@CLSChen
2019-08-21T01:33:34.000000Z
字数 36593
阅读 2264
Java基础
编程 JAVA
- 课本链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/184nwV1VfvKRJMiCjYZaqJQ
提取码:wyzl
第一、二章 基本程序设计
java.包.类.对象.方法 java.util.Scanner.out.ptintln
- 变量在使用之前必须初始化
System.out.println(x = 1)是正确的
相当于
int x = 1;
System.out.println(x);
- final用来声明常量 常量名称大写
final double PI = 3.14159 - 变量、方法全小写,多个单词则首字母大写——驼峰命名法
- 类首字母大写
- 常量所有字母大写 两个单词用下划线连接如 MAX_VALUE
- JAVA整数:byte、short、int、long。
浮点数:float和double。后者是前者的两倍大小。
通常情况下使用double,因为它比float精确。 - Scanner的方法 如nextByte() 读取一个byte类型的整数
Scanner input = new Scanner(system.in) - %用于除余数 如20%3=2 可以求负数 如-7%3=-1 7%-3=1
偶数%2为0而奇数总为1可以用来判断奇偶 - -5的-号是一元操作符,4-5这里的-号是二元操作符
Math.pow(a,b)可以计算a^b并返回结果,Math类隐藏在java.lang包中,此包为隐式导入的,因此,不需要在开始声明。
如System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3))- 只要两者有一个浮点数结果就是浮点数
5.0/2=2.5 5/2.0=2.5 5/2=2
整形字面值
- int 最大2147483648
- 若超过的整形字面值要在后面加
l or L来示意这个数值是long类型 如2147483648L同理1010.2d代表double1002F代表float 这里不区分大小写 - 二进制0B
0B1111=15 - 八进制0
07777=4095 - 16进制0x
0XFFFF=65535 - 数字之间加_是被允许的 如
124_123=124123
浮点型字面值
- double精确到小数点后16位 而float只到8位 因此double更加精确
科学计数法
- E即为*10 不区分大小写
- 123.456 = 1.23456E2 = 1.23456E+02
返回UNIX时间戳
System.currentTimeMillis()可以返回从1970年1月1号到现在的毫秒数- 通过毫秒数/1000可以得出秒数 秒数/60可以得出分钟数 分钟数/60为小时数 小时数/24为天数
- 通过秒数%60可以得出当前秒数 分钟数%60可以得出当前分钟数 小时数%24可以得出当前小时数
增强复制操作符
- += -= *= %= /=
- 中间没有空格!
- Java支持i++ i-- ++i --i
int a = ++i;先加了 返回新值
int a = i++;加了但返回旧值
double x = 1.0;double y = 5.0;double z = x-- + (++y);x=0.0 y=6.0 但z=7.0
5.从左到右对操作数求值 此规则高于一切
int i = 1;int k = ++i + i*3i = 2, k =8int i = 1;int k = i++ + i*3i = 2, k = 7
6.应该避免在同一个表达式中多次使用该规则防止混乱
增强类型转换
- 将数值赋给范围更大的类型——扩展类型
- 将数值赋给范围更小的类型——缩小类型——必须显式
- (类型)数值 如
(double)8为8.0 - 类型转换不改变被转换的变量 上面的8仍然是8 不会变成8.0
int sum = 0;sum += 4.5;//sum += 4.5 等价于 sum = (int)(sum += 4.5)//该式子是正确的
int i = 1;byte b = 1;//错误 必须使用显性的类型转换int i = 1;byte b = (byte)i;//正确
(int)(tax * 100) / 100 //默认——将tax向下四舍五入保留小数点后两位(int)(x + 0.5) //将任意的tax向上四舍五入==>(int)(x * 100 + 0.5)/100
软件开发过程
- 需求规范:旨在理解软件所要处理的问题,以及将软件系统的功能详细记录到文档中。
- 系统分析:旨在分析数据流,并能确定系统的输入和输出。
- 系统设计:设计一个从输入获得输出的过程。
- 实现:将系统设计翻译成程序。
- 测试:确保代码符合需求规范,并且排除错误。
- 部署:使得软件可以被使用。
- 维护:对软件产品进行更新和改进。
常见错误 P58
- 未声明、未初始化的变量和未使用的变量
- 整数溢出
- 舍入错误
- 冗余的输入对象
- 将一个对象重复定义是不行的
int a = 1;double a = 1.0;//会报错重复变量
求一个整数各位数的和 P61 2.6题解答 哦也!
package demo;import java.util.Scanner;public class Plus {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter a number between 0 and 1000:");int number = input.nextInt(); //输入一个三位数int units = number % 10; //932 % 10 = 2 并赋给个位number = number / 10; //932 / 10 = 93 修改number的值int tens = number % 10; //93 % 10 = 3number = number / 10; //93 / 10 = 9int huns = number;int plus = huns + tens + units;System.out.println(plus); //9+3+2=14}}
第三章 选择
- boolean和int相互不能转换
if(boolean){}- bool表达式必须用括号包围
if() //if后面没有分号 有分号则等于后面有一个空的块 如if{}; 这是一个逻辑错误 很难被发现{}else if(){}else if(){}else{}
- else总是与最近的if匹配 所以要尽量添加花括号
两个浮点数不能比较直接相等 可以用Math.abs()返回绝对值后定义一个极小的值来比较差距 如:
final double EPSILON = 1E-14;double x = 1.0 - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1;if (Math.abs(x - 0.5) < EPSILON) //与0.5无限接近System.out.println(x + "is approximately 0.5");
-
-
Math.random() //可以获得一个0.0到1.0之间的随机double值,不包括1.0(int)(Math.random() * 10) //因此可以获得一个0~9的整数
逻辑操作符
! //非&& //与|| //或^ //异或
- 异或:两者不同值为真 因此
p1 ^ p2 == p1 != p2
switch
switch(year % 12){ //输入一个值 不可以是判断case 1:break;case 2:break;default: ; //默认语句}
- 输入boolean值的情况
条件操作符
max = (num1 > num2) ? num1 : num2;
若是括号里的为true,则执行结果为第一个代码块,若为false,则执行结果为第二个代码块。
右边的执行完毕后,再赋值给左边的max,起到取大的效果。
操作符优先级和结合规则
所有二元操作符都是左结合的
所有的赋值运算符是右结合的 因此
a = b += c = 5 等价于 a = (b += (c = 5))先与后或再赋值
第四章 数学函数、字符和字符串
函数列表:P103 包括:
- 三角函数方法
sin(radians),asin(a),toRadians(degree),toDegrees(radians); - 指数函数方法
exp(x),log(x),log10(x),pow(a,b),sqrt(x)//x >= 0; - 取整方法
ceil(x),floor(x),rint(x),round(x) - min、max、abs方法
- random方法
a + Math.random() * b; //返回a ~ a+b之间的一个随机数,不包括a+b15 + Math.random() * 30; //返回15~44的一个随机数
字符数据类型和操作
char用于表示单个字符,用单引号扩住。
而字符串字面值必须扩在双引号中。
因此,"A"是一个字符串,'A'是一个字符。
Unicode和ASCII码
| 字符 | 十进制编码值 | Unicode值 |
|---|---|---|
'0' ~ '9' |
48~57 | \u0030~ \u0039 |
'A' ~ 'Z' |
65~90 | \u0041 ~ \u005A |
'a' ~ 'z' |
97~122 | \u0061 ~ \u007A |
char letter = 'A';char letter = '\u0041';//这两行语句等价
- 自增和自减操作符可以用在char类型变量上
char ch = 'a';System.out. println(++ch);//将输出字符b
转义 P108
\t相当于Tab 输出四个空格
\n换行符
\"双引号

字符测试

*数值转换 P109
char型数据可以转换成任意一种数值类型,反之亦然,将整数转换成char类型只用到该数据的低16位。
char ch = (char)0XAB0041;System.out.println(ch);//char为Achar ch = (char)65; //0041(16)== 65(10)System.out.println(ch);//char为A//第一个char是16进制,将其转换的原理为先截取后四位,再转换为十进制值对应十进制编码值输出。//0041(16)== 65(10),因此上面两式子是等价的。char ch = (char)0041;System.out.println(ch);//char为!//如果直接截取后四位将其作为十进制数处理,结果将不同,是错误的。
int i = (int)'A';//i is 65.
String 字符串
函数列表
从控制台输入字符串
String s = input.next() //以空格区分 字符串中不能有空格String s = input.nextLine(); //可以有空格 输入单个字符也用它
- 字符串转换为整数和浮点数
int int1 = Integer.parseInt(intString);double double1 = Double.praseDouble(doubleString);
- 整数和浮点数转换为字符串
String s = Integer.valueOf(23).toString();String s = Double.valueOf(23).toString();
- 这些方法只能通过一个特定的字符串来调用 称为实例方法 如:
s.length();
注意,这里要加括号。
如果是数组长度,则不需要加括号,如array.length
- 非实例方法称为静态方法 他们没有绑定到一个特定的对象 如Math方法:
Math.pow(2,2.5) - Java允许通过字符串字面值直接引用字符串 如:
"jfisogh".lenth();是正确的 - 可以用 + 号连接两个字符串
- 不能用 == 判断两个字符串是否相同 应该用equal方法 如:
- 非实例方法称为静态方法 他们没有绑定到一个特定的对象 如Math方法:
month == "Feb";//是错误的 它永远为falsemonth.equal("Feb");//是正确的
- 单个字符Char与字符串String是不同的 可以用双引号扩单个字符 但不能将单引号括起来的char字符赋给一个string对象 会报错为:
//类型不匹配:不能从 char 转换为 String - String类包含的获取子串的方法 和 获取子串地址的方法
格式化控制台输出printf
- 简单的格式标识符是以百分号%开头的转化码。
%10.2f输出的浮点数的宽度至少为10,包括小数点和小数点后的数字,即前面至少7位整数,小于则加空格,大于则自动增加宽度,后面保留两位小数。- %后加-可以向左对齐 加0可以在不足的地方补上0
%10.2e输出123.0为001.23e+02

第五章 循环
三种循环
while(){}---do{}while(); //只有dowhile有分号---for( ; ; ){}
无限循环错误
int i = 1;while (i < 10)if(i % 2 ==0 )System.out.println(i);//无限循环错误 没有出现自增模块int i = 1;while (i < 10)if(i % 2 == 0)System.out.println(i++);//无限循环错误 自增模块在if里没机会得到执行int i = 1;while (i < 10)if((i++) % 2 == 0) //先以i=1判断 然后在下一句语句中得到自增System.out.println(i); //在i = 2,4,6,8 得到满足//输出i = 3,5,7,9
可以通过System.currentTimeMillis()计算测试所花的时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();long testTime = endTime - startTime;System.out.println(testTime/1000);
不要比较浮点数是否相等来进行循环控制 因为浮点数是近似值
double item = 1; double sum = 0;while(item != 0){sum += item;item -= 0.1;}//item永远不可能减到完全等于0,它会跳过0向负数进发,这将是一个无限循环。
输入重定向 可以将数据存在文件中来一次性输入大量的数据值
java ClassName < input.txt//输入重定向,前面的是类名,将后面文件里面的数据导入类。java ClassName > output.txt//输出重定向,将类中产出的数据导入文件。java CLassName < input.txt > output.txt//输入输出重定向 先输入后输出 看起来就像把input文件括在里面
while和do-while循环的区别
do-while至少执行一次,某些情况下这两种会有一种更方便。
do-while改成while的话,某些语句需要在循环前和循环内重复出现以达到至少执行一次的效果。如:
while和for循环的区别
基本上都可以转换 但是for循环定义的变量是在内部,不会影响到后面的代码。
while循环定义的变量是会影响到之后的代码的。
嵌套循环
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)System.out.println(i * j);//该程序执行了多少次?//45次 = 1*1 + 2*2 + …9*9
最小化数值错误
在循环条件中使用浮点数将导致数值错误。
浮点数不够精确 可能会导致无限循环
double item = 1; double sum = 0;while(item != 0){sum += item;item -= 0.1;}//item永远不可能减到完全等于0,它会跳过0向负数进发,这将是一个无限循环。for(double i = 0.01; i ,<= 1.0; i = i + 0.01)sum += i;// i可能最后会比1稍微大一点,而这将导致最后一次求和失败!数据偏差将会很大。
十进制转换16进制并且在最后通过用户标记控制循环!
package demo;import java.util.Scanner;public class Dec2Hex {public static void main(String[] args) {char a = ' ';do {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Please input a Dec:");int dec = input.nextInt(); //将十进制数存入dec变量String hex = " "; //定义一个空字符串do{int hexValue = dec % 16; //个位等于十进制数对16取余char hexDigit = (0 <= hexValue && hexValue <= 9) ?(char)(hexValue + '0') : (char)(hexValue - 10 + 'A');//定义一个字符,如果个位在0~9之间,则将其与'0'相加,//此时的答案是一个ASCII码,如45。//再通过char将其转化为字符,如'2'。//如果在10到16之间,则通过 - 10 + 'A'来计算。//如11 => 66 => Bhex = hexDigit + hex;//将其插入空字符串的前面//注意:此处后面两个变量位置不能互换。dec = dec / 16;//新的十进制数由十进制数除以16得出}while(dec != 0);//直到dec/16为0为止,也就是dec<16为止//此时的dec就是16进制的最大位数上的数System.out.println("The hex number is:" + hex);System.out.print("Put Y to continue and N to exit:");a = input.next().charAt(0);//取一个字符串,并返回它的第一个字符给a。}while(a == 'Y');//如果a为'Y',则重新开始第一个循环。}}
break和continue 和if配合使用
break跳出整个循环
continue跳出一次循环 直接下一次
第六章 方法
方法定义
- 在其他语言中,方法也成为过程或者是函数。
- 在方法头中,需要对每一个参数进行单独的数据类型说明。即每个参数前都要说明它是哪种类型,int还是别的什么。
- 其他类可以通过类名.方法名来调用你在这个类里定义的方法,如TextMax.max。
- 每当调用一个方法时,系统会创建一个活动记录(也称为活动框架),用于保存方法中 的参数和变量。活动记录置于一个内存区域中,称为调用堆栈(call stack)。
- 函数参数的使用和栈“后进先出”的特性有关,m1引用了m2,m2引用了m3,则先处理m3,再处理m2,再处理m1。
- 无论形参在方法中作何改变,该变量都不受影响。
- 霍纳算法

package demo;import java.util.Scanner;public class Hex2Dec {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter a hex number: ");String hex = input.nextLine();System.out.println("The decimal value for hex number "+ hex + " is " + hexToDecimal(hex.toUpperCase()));}public static int hexToDecimal(String hex){int decimalValue = 0;for (int i = 0; i < hex.length(); i++){char hexChar = hex.charAt(i);decimalValue = decimalValue * 16 + hexCharToDecimal(hexChar);}return decimalValue;}public static int hexCharToDecimal(char ch){if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'F')return 10 + ch - 'A';elsereturn ch - '0';}}
- 方法可以重载(同名),一个类中有两个方法,它们具有相同的名字但有不同的参数列表,是可以的。Java编译器通过方法签名决定使用哪个方法。
注意:必须是具有不同的参数列表才行,不同修饰符或者返回值类型不行。 - 生成任意两个字符ch1和ch2之间的随机字符 P194
输出一个数的反序数(ReverseNumber)
package demo;import java.util.Scanner;public class ReverseNumber {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Please inter a int number: ");int number = input.nextInt();reverse(number);}public static void reverse(int number){StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(number + "");//利用StringBuilder方法来新建一个string字符串以方便修改int length = str.length();for(int j = 0,k = 1; j < length - 1; j++,k++) {//一共循环长度-1次,并定义k变量来每次排序后将排序位数减一for (int i = 0; i < length - k ; i++){ char a = str.charAt(i);char b = str.charAt(i + 1);str.setCharAt(i , b);//利用setCharAt方法str.setCharAt(i + 1 , a);//将提取出来的两个位置上的字符互换}}System.out.println("The inversion number is: "+ str);}}
第七章 一维数组
- 可以用
double[] myList;或者double myList[];来声明数组变量。 - 注意:数组变量不是数组。
- 接下来可以使用new操作符创建数组,并且将它的引用赋给一个变量。
如myList = new double[10];
这样,myList指向一个大小为10的数组,才是一个合格的数组变量。 - 以上的语句可以合并为一句完成:
double myList[] = new double[10];
- 该语句声明了数组变量myList,创建了一个由10个double型元素构成的数组,
并将该数组的引用赋值给myList。
myList是一个含有double型元素数组的引用变量。 - 可以使用赋值法给数组赋值。
myList[0] = 5.6; - 数组创建了就不能修改它的大小,可以使用
arrayRefVar.length获取大小
如myList.length为10。 - 数值型默认为0,char型默认为'\u0000',boolean型的默认值为false,也有字符串数组。
- 数组初始化简写方式:
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};//这条语句声明、创建并且初始化包含4个元素的数组myList。//大括号!!!//该语句相当于double[] myList = new double[4];myList[0] = 1.9;myList[1] = 2.9;myList[2] = 3.4;myList[3] = 3.5;
- 打印数组需要使用for循环:
for(int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");//数值类型的数组需要for循环。char[] city = {'a','a'};System.out.print(city);//char类型的数组可以直接打印。
数组数值处理 P216
- 随机初始化数组
- 显示数组
- 对所有元素求和
- 找出最大元素
- 找出最大元素的最小下标值
- 随机打乱
- 移动元素
- 简化编码
foreach循环
for (double e : myList)System.out.print(e);//对myList中每个元素e进行以下操作,即遍历整个数组。//注意:变量e的数据类型必须与数组类型相同。
复制数组
- 利用for循环逐个复制
- 利用静态方法arraycopy(注意此方法copy的c没有大写)
arraycopy(原数组,原数组起始位置,目标数组,目标数组起始位置,元素个数)System.arraycopy(sourceArray, 0, targetArray, 0, sourceArray.length);System.arraycopy(source, 0, t, 0, source.length);//用此方法前要先声明目标数组并分配内存空间。
数组传递给方法后值会改变
- 对于基本数据类型参数,传递的是实参的值。
- 而对于数组,传递的是引用。最好的描述为传递共享信息。
- 比如:要使用方法来改变数组,最好把数组传进去,不要使用数组下标的类型如int来定义方法参数。
- 如
swap(a[0], a[1])public static void swap(int a1, int a2){}//这样改变的只是实参,而不会涉及数组。 ×swap(a)public static void swap(int[] array){}//这样传递的是整个数组。 √
可变长参数列表
- 在指定类型后紧跟省略号如(double…numbers)
- 只能给方法中指定一个可变长参数。同时该参数必须是最后一个参数。
public static viod printMax(double…numbers) {if (numbers.length == 0)System.out.println("No argument passed");return;}
二分查找法 需要先从小到大排好序
package demo;public class BinarySearch {//二分查找法(不含main函数)public static int binarySearch(int[] list, int key) {int low = 0;int high = list.length - 1;while (high >= low) { //此处不能用 > ,不然对只有一个元素的数组无法处理。int mid = (low + high) / 2;if (key < list[mid])high = mid - 1;else if (key == list[mid])return mid;else {low = mid + 1;}}return -low-1;}}
选择排序算法
package demo;import java.util.Scanner;public class SelectSort {//选择排序算法:从所有数中选择最小的与第一个交换。public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int[] list = { 5, 2, 3, 7, 9, 8, 1 };for (int j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {//用j < list.length 也可运行,但是要多运算一步。int min = list[j];//将第一个值赋给min,后面的值与其比较。int tag = j;for (int i = j + 1; i < list.length; i++) {//用i = j也可运行,但是要多运算一步。if (list[i] < min) {min = list[i];//记录最小值。tag = i;//标记最小下标。}}list[tag] = list[j];list[j] = min;//将当前最前面的值于min所处位置的值交换。}for (int e : list)System.out.println(e);//for each循环输出。}}
Arrays类
- 使用import.util.Arrays导入
Arrays.sort(list, indexStart, indexEnd);//从小到大对start和end里面进行排序,不包括end。Arrays.parallelSort();//同上,但是多处理器这个会快些。Arrays.binarySearch();//二分查找法,必须提前按升序排好。Arrays.equals(list1, list2);//严格比较相等,一对一。Arrays.fill(list1, 5);//使用5填充整个数组。Arrays.fill(list1, 1, 5, 8);//使用8填充1至5地址,不包括5。Arrays.toString(list);//将数组返回成一个字符串。
向main方法传递参数
main就像一个普通的函数,它可以接收字符串args。
不仅可以直接在其他类调用它,还可以从命令行向他传递参数。
第八章 多维数组
多维数组的定义
int[][] matrix;matrix = new int[5][11];//两句可以合并成一句:int[][] matrix = new int[5][12];
注意:第一个下标表示行数,第二个下标表示列数。
注意:每个下标必须放在一对方括号中。
matrix[2][14] = 7; //是正确的matrix[2,7] = 7; //是错误的
- 二维数组实际上就是很多一维数组的集合。
它的每一行都是一个一维数组,所以它的长度为一维数组的个数。
每个一维数组又有自己的长度,都可以用array.length表示
array.length//行数array[0].length//第一行的长度
二维数组初始化
int[][] array ={{1,2,3},{1,2,3},}int[][] array2 ={{1,2,3},{1,2},}//不规则数组是被允许的如果不想一开始就给不规则数组赋值 可以使用空括号int[][] array = new int[5][];//第一个括号必须有值。
处理二维数组 P251
- 嵌套的for循环常用来处理二维数组。
- P251
1.使用输入值初始化数组。
2.使用随机值初始化数组。
3.打印数组
4.对所有元素求和
5.按列求和
6.哪一行的和最大?
7.随机打乱
将二维数组传递给方法
- 将一个二维数组传递给方法时,数组的引用传递给了方法。
package demo;import java.util.Scanner;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] m = getArray();System.out.println("\nSum of all elements is " + sum(m));}// 返回一个二维数组public static int[][] getArray() {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int[][] m = new int[3][15];System.out.println("Enter " + m.length + " rows and " + m[0].length + " columns: ");for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++)for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++)m[i][j] = input.nextInt();return m;}// 对一个二维数组求和public static int sum(int[][] m) {int total = 0;for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++)total += m[i][j];}return total;}}//for(int e :list)//System.out.print(e);
矩阵乘法!哦也!
package demo2;import java.util.Scanner;public class MultiplyMatrix {//矩阵乘法public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("请输入第一个矩阵的行数和列数,如(2 3):");int arow = input.nextInt();int acol = input.nextInt();int[][] a = new int[arow][acol];System.out.print("请输入第二个矩阵的行数和列数,如(2 3):");int brow = input.nextInt();int bcol = input.nextInt();int[][] b = new int[brow][bcol];if (arow != bcol) {System.out.print("Input invalid.");System.exit(0);}System.out.println("请输入第一个矩阵的数值:");for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {a[i][j] = input.nextInt();}}System.out.println("请输入第二个矩阵的数值:");for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < b[0].length; j++) {b[i][j] = input.nextInt();}}int[][] c = multiplyMatrix(a, b);for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < c[0].length; j++) {System.out.print(c[i][j] + " ");}System.out.println();}}public static int[][] multiplyMatrix(int[][] a, int[][] b) {if (a.length != b[0].length) {System.out.print("The input is invalid.");return null;}int[][] c = new int[a.length][b[0].length];int length = a.length;for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {for (int j2 = 0; j2 < a[0].length; j2++) {c[i][j] += a[i][j2] * b[j2][j];}}}return c;}}
第九章 对象和类
UML类图详解:https://www.cnblogs.com/pangjianxin/p/7877868.html
Date类和Random类、Print2D类

静态方法和静态数据 static
- 静态方法用static修饰如
static int getNumberOfObjects() {return numberOfObjects;}可以直接通过类名调用而不用声明对象Circle.getnumberOfObjects;
- 注意:实例方法可以调用静态方法,而静态方法不能调用实例方法。
- 如:在main函数中不声明新对象调用实例方法和实例变量是错误的,因为对象都没有被创建,并且main函数是static方法。
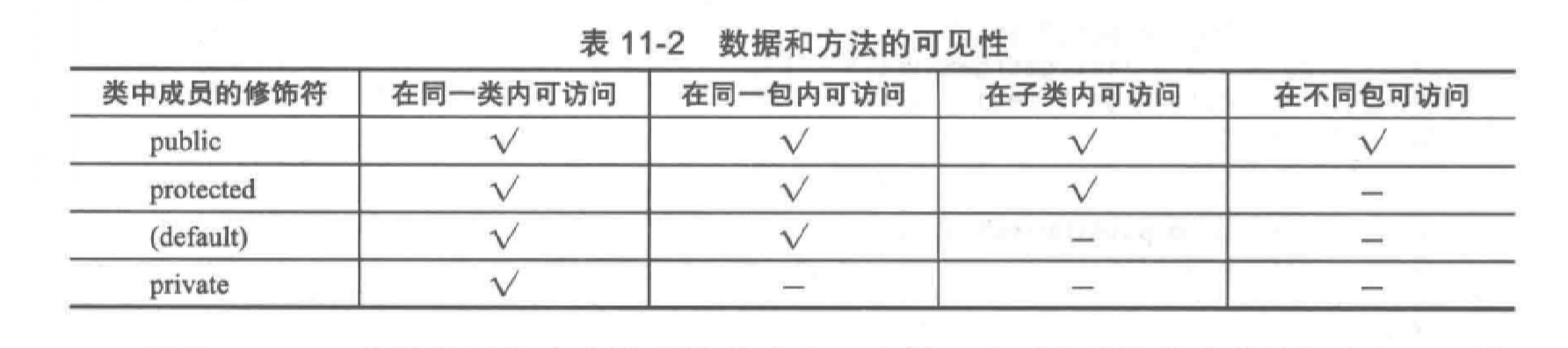
可见性修饰符
- public修饰的方法和变量可以被包外访问。
- 不加前缀的只能在包内访问。
- private修饰的包内都不能访问。
对象数组
- 数组可以装载对象,但是一定要记得对里面的每一个成员初始化。
Circle[] cir = new Circle[5];for (i = 0; i < Circle.length; i++) //创建一个新数组。cir[i] = new Circle(); //为每一个成员初始化。
不可变对象
- 如果一个类是不可变的,那么它的所有数据域必须都是私有的,而且没有对任何一个数据域提供公共的set方法。
- 但是!一个类的所有数据都是私有的且没有修改器并不意味着它一定是不可变类。
如果有一个函数传出了对类内对象的一个引用,那么就可以通过修改这个引用来修改类内的对象。如:
public class Student{private java.util.date dateCreated;public java.util.Date getDateCreated{return dateCreated;}}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){Student student = new Student(m223333, "John");java.util.Date dateCreated2 = student.getDateCreated();// 传出了dateCreated对象的引用// dateCreated2和dateCreated其实指向的是同一个对象dateCreated2.setTime(200000);// 达到修改对象的目的
因此要创建一个不可变对象,要满足三点:
- 所有数据都是私有的。
- 没有set方法。
- 没有一个返回指向可变数据域的引用的访问器方法。
变量的作用域
- 一个类的实例变量和静态变量称为类变量(class’svariables)或数据域(data field)。在方法内部定义的变量称为局部变量。
- 如果一个局部变量和一个类变量具有相同的名字,那么局部变量优先。而同名的类变量将被隐藏(hidden)
this引用
https://blog.csdn.net/Return_head/article/details/80744056
1.假如在一个构造方法中使用了this语句,那么它必须作为构造方法的第一条语句(不考虑注释语句)。
2.只能在一个构造方法中使用this语句来调用类的其他构造方法,而不能在实例方法中用this语句来调用类的其他构造方法。
3.只能用this语句来调用其他构造方法,而不能通过方法名来直接调用构造方法。
第十章 面向对象思考
- Java对象——依赖、关联、聚合和组合之间的区别与理解
https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghuaijun/p/5421419.html
将基本数据类型值作为对象处理——包装类 P349

BigInteger and BigDecimal
- BigInteger用于处理大数据,它继承自
java.math.BigInteger。
初始化:BigInteger sum=new BigInteger("0");加法:sum=sum.add(n1); //这里sum和n都为BigInteger类型减法:sum=sum.subtract(n1);乘法:sum=sum.multiply(n1);除法:sum=sum.divide(n1);幂运算:sum=sum.pow(10);取相反数:sum=sum.negate();
- 同理,BigDecimal是处理浮点数的大数据运算,继承自
java.math.BigDecimal.
初始化:BigDecimal num1=new BigDecimal("1234.56453324");加法:sum=sum.add(n1); //这里sum和n都为BigDecimal类型减法:sum=sum.subtract(n1);乘法:sum=sum.multiply(n1);除法:sum=sum.divide(n1);将BigDecimal类型转换为double类型:num1.doubleValue();比较大小:num1.compareTo(num2);//小于时,返回-1; 等于时,返回0; 大于时,返回1。四舍五入处理:num1.divide(num2,scale,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();//scale表示保留几位小数
String类
String类源码:
https://blog.csdn.net/ylyg050518/article/details/52352993
构造字符串
String message = new String("hello");// 一般用法String message = "hello";// Java将字符串直接看做String对象,这样也合法。
不可变字符串与限定字符串
- String对象是不可变的,当你把一个String对象的“字面”改变,实际上只是改变了它的引用,将其引用给一个新的对象,而原来的对象被抛弃。
String s = "Java";s = "HTML": ;// "Java"对象被抛弃,s引用为新的string对象"HTML"。
- Java 虚拟机为了提高效率并节约内存,对具有相同字符序列的字符串直接量使用同一个实例。
String s1 = "Welcome to ]ava";String s2 = new String("Welcome to ]ava");String s3 = "Welcome to ]ava";//s1 == s3, s1 != s2;
字符串的替换和分隔

- 注意:replace用来替换字符,而replaceAll用来替换字符串。
str.replace('a','b');str.replaceAll("ab","abc");
- 一旦创建了字符串,它的内容就不能改变。但是,方法 repalce、replaceFirst和replaceAll会返回一个源自原始字符串的新字符串(并未改变原始字符串!)。
- split 方法可以从一个指定分隔符的字符串中提取标识。
String[] tokens = "Java#HTML#Perl".split("#");for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++)System.out.print(tokens[i] + " ");// split将字符串分割成了三个小字符串并存入数组。//显示Java HTML Perl
正则表达式
- JAVA 正则表达式 (超详细):
https://www.cnblogs.com/xyou/p/7427779.html - Java正则表达式的语法与示例:
https://www.cnblogs.com/lzq198754/p/5780340.html - String类自带的matches方法就可以使用正则表达式
"Java".matches("Java");"Java is fun".matches("Java.*");"Java is cool".matches("Java.*");//字符串.*与零个或多个字符相匹配。// . 任意字符 *任意长度String s = "a$b%c^".replaceAll("[$%^]","NNN");System.out.println(s);//aNNNbNNNcNNNString[] tokens - "Java.C?C#,C++".split("[.,:;?]");for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) System.out.println(tokens[i]+" ");//Java C C# C++
字符串与字符数组的相互转换
- 字符串转换为字符数组。
char[] a = "Java".toCharArray();char[] dst = {'J','A','V','A','1','3','0','1'};"CS3720".getChars(2,6,dst,4);//dst{'J','A','V','A','3','7','2','0'};
- 字符数组转换为字符串
String str = new String(new char[]{'a','a'});// 可以直接使用构造方法。String str = String.valueOf(new char[]{'a','a'});// 也可以使用valueOf方法。
字符串和数值的相互转换
- 可以使用包装类中的方法将字符串转换为数值,如:
Double.parseDouble(str);Integer.parseInt(str);
- 可以使用valueOf方法转换回字符串
String a = String.valueOf(5.44);//a:{'5','.','4','4'}
格式化字符串
String s = String.format("%7.2f%6d%-4s", 45.556, -4s, "AB");System.out.println(s)//□□45.56□□□□14AB□□注意System.out.printf();等价为System.out.print(String.format());
StringBuilder And StringBuffer Class
- 效率:stringBuilder > stringBuffer > String;但是StringBuilder线程不安全,StringBuffer线程安全;
- Java中的String,StringBuilder,StringBuffer三者的区别:
https://www.cnblogs.com/su-feng/p/6659064.html

append重载方法
StringBuilder StringBuilder = new StringBuilder();stringBuilder.append("Welcome");stringBui1der.append(' ');stringBuilder.append("to");stringBui1der.append(' ');stringBui1der.append("Java");//"Welcome to Java"
insert、delete、deleteCharAt、reverse、replace、setCharAt重载方法
//"Welcome to Java"StringBuilder.insert(11, "HTML and ");//"Welcome to Html and Java"
stringBui1der.delete(8,11) // Welcome Java。stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(8) // Welcome o Java。stringBuilder.reverse() // avaJ ot emocleW。stringBuilder.replace(11,15,"HTML") // Welcome to HTML。stringBuilder.setCharAt(0,'w') // welcome to Java
toString、capacity、length、setLength和charAt构建器和返回方法

去除字符串中除了数值和字母的字符并判断是否为回文
package demo2;import java.util.Scanner;public class PalindromelgnoreNonAlphanumeric {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("input a string: ");String s = input.nextLine();System.out.print(s + " " + isPalindrome(s));}public static boolean isPalindrome(String s) {StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder();//将字符串转换为stringbuilder对象for(int i = 0; i<s.length();i++) {if(Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(i))) {//使用character类中的方法来判断是否为数字和字母//也可以使用编码。s1.append(s.charAt(i));}}StringBuilder s2 = s1;s2 = s2.reverse();return s1.equals(s2);}}
String类的实现 oh yeah!
package demo2;public class MyString1 {private final char value[];public static void main(String[] args) {// char[] a = "Hello World".toCharArray();// MyString1 s = new MyString1(a);// char[] b = "Hello World".toCharArray();// MyString1 s2 = new MyString1(b);System.out.print(MyString1.valueOf(123455).value);}public MyString1(char[] chars) {value = chars;//源码中用copy实现}public MyString1() {this.value = new char[0];}public char charAt(int index) {return value[index];}public int length() {return value.length;}public MyString1 substring(int begin, int end) {char[] newValue = new char[end - begin];for (int i = begin, j = 0; i < end; i++, j++) {newValue[j] = value[i];}MyString1 s1 = new MyString1(newValue);return s1;}public MyString1 toLowerCase() {MyString1 s1 = new MyString1(value);for (int i = 0; i < s1.value.length; i++) {if (s1.value[i] >= 'A' && s1.value[i] <= 'Z') {s1.value[i] = (char) (s1.value[i] - 'A' + 'a');}}return s1;}public boolean equals(MyString1 s) {boolean isequal = true;if (s.length() != value.length) {return false;}for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {if (s.value[i] != value[i])isequal = false;}return isequal;}public static MyString1 valueOf(int i) {int digit = 1;int k = i;while (k / 10 > 0) {digit++;k = k / 10;}char[] ch = new char[digit];for (int j = digit - 1; j >= 0; j--, i = i / 10) {if (j == 0) {ch[j] = (char)(i + 48);} else {ch[j] = (char)((i % 10) + 48);}}return new MyString1(ch);}}
第11章 继承和多态
继承
public class Circle extends CeometricObject// Subclass 继承于 Superclass
- 父类的普通方法由子类继承。但是私有数据域和构造方法不继承。子类虽然也有这些数据域,但是得用set和get访问它。构造方法可以使用super关键字访问。
- 因为子类拥有父类的数据域,因此不能随意定义子类。如:正方形是一种矩形。但不能用正方形类去继承矩形类,因为矩形的长宽数据域在正方形中并没有意义。
- Java中,如果使用extends来继承,子类只允许有一个父类。即不允许多重继承。
使用super关键字
- 关键字
super用来指代上一个父类,可以用来调用父类的普通方法和构造方法。 - 注意:不能用来调用静态方法!
静态方法直接使用父类名调用即可。 - 子类调用父类的构造方法只能使用
super,而不能使用构造方法名。
普通函数super.toString();Superclass.toString();// 等价构造函数super();// 正确Superclass();// 错误!在子类中不能直接用函数名调用父类的构造函数,只能使用super。
- 语句
super()和super(arguments)必须出现在子类构造方法的第一行。 - 如果子类构造方法没有使用
super,那就会默认在第一行加入隐形的super函数(无参),来调用父类的无参构造方法。
public ClassName(double a){//some statements}等价于public ClassName(double a){super();//some statements}
因此,如果父类没有无参构造方法,会出现一个错误。
- 当构造一个子类的对象时,子类构造方法会在完成自己的任务之前,首先调用它的父类的构造方法。如果父类继承自其他类,那么父类构造方法又会在完成自己的任务之前,调用它自己的父类的构造方法。
- 这就是构造方法链。
问题:子类继承了父类的普通方法,那为什么还要用super调用父类的普通方法?
- 因为存在方法重写,子类可能会改变从父类那继承的方法,要调用原汁原味的父类方法,只能使用super。
方法重写
POINT:
要重写一个方法,需要在子类中使用和父类一样的签名以及一样的返回值类型来对该方法进行定义。
- 方法重写就是把父类的普通方法重新定义,除了{ }里头不同看起来全都一样。
- 方法重载可以在同一个类也可以是子类和父类,除了{ }里头不同括号( )里的参数也不同。
- 注意:两个方法都没有用更改返回值类型和方法名。
重写标注:@Override
- 该标注重写一个方法,在该标注后的方法必须被重写,否则会报错。
- 好处:系统会帮你检测重写是否成功,不然如果出错,系统可能只会以为这是你新定义的一个方法。
Object类与toString( )方法和equals()方法
Java中的所有类都继承自java.lang.Object类。
- == 和 equals的区别:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hJRx42sQs5i0NHMQj3_m4A
- 因此Object类是所有类的父类,他其中有toString()方法。
- 一般情况下,toString( )返回 [类名@地址]
这没有什么用,因此一般需要重写toString( )方法。
Object类中的euqals()方法用来测试两个对象是否相等
object1.equals(object2);
默认的equals只能判断两个是否指向同一对象。
- 这也没什么用,因此也需要重写equals方法。如将圆类的equals方法定义为比较半径大小,如果相等则返回true。
注意,在object类中,equals的参数是object类,因此重写的时候要遵循这个规则。
public boolean equals(Circle o){} //是错误的public boolean equals(Object o){} //是正确的
例子:
public class Text {public static void main(String[] args) {Object a = new Circle();Object b = new Circle();System.out.print(a.equals(b));}1.public class Circle {double radius;public boolean equals(Object circle) {return this.radius == ((Circle) circle).radius;}}// 输出为true。两者的半径相同。2.public class Circle {double radius;public boolean equals(Circle circle) {return this.radius == circle.radius;}}// 输出为false。它根本就没有调用Circle里的这个euqals方法,因为传入的值是object类型,它直接调用了Object类中的equals去了!因为比较的是引用,两者没有指向同一个变量,所以为false。
多态
面向对象程序设计的三大支柱是封装、继承和多态。
- 总可以将子类的实例传给需要父类型的参数。
- 即:方法参数只需要要求了父类型,所有的子类型对象都可以传进方法。
动态绑定
方法可以在沿着继承链的多个类中实现。JVM决定运行时调用哪个方法。
Object o = new GeometricObject();//声明类型 实际类型
- 现在实际类型中寻找方法,找不到就在父类中找,直到找到为止。以找到的第一个为准。
对象转换和instanceof运算符
对象转换和强制类型转换很像。可以将子类隐式转换为父类,但父类下来必须用强制转换。就像byte可以直接转换为int,但是int赋值给byte而不用(int)byte就会出错。
Object o = new Student;// 可以将一个Student对象的引用赋给object变量Student b = o;// 错误!原因是Student对象总是Object的实例,但是,Object对象不一定是 Student的实例。// 即使可以看到o实际上是一个Student的对象,但是编译器还没有聪明到知道这一点。Student b = (Student)o;
转换记住左大右小。
- 使用instanceof关键字
Object a = new Circle();if(a instanceof Circle){// *使用instanceof关键字*来确定这个实例是不是这个类的实例。System.out.print(((Circle)a).getYou());}// 然后再将Object变量的*引用强制转换*为对Circle对象的引用,才能调用Circle中的getYou方法。
即使需要进行如此复杂的对象类型转换,一开始也要定义为父类(Object),这样,它就能接受任意子类型的值。
- 如:我们可以定义一个方法,其参数为object对象,在方法内再进行对象类型判定,这样可以简化参数。
- 注意:圆点运算符的优先级高于类型转换,因此,要将对象用括号括起来。如:
((class)a).getYou(); - 虽然它和基本类型强制转换很像,但是基本类型强制转换会返回一个新的值,而对象类型转换只是将引用转移。
- 总是可以将子类的实例转换为父类。比如:苹果总是水果。
ArrayList类
可以创建一个数组存储对象,但是这个数组一旦创建,它的大小就固定了。
因此,Java提供ArrayList类来存储不限定个数的对象。
即可变对象列表(不叫数组)。

- ArrayList类在java.util包中,因此要导入该包
import java.util.ArrayList
- 创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Class> a = new ArrayList<Class>();JDK1.7后也可以简写为ArrayList<Class> a = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList虽然和数组很像,但是还是有不同之处。
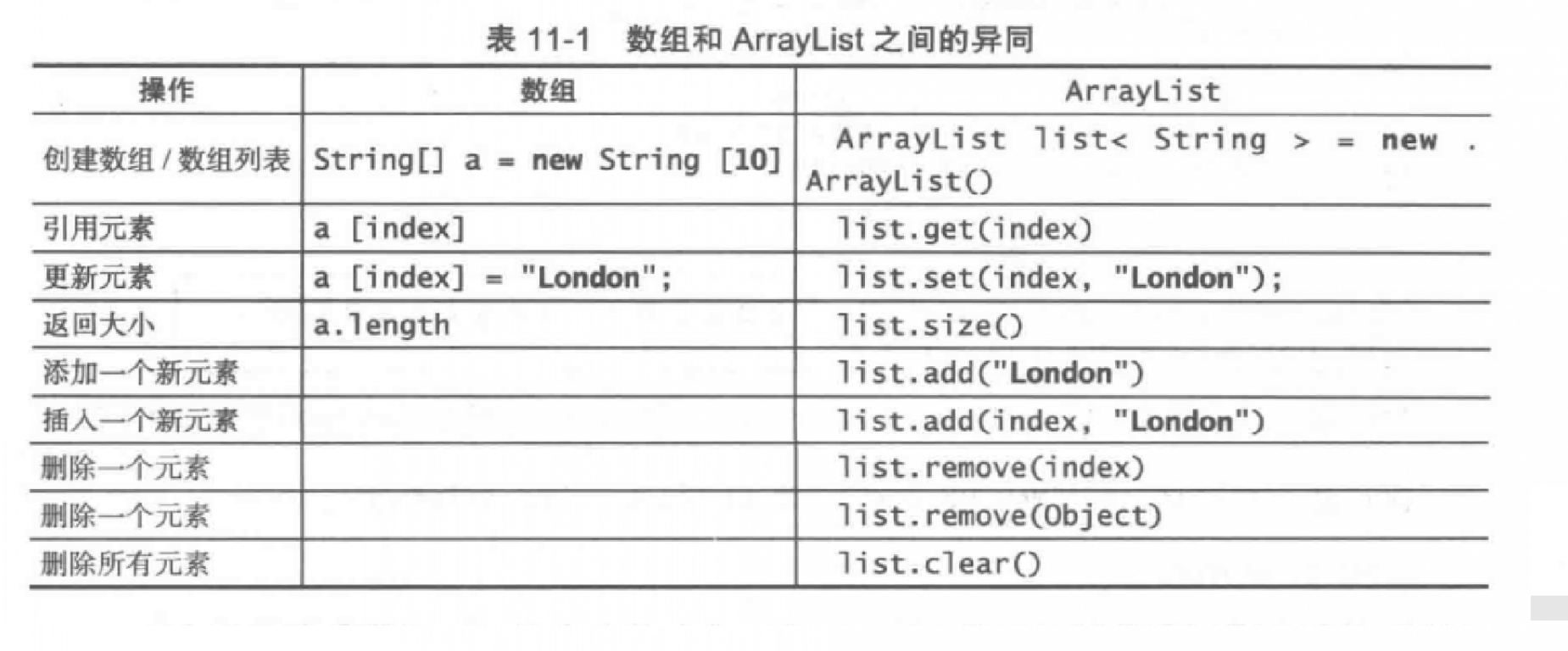
ArrayList和数组可以相互转换。
将数组转换为列表String[] a = {"a","b","c"};ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(a));// 使用Arrays类中的静态方法asList()。将列表转换为数组String[] b = new String[list.size()];list.toArray(b);// ArrayList类中的普通方法toArray()将list中的元素复制到数组内。
java.util.Collections类中有一些有用的方法。如:排序,最大值,随机打乱。
import java.util.CollectionsIntege [] array = {3, 5, 95, 4, 15, 34, 3, 6, 5};ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(array));Collections.sort(list);// 排序Collections.max(list);Collections.min(list);Collections.shuffle(1ist);// 随机打乱
protected数据和方法
一个类中的受保护成员可以从子类中访问。
在UML类图中,protected的方法前面加#
例子:
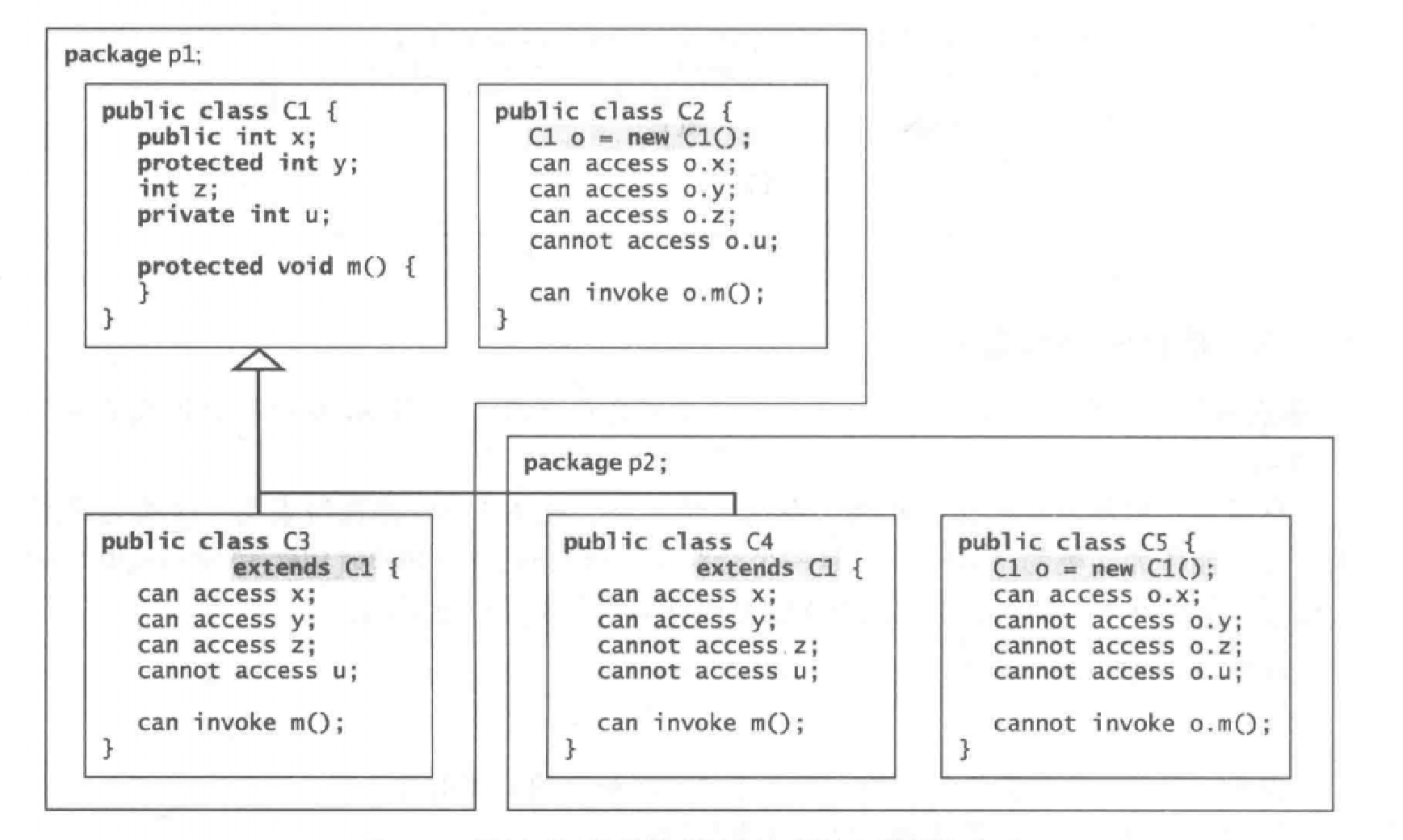
可以看出,protected只比默认开放一点点,只是增加了在继承类中可以访问,而在不同包里仍不可以访问。而同一个包里不管继不继承,只要不是private就可以访问
第12章 异常处理和文本I/O
异常是从方法抛出的。方法的调用者可以捕获以及处理该异常。
异常需要消耗系统资源,因此,可以预料的错误尽量使用if。
并且,不要将异常处理当做简单的逻辑测试。
- 可以在方法中抛出一个异常,异常就是异常类的一个对象。
- 如果一个异常没有被当前方法捕获,则该异常被传给调用者。这个过程不断重复直到异常被捕获或者传递给main 方法。
- 在抛出错误后
try字块内之后的语句就不会再运行。
public static int quotient(int num1,int num2){if (num2 == 0){throw new ArithmeticException("Divisor can not be Zero. ")}return num1 / num2;}public static void main(String[] args){try{int result = quotient(1, 0);System.out.print(result);} //如果遇到异常,则抛出一个异常对象,并被catch捕获。catch(ArithmeticException ex){//程序跳转至catch功能块,并在处理完catch块后接着往下运行。System.out.print("Invaild input. ")}}
- 异常类型:系统错误、异常、运行时异常。


- RuntimeException、Error和他们的子类都被称为免检异常。所有其他异常都被称为必检异常。
免检异常通常为逻辑错误,可能在程序的任何一个地方出现,为了避免过多的使用try-catch块,不强制要求编写代码捕获或者声明免检异常。 - 不管是否在方法头中声明,每个方法都能抛出 RuntimeException 异常(免检异常)。
声明异常,抛出异常和捕获异常
- 为了在方法中声明一个异常,需要使用关键字
throws
public void method() throws IOException//多个异常public void method()throws IOException,Exception2,Exception3...ExceptionN
- 程序可以创建异常类的一个实例并抛出它
IllegalArgumentException ex = new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong Argument");throw ex;//可以使用简写throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong Argument");
- 注意:声明异常的关键字是
throws,抛出异常的关键字是throw。 - 异常类包含一个无参构造方法和带字符串的构造方法。可以用
getMessage()获取。
- 使用try-catch块来捕获异常
try{statements;}catch (Exception1 exVarl){handler for exceptionl;}catch (Exception2 exVar2){handler for exception2;}..catch (ExceptionN exVarN){throw exVarN;// Java允许重新抛出异常。}//JDK7的新的多捕获特征可以用来简写catch(Exception1 | Exception2 | ... | ExceptionN){//same handling these exceptions}
- 一个通用的父异常类可以衍生出各种子类,因此,如果父类可以被catch捕获,他的所有子类都会被捕获。
- 因此,不能将父类的catch块放到子类之前,编译将不会通过。
从异常中获取信息
- 可以使用java.lang.Throwable类中的实例方法来打印异常信息。
- Throwable是所有异常类的根类,因此所有异常类都可以调用它的这些方法。

finally子句
- 无论异常是否产生,finally子句总是会被执行。
- 即使前面有return语句也不例外。
try{statements;}catch(TheException ex){handling ex;}finally{finalStatements;}
链式异常
和其他异常一起抛出一个异常,形成了链式异常。
catch(Exception ex){throw new Exception("new error", ex);}
创建自定义异常类 P426
可以通过派生java.lang.Exception类来定义一个自定义异常类。
public class InvalidRadiusException extends Exception {private double radius;● public InvalidRadiusException(double radius) {● super("Invalid radius " + radius);//调用父异常类Exception的构造方法。this.radius = radius;}public double getRadius() {return radius;}}
File类 文件处理
java.io.File类包含了获得一个文件/目录的属性,以及对文件/目录进行改名和删除的方法。
- 绝对文件名:由文件名和他的完整路径以及驱动器字母组成。
c:\book\Welcome.java
绝对文件名是依赖机器的,
而相对文件名是相对于当前工作目录的。
- 相对文件名
Welcome.java如果当前工作目录是c:\book绝对文件名: c:\book\Welcome.java
- 新建File对象可以是一个目录或者文件,尽量不要使用绝对文件名,因为这样它将不能在其他平台上工作。
- 注意:构建一个File类实例并不会在机器上创建一个文件。可以调用File实例上的exists()方法来判断这个文件是否存在。
- 目录分隔符的区别
Windows:" \ "// Java中,反斜杠要写成"\\"new File("c:\\book\\test.dat")
Unix: " / "// Java支持直接使用"/"new File("c:/book/test.dat")
- File类的UML类图

文件输入和输出(文本文件)
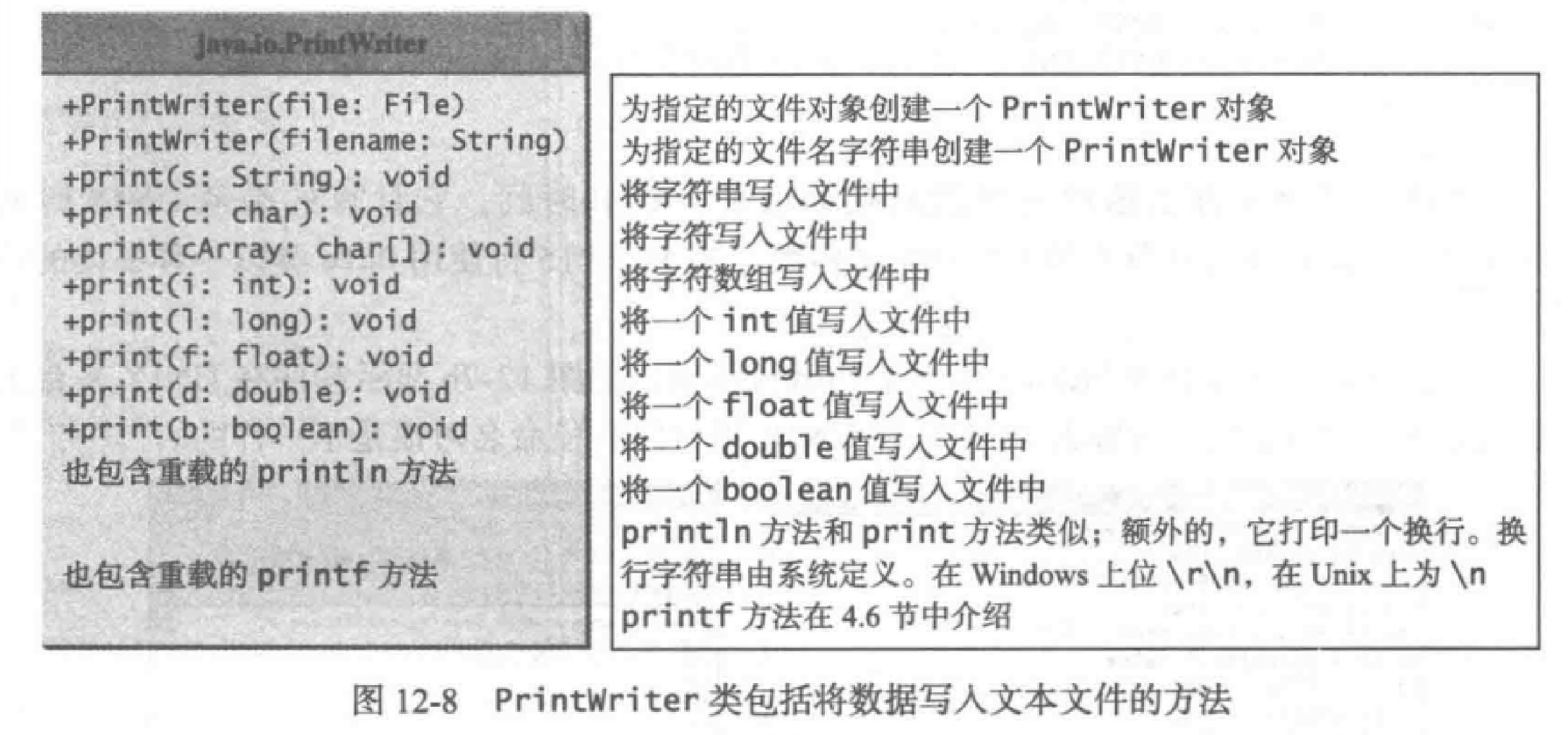
使用Scanner类从文件中读取文本数据,使用PrintWriter类向文本文件中写入数据。
PrintWriter类
Java.io.PrintWriter类可以用来创建一个文件并写入数据。
PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(filename);
- 调用该构造方法可能会造成IO异常,需要在方法头声明异常。
该声明方法创建并打开了一个文件,因此在最后面一定要用close()来关闭文件。 - PrintWriter类UML图

注意:PrintWriter可以直接使用File类的对象作为构造方法的参数。
也就是说它可以以指定文件名创建对象,也可以直接利用现成的File类对象。
调用PrintWriter类构造方法将直接新建一个文件。
public class WriteData {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{//使用File类来检测scores.txt是否已经存在java.io.File file = new java.io.File("scores.txt");if(file.exists()){System.out.println("File already exists");System.exit(1);}//直接新建一个文件,利用File的对象filejava.io.PrintWriter output = new java.io.PrintWriter(file);//调用实例方法来写入文件output.print("John T Smith ");output.println(90);output.print("Eric K Jones ");output.println(85);//不要忘记关闭文件output.close();}}
你知道的,程序员总是会忘记关闭文件。所以我们可以使用try-with-resources语法来自动关闭资源。
- try-with-resources语法
try(声明和创建资源){处理文件;}
注意:try后面跟着的是小括号()
- 利用它,我们可以修改上面的代码来省去close()方法。
public class WriteData {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{//使用File类来检测scores.txt是否已经存在java.io.File file = new java.io.File("scores.txt");if(file.exists()){System.out.println("File already exists");System.exit(1);}//在try的括号中声明并新建● try(java.io.PrintWriter output = new java.io.PrintWriter(file);){//调用实例方法来写入文件output.print("John T Smith ");output.println(90);output.print("Eric K Jones ");output.println(85);}// 不需要用到close方法!}}
- 注意:虽然看上去不需要close方法了,但其实资源声明类中必须自带close方法,它必须是AutoCloseable的子类型,在块结束后,资源的close方法自动调用以关闭资源。
- 资源的声明和创建必须在同一语句中,不过可以在括号中进行多个资源的声明和创建。
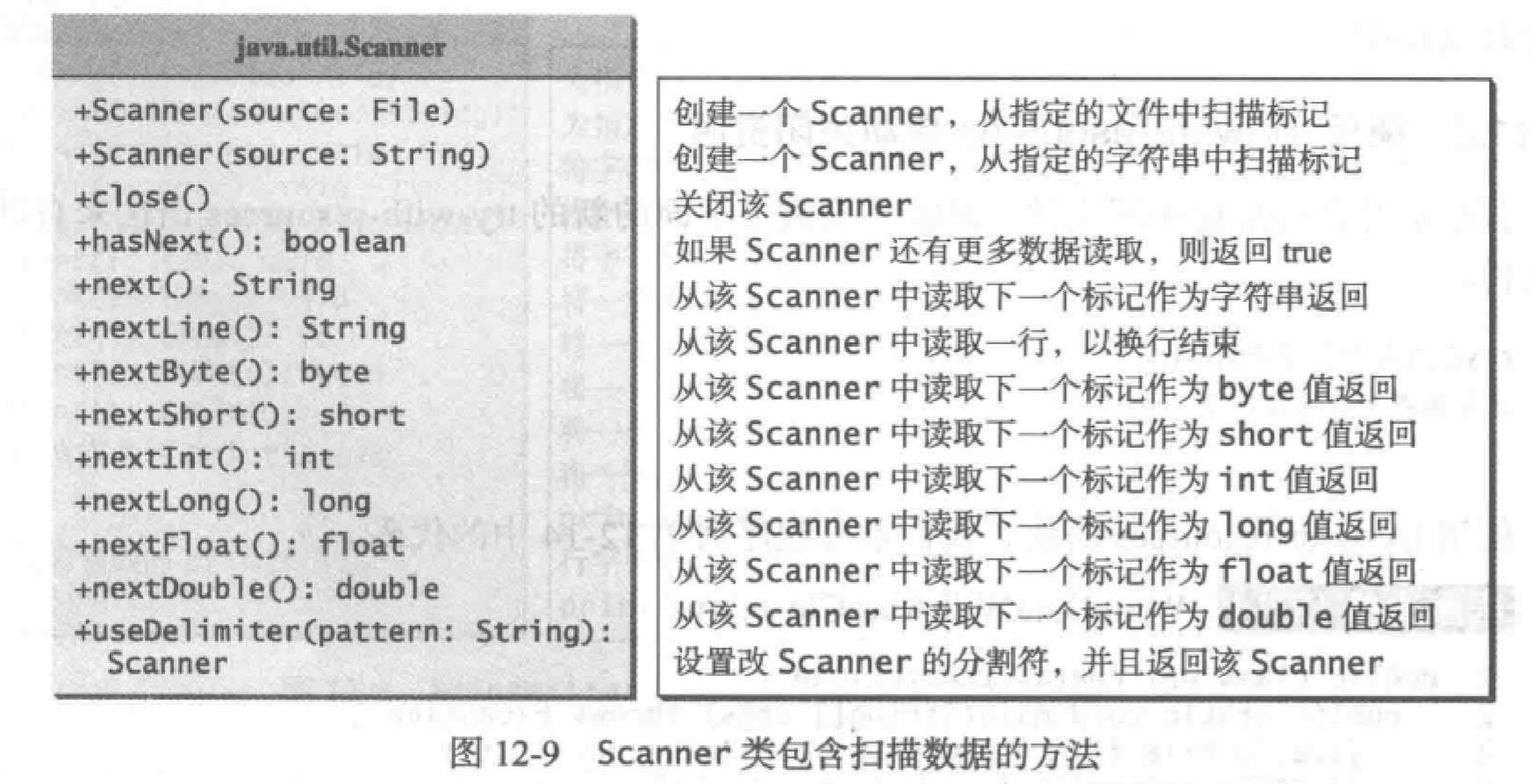
Scanner类
- java.util.Scanner类不仅能从键盘读取数据,也可以从文件中读取数据。
Scanner input = new Scanner(new File(filename));
- Scanner类和PrintWriter类一样,都可能抛出I/O异常,要在调用了它们的方法中声明异常
throws Exception - Scanner类UML类图

注意:new Scanner(String)为给定的字符串创建一个Scanner对象。
等价于:从给定的字符串读取数据。
当要从文件读取数据时,要先用new File(filename)创建一个File对象,
然后用new Scanner(filename)来从文件读取数据。
- Scanner从文件中读取数据,默认以空格为分隔符。
scores.txt{John T Smith 90Eric S Cgjlj 99}public class ReadData {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{● java.io.File file = new java.io.File("scores.txt");try(● Scanner input = new Scanner(file);){while(input.hasNext()){//每次迭代(到没有标记为止)都从文本文件中读取名字、中间名、姓和分数String firstname = input.next();String mi = input.next();String lastname = input.next();int Score = input.nextInt();System.out.println(firstName + " " + mi + " " + lastName + " " + Score);}}}}
从Web读取数据
java.net.URL类可以用来读取web的文件。
注意:URL全大写。
- URL类的构造方法
public URL(String spec)throws MalformedURLException
- 新建一个URL对象
try{URL url = new URL("https:/www.google.com/index.html")}catch (MalformedURLException ex){ex.printStackTrace();}
- 此处的异常
MalformedURLException是用来检验URL是否正确的。
URL必须以http://开头
以/为分隔符
- 创建一个URL后,可以用其中的实例方法openStream()`来开放输入流和输出流来创建Scanner对象。
- urlname.openStream就相当于之前的filename!
URL url = new URL("https:/www.google.com/index.html")Scanner input = new Scanner(url.openStream());
- 输入一个URL,然后显示文件的大小。
import java.util.Scanner;import java.net.URL;public class ReadFileFromURL {public static void main(String[] args){System.out.print("Enter a URL: ");● String URLString = new Scanner(System.in).next();// 读取URL内容字符串try {● URL url = new URL(URLString);// 以URL内容字符串构造URL对象int count = 0;● Scanner input = new Scanner(url.openStream());// 开放url数据流以读取其中数据。while(input.hasNext()){● String line = input.nextLine();count += line.length();// 读取每个字符串的长度并相加。}System.out.println("The file size is " + count+ " characters");// 输出文件长度}● catch (java.net.MalformedURLException ex)ex {System.out.println("Invaild URl");}catch (java.io.IOException ex){System.out.println("I/O Errors: no such file");}}}
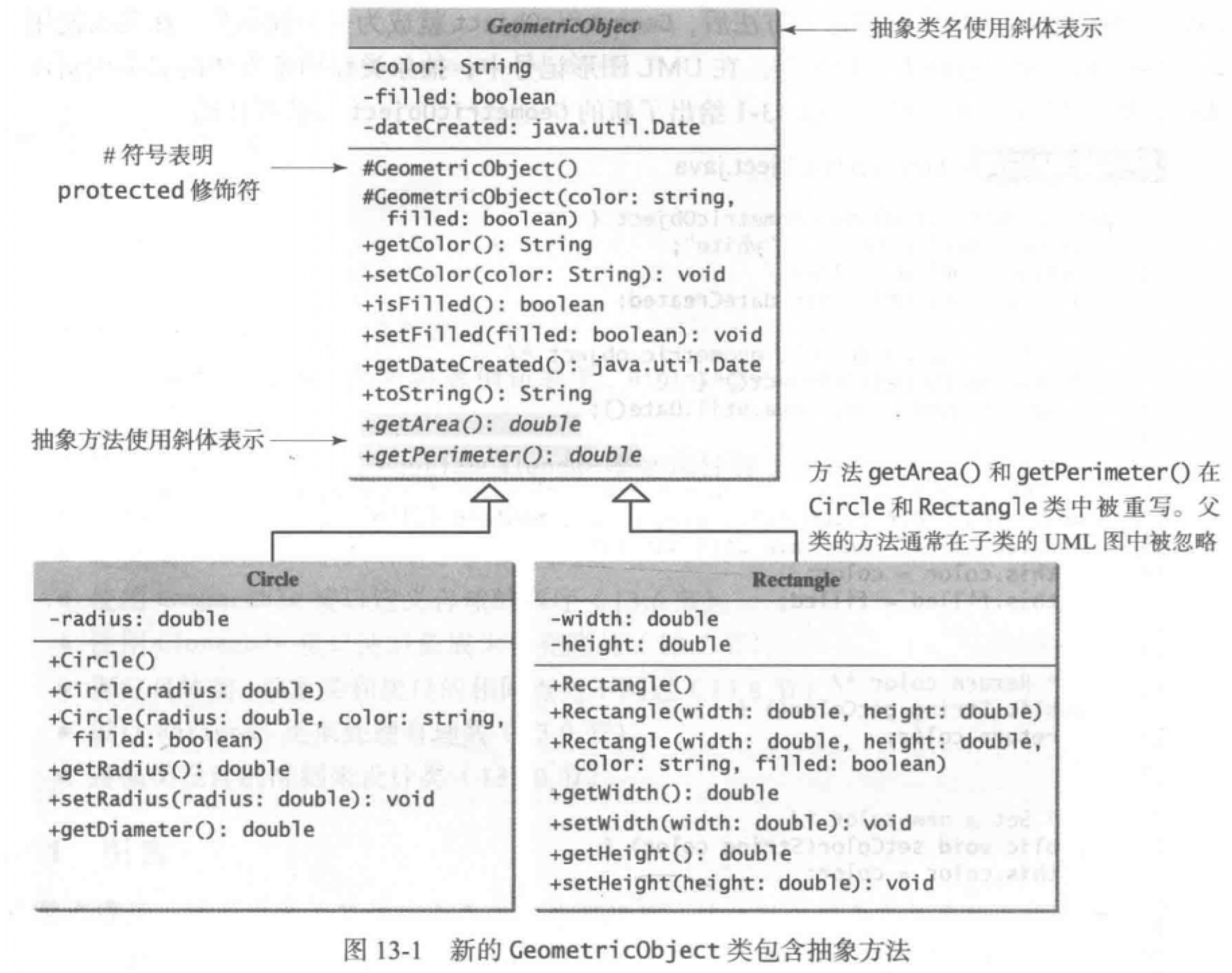
第13章 抽象类和接口
父类定义了相关子类中的共同行为,接口可以用于定义类的共同行为。
抽象类
- 一个父类可以定义的非常抽象,以至于他没有特定的实例,这就是抽象类。
- 抽象类含有抽象方法,抽象方法是允许创建它但是不实现它的方法。
- 抽象类和抽象方法都用
abstract修饰符表示。
// 抽象类public abstract class Geo{}// 抽象方法public abstract double getArea();public abstract double getPerimeter();
- 在UML类图中,抽象类和抽象方法用斜体表示。
- 抽象类的构造方法因为只需要在子类中使用,被定义为protected。

抽象类和常规类很像,但是不能使用new来创建它的实例。
抽象类只有定义而没有实现,只能被继承。抽象方法不能包含在非抽象类中。如果抽象父类的子类不能实现父类的所有抽象方法,那么子类也必须定义为抽象的。
- 虽然不能创造抽象类的实例,但是可以创建它的数组。
Geo[] objects = new Geo[10];// 然后可以创造一个Geo子类的实例,并将它的引用赋值给数组。objects[0] = new Circle();
接口
- 抽象类代表父类与子类会有一些相同方法,如动物类和鸡类都可以发出声音。但是再加上个芹菜呢?它显然不是动物类的子类,但是它们有个共同点:都可以吃。这种不相关类的相同方法就需要用到接口。
- 接口是一种与类相似的结构,只包含常量和抽象方法。
- 接口中所有的数据域都是
public static final的,
并且所有方法都是public abstract,不过java默认可以省略这些修饰符。
使用interface关键字声明接口。
public interface T{int K = 1;void p();}// 等价于public interface T{public static final int K = 1;public abstract void p();}
- 使用
implements关键字来实现接口。
class Chicken extends Animal implements Edible{}// 在子类中必须实现抽象类和接口中的所有抽象方法。@Overridepublic String howToEat(){return "Chicken: Fry it.";}@Overridepublic String sound(){return "Chicken: cock-a-doodle-doo";}
Comparable接口
Comparable接口定义了compareTo对象,用来比较对象。
- 如果对象是Comparable接口类型的实例的话,
java.util.Arrays.sort(Object[])方法就可以被使用来进行排序。 - 实现了Comparable接口的类:
基础类型的封装类,BigInteger、BigDecimal、Calendar、String、Date等。
- 如果Object类中包含了compareTo方法,那么sort就可以来比较任意一组对象,但是对于Object类中是否应该包含一个compareTo方法尚有争论。
- 由于Object类中没有定义compareTo方法,所以Java中定义了Comparable接口,以便能够对两个comparable接口的实例对象来进行比较,建议compareTo应该与equals保持一致,也就是说,对于两个对象o1和o2,应该确保当且仅当o1.equals(o2)为TRUE时o1.compareTo(o2)==0成立。
Cloneable接口
Cloneable接口给出了一个可克隆的对象。
- java中的很多类支持这个接口,如Date、Calcalendar、ArrayList。
- 克隆是克隆一个完全一样的新对象,不是传入对象的引用。
浅复制和深复制
- 浅复制:克隆时,类的基本类型数据域被复制过去,而如果一个数据域是对象,那么只是它的引用被复制过去。
- 深复制:将类的对象数据域也复制出一个新对象。
- 可以对clone()方法进行定制来将其中的对象单独克隆,这样,整个clone方法就是深复制的了。
接口与抽象类
一个类可以实现多个接口,但是只能继承一个父类。
其他区别:

- Java允许多重拓展接口
public class NewClass extends BasicClass implementsInterface1,Interface2...InterfaceN
- 接口也可以用extends拓展其他接口,这样的接口称为子接口
public interface Interface1 extends Interface2,Interface3..
注意,继承了子接口的类要实现其上所有类中的构造方法。
类的设计原则
- 内聚性
类应该描述一个单一的实体,而所有的类操作应该在逻辑上相互配合,支持一个一致的目的。 - 一致性
遵循java语言设计风格和命名习惯,通常的风格是将数据域置于构造方法之前,构造方法置于实例方法之前。 - 封装性
一个类应该使用private修饰符隐藏其数据。只有在想要修改数据域的时候,才提供set方法。在想要数据域可读的情况下,才提供get方法。 - 清晰性
类应该有一个很清晰的合约,如方法定义,还有,不要设置一个可以来自其他数据域的数据域。 - 完整性
为了能在一个广泛的应用中使用,类应该通过属性和方法提供多种方案以满足用户的不同需求。 - 实例和静态
依赖于类的具体实例的变量或方法必须是一个实例变量或方法,如果一个变量被类的所有对象所共享,那么它就应该是静态的。
数据域或方法要么是实例的,要么是静态的。构造方法一定是实例的,因为它是用来创造实例的。 - 继承和聚合
可以用继承来对Apple和Fruit类建模。
可以用聚合来对People和Name建模。 - 接口和抽象类
强的is-a关系用类来建模。
弱的is-a关系用接口来建模。
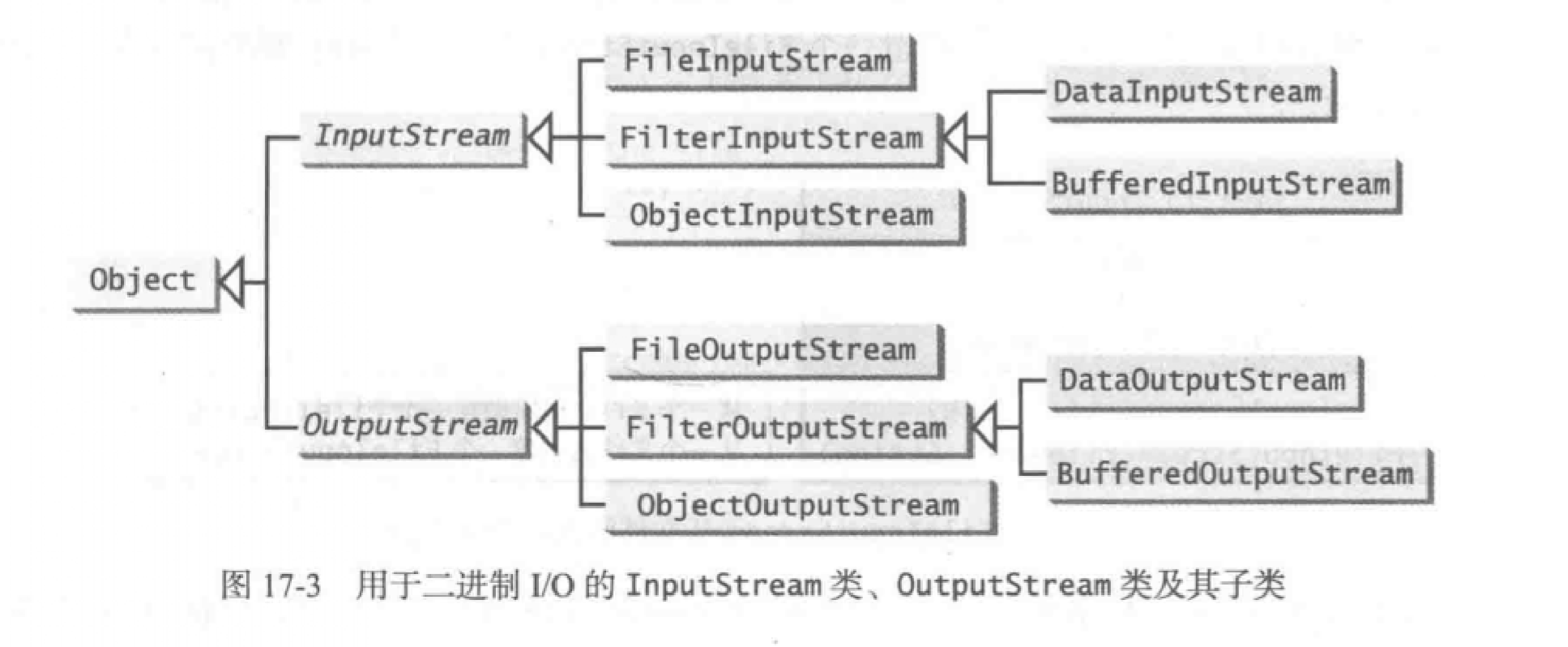
第17章 二进制 I/O
- 可以用记事本等修改的叫文本文件,其他的所有文件称为二进制文件。
- 二进制I/O 不需要转化。如果使用二进制I/O向文件写入一个数值,就是将内存中 的那个值复制到文件中。二进制文件与主机的编码方案无关,因此,它是可移植的。在任何机器上的Java程序可以读取Java程序所创建的二进制文件。这就是为什么Java的类文件存储为二进制文件的原因。Java类文件可以在任何具有 Java 虚拟机的机器上运行。
- 在12章中介绍的Scanner类和PrintWriter是文本IO类,本章是二进制IO类。
二进制IO根类
类继承树

- InputStream类和OutputStream类是输入类和输出类的根类。
- 注意,这是两个抽象类,因此不能创造实例。我们只能创造FileInputStream等的实例。


FileInputStream类和FileOutputStream类
- 我们可以定义FileInputStream类和FileOutputStream类来向一个文件读取或者写入字节。
- 注意,input是指将文件内容输入到工作区域。
- 新建实例:
// 利用File类来新建对象FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(new File("abc.dat"));// 也可以直接使用文件名来新建对象FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("abc.dat");如果对象名的文件没存在,则创建这个文件。如果对象名的文件存在,那么将会清除文件的内容。如果不想清空内容,可以使用另一个构造方法。// 在后面增加一个true来在文件中增添内容FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("abc.dat", true);
- FileOutputStream UML类图 FileInputSt

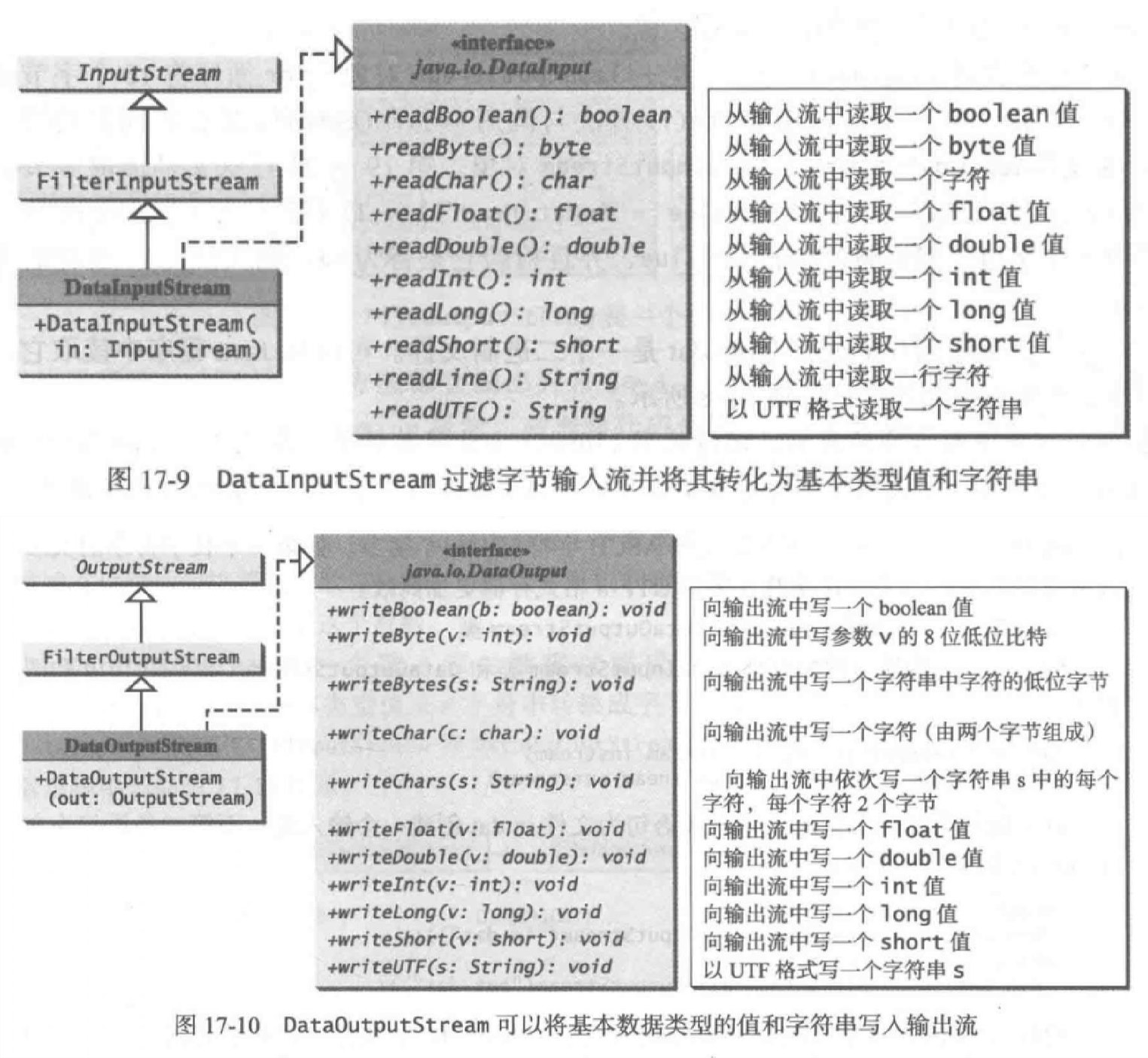
FilterInputStream类和旗下的DataInputStream与BufferedInputStream
- 基本字节输入流提供的读取方法read只能用来读取字节。如果要读取整数值、双精度值或字符串,那就需要一个过滤器类来包装字节输入流。
- 基本数据处理用DataInputStream,BufferInputStream拥有一个缓冲区。
- DataInputStream需要使用InputStream类的子类来创建。
DataInputStream input =new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("in.dat"));DataOutputStream Output =new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.dat"));
- DataInputStream拓展FilterInputStream类并实现了DataInput接口。Output也同理

- 将数据写入文件并读取
import java.io.*;public class TestDataStream {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{try(● DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("temp.dat"));){output.writeUTF("John");output.writeDouble(85.5);output.writeUTF("Jim");output.writeDouble(185.5);output.writeUTF("George");output.writeDouble(105.25);}try(● DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("temp.dat"));){System.out.println(input.readUTF() + " " +input.readDouble());System.out.println(input.readUTF() + " " +input.readDouble());System.out.println(input.readUTF() + " " +input.readDouble());}}}
- 如果到达 InputStream 的末尾之后还继续从中读取数据,就会发生 EOFException异常。这个异常可以用来检査是否已经到达文件末尾。
- BufferedInputStream类和Output类继承于FilterInputStream类,但是没有任何另外的方法,但是使用他们能够显著提升程序效率。因此,尽量使用buffer。使用data调用buffer再调用file来新建对象。
DataInputStream input =new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("fuck.dat")));
第18章 递归
递归是程序的一种替换形式,实际上就是不用循环控制的重复。
百度百科:
程序调用自身的编程技巧称为递归( recursion)。递归做为一种算法在程序设计语言中广泛应用。一个过程或函数在其定义或说明中有直接或间接调用自身的一种方法,它通常把一个大型复杂的问题层层转化为一个与原问题相似的规模较小的问题来求解,递归策略只需少量的程序就可描述出解题过程所需要的多次重复计算,大大地减少了程序的代码量。递归的能力在于用有限的语句来定义对象的无限集合。一般来说,递归需要有边界条件、递归前进段和递归返回段。当边界条件不满足时,递归前进;当边界条件满足时,递归返回。
- 递归通常用来解决本质上具有递归性质的问题,如汉诺塔问题,递归目录,和思瑞平斯基三角形。
- 递归会占用相当大的系统资源,因为每调用一个方法就要给方法中的所有局部变量和参数分配空间,如果用完内存,可能会产生一个StackOverflowError错误。
- 如果关注系统的性能,就要避免使用递归。
汉诺塔问题
https://www.cnblogs.com/antineutrino/p/3334540.html
- 目标:将n个盘子从A移动到C
开始情况A:n B:0 C:0F(n, A, B, C);他的功能是将n个盘子以某个塔作为辅助,然后将A上的n个盘子移动到C。不用考虑是如何实现的,我们只知道它能完成移动就好!这个方法的精妙之处在于,他考虑的是这样一种情况:--------------------------------考虑已经成功将n-1个盘子移动到B上,此时只要将最大的盘子从A移动到C即可。fun(n-1,A,C,B)A:1 B:n-1 C:0现在最大的盘子到了C上,因为它最大,所以其他盘子在它身上可以随意移动,此时可以无视它,那么场上的盘子数量只有B上的n-1个盘子。这个问题就变成了一个n-1的移动问题,只是开始的柱子变成了B而已。move(A->C)A:0 B:n-1 C:1这时再把B上的n-1个盘子移动到C上A:0 B:0 C:n--------------------------------// 这整个是一次递归过程。(中间参数是辅助柱子)func:if n!=0 then ;预定值func(n-1, a, c, b) ;将n-1个盘子由a移动到b,以c为辅助柱子move a[n] to c ;将a上的最后一个盘子移动到cfunc(n-1, b, a, c) ;将n-1个盘子由b移动到c,以a为辅助柱子endif ;完成
如果一个大问题可以分解成无数小一步的子问题,那么方法直接定义为大问题的解决方案!然后找到小问题和大问题之间的联系!
课本上的解决方法:(最后一个参数是辅助柱子)
package demo2;import java.util.Scanner;public class TowerOfHanoi {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter number of disks: ");int n = input.nextInt();System.out.println("The moves are:");moveDisks(n, 'A', 'B', 'C');}public static void moveDisks(int n, char fromTower, char toTower, char auxTower) {if (n == 1) {System.out.println("Move disk" + n + " from " + fromTower + " to " + toTower);} else {moveDisks(n - 1, fromTower, auxTower, toTower);System.out.println("Move disk" + n + " from " + fromTower + " to " + toTower);moveDisks(n - 2, auxTower, toTower, fromTower);}}}
尾递归优化
递归要消耗大量资源,而尾递归就不会。
在Java中谈尾递归:尾递归和垃圾回收的比较。
https://www.cnblogs.com/bellkosmos/p/5280619.html
- 顾名思义,尾递归就是从最后开始计算,每递归一次就算出相应的结果。
也就是说, 函数调用出现在调用者函数的尾部,因为是尾部,所以根本没有必要去保存任何局部变量.直接让被调用的函数返回时越过调用者,返回到调用者的调用者去。
尾递归就是把当前的运算结果(或路径)放在参数里传给下层函数,深层函数所面对的不是越来越简单的问题,而是越来越复杂的问题,因为参数里带有前面若干步的运算路径。 - 尾递归的判断标准:方法运行的最后一步是不是调用自身。注意:不是方法运行的最后一行!如:
// 这是尾递归def tailrecsum(x, running_total=0):if x == 0:return running_totalelse:● return tailrecsum(x - 1, running_total + x)// 这不是尾递归def recsum(x):if x == 1:return xelse:● return x + recsum(x - 1)
- 使用尾递归可以带来一个好处:因为进入最后一步后不再需要参考外层函数(caller)的信息,因此没必要保存外层函数的stack,递归需要用的stack只有目前这层函数的,因此避免了栈溢出风险。
- 尾递归的每层调用是单独的,在这层调用完毕后,这一层的所有变量都不会再用到了。
Java进阶篇已经开始更新了
链接:https://www.zybuluo.com/CLSChen/note/1438410
