thread.currentThread());};}.start();}public void insert(Thread thread) {lock.lock();try {System.out.println(thread.getName()+"得到了锁");for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {arrayList.add(i);}} catch (Exception e) {// TODO: handle exception}finally {System.out.println(thread.getName()+"释放了锁");lock.unlock();}}}
第三部分 java集合框架中的一些数据结构的并发实现
- ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap为了提高本身的并发能力,在内部采用了一个叫做Segment的结构,一个Segment其实就是一个类HashTable的结构,Segment内部维护了一个链表数组。
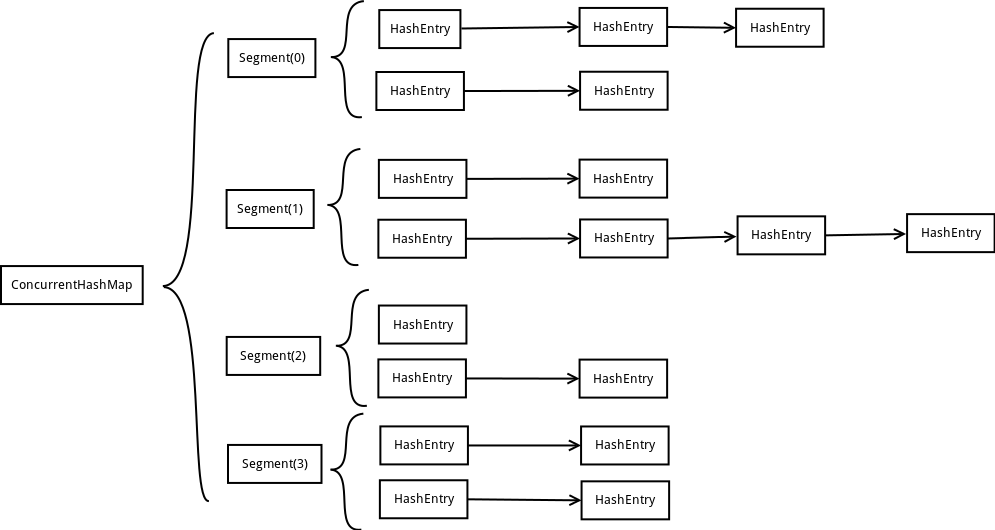
从上面的结构我们可以了解到,ConcurrentHashMap定位一个元素的过程需要进行两次Hash操作,第一次Hash定位到Segment,第二次Hash定位到元素所在的链表的头部,因此,这一种结构的带来的副作用是Hash的过程要比普通的HashMap要长,但是带来的好处是写操作的时候可以只对元素所在的Segment进行加锁即可,不会影响到其他的Segment,这样,在最理想的情况下,ConcurrentHashMap可以最高同时支持Segment数量大小的写操作(刚好这些写操作都非常平均地分布在所有的Segment上),所以,通过这一种结构,ConcurrentHashMap的并发能力可以大大的提高。
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {transient volatile int count;transient int modCount;transient int threshold;transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;final float loadFactor;}static final class HashEntry<K,V> {final K key;final int hash;volatile V value;final HashEntry<K,V> next;}
- 阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue
LinkedBlockingQUeue
boolean offer(E e); //用来向队尾存入元素,如果队列满,则等待一定的时间,当时间期限达到时,如果还没有插入成功,则返回false;否则返回true;E poll(); //用来从队首取元素,如果队列空,则等待一定的时间,当时间期限达到时,如果取到,则返回null;否则返回取得的元素;void put(E e) throws InterruptedException; //用来向队尾存入元素,如果队列满,则等待;E take() throws InterruptedException; //用来从队首取元素,如果队列为空,则等待
//以ArrayBlockingQueue为例,思路是生产者 消费者 模式public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();final E[] items = this.items;final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lockInterruptibly();try {try {while (count == items.length)notFull.await();} catch (InterruptedException ie) {notFull.signal(); // propagate to non-interrupted threadthrow ie;}insert(e);} finally {lock.unlock();}}private void insert(E x) {items[putIndex] = x;putIndex = inc(putIndex);++count;notEmpty.signal();}
- 读写分离 CopyOnWrite
CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArraySet
CopyOnWrite容器即写时复制的容器。通俗的理解是当我们往一个容器添加元素的时候,不直接往当前容器添加,而是先将当前容器进行Copy,复制出一个新的容器,然后新的容器里添加元素,添加完元素之后,再将原容器的引用指向新的容器。这样做的好处是我们可以对CopyOnWrite容器进行并发的读,而不需要加锁,因为当前容器不会添加任何元素。所以CopyOnWrite容器也是一种读写分离的思想,读和写不同的容器。CopyOnWrite并发容器用于读多写少的并发场景
缺点:
CopyOnWrite容器有很多优点,但是同时也存在两个问题,即内存占用问题和数据一致性问题。所以在开发的时候需要注意一下。
/**在添加的时候是需要加锁的,否则多线程写的时候会Copy出N个副本出来* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.** @param e element to be appended to this list* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/public boolean add(E e) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);newElements[len] = e;setArray(newElements);return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}
第四部分 多线程任务执行
| --类-- | --功能-- |
|---|---|
| Callable Runable | 被执行的任务 |
| Executor | 执行任务 |
| Future | 异步提交任务的返回数据 |
| Executors | 为Executor,ExecutorService,ScheduledExecutorService,ThreadFactory和Callable类提供了一些工具方法。 |
V call() throws Exception;
- Runable
public abstract void run();
- Future
V get() //阻塞方法,等待线程返回V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) //等待线程一段时间,如果未返回,则抛出异常
- ExecutorService
Future<?> submit(Runnable task); //如果线程运行完成,返回null<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); //返回线程运行结果void execute(Runnable command);void shutdown(); //关闭线程池
第五部分 线程管理类
这部分主要是对线程集合的管理的实现,有CyclicBarrier, CountDownLatch,Exchanger等一些类
- CountDownLatch
public CountDownLatch(int count) { }; //参数count为计数值public void await() throws InterruptedException { }; //调用await()方法的线程会被挂起,它会等待直到count值为0才继续执行public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { }; //和await()类似,只不过等待一定的时间后count值还没变为0的话就会继续执行public void countDown() { }; //将count值减1
/***比如有一个任务A,它要等待其他4个任务执行完毕之后才能执行。**/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);new Thread(){public void run() {try {System.out.println("子线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("子线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕");latch.countDown();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}};}.start();new Thread(){public void run() {try {System.out.println("子线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("子线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕");latch.countDown();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}};}.start();try {System.out.println("等待2个子线程执行完毕...");latch.await();System.out.println("2个子线程已经执行完毕");System.out.println("继续执行主线程");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
- CyClicBarrier
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {}public CyclicBarrier(int parties) {}public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException { }; //挂起当前线程,直至所有线程都到达barrier状态再同时执行后续任务public int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException,BrokenBarrierException,TimeoutException { };
/***有若干个线程都要进行写数据操作,并且只有所有线程都完成写数据操作之后,这些线程才能继续做后面的事情**/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int N = 4;CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(N,new Runnable() {//想在所有线程写入操作完之后,进行额外的其他操作可以为CyclicBarrier提供Runnable参数@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());}});for(int i=0;i<N;i++)new Writer(barrier).start();}static class Writer extends Thread{private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;public Writer(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) {this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在写入数据...");try {Thread.sleep(5000); //以睡眠来模拟写入数据操作System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入数据完毕,等待其他线程写入完毕");cyclicBarrier.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}catch(BrokenBarrierException e){e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("所有线程写入完毕,继续处理其他任务...");}}}
- Semaphore
public Semaphore(int permits) {} //参数permits表示许可数目,即同时可以允许多少线程进行访问}public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {} //这个多了一个参数fair表示是否是公平的,即等待时间越久的越先获取许可public void acquire() throws InterruptedException { } //获取一个许可,若无许可能够获得,则会一直等待,直到获得许可。public void acquire(int permits) throws InterruptedException { } //获取permits个许可public void release() { } //释放一个许可public void release(int permits) { } //释放permits个许可public boolean tryAcquire() { }; //尝试获取一个许可,若获取成功,则立即返回true,若获取失败,则立即返回falsepublic boolean tryAcquire(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { }; //尝试获取一个许可,若在指定的时间内获取成功,则立即返回true,否则则立即返回falsepublic boolean tryAcquire(int permits) { }; //尝试获取permits个许可,若获取成功,则立即返回true,若获取失败,则立即返回falsepublic boolean tryAcquire(int permits, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { }; //尝试获取permits个许可,若在指定的时间内获取成功,则立即返回true,否则则立即返回false
/***一个工厂有5台机器,但是有8个工人,一台机器同时只能被一个工人使用,只有使用完了,其他工人才能继续使用。**/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int N = 8; //工人数Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5); //机器数目for(int i=0;i<N;i++)new Worker(i,semaphore).start();}static class Worker extends Thread{private int num;private Semaphore semaphore;public Worker(int num,Semaphore semaphore){this.num = num;this.semaphore = semaphore;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("工人"+this.num+"占用一个机器在生产...");Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println("工人"+this.num+"释放出机器");semaphore.release();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
- Exchanger
Exchanger可以在两个线程之间交换数据,只能是2个线程,他不支持更多的线程之间互换数据。
当线程A调用Exchange对象的exchange()方法后,他会陷入阻塞状态,直到线程B也调用了exchange()方法,然后以线程安全的方式交换数据,之后线程A和B继续运行
public class ExchangerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Exchanger<List<Integer>> exchanger = new Exchanger<List<Integer>>();new Consumer(exchanger).start();new Producer(exchanger).start();}}class Producer extends Thread {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();Exchanger<List<Integer>> exchanger = null;public Producer(Exchanger<List<Integer>> exchanger) {super();this.exchanger = exchanger;}@Overridepublic void run() {Random rand = new Random();for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {list.clear();list.add(rand.nextInt(10000));list.add(rand.nextInt(10000));list.add(rand.nextInt(10000));list.add(rand.nextInt(10000));list.add(rand.nextInt(10000));try {list = exchanger.exchange(list);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}}class Consumer extends Thread {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();Exchanger<List<Integer>> exchanger = null;public Consumer(Exchanger<List<Integer>> exchanger) {super();this.exchanger = exchanger;}@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {try {list = exchanger.exchange(list);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}System.out.print(list.get(0)+", ");System.out.print(list.get(1)+", ");System.out.print(list.get(2)+", ");System.out.print(list.get(3)+", ");System.out.println(list.get(4)+", ");}}}
