@duanyubin
2016-04-26T01:58:02.000000Z
字数 2894
阅读 597
React Performance && Immutablejs
javascript
Avoiding reconciling the DOM
VIRTUAL DOM
React abstracts away the DOM from you, giving a simpler programming model and better performance.
在内存中,通过比较更新js object来更新dom,而不是直接操作dom。
此过程发生在render函数执行之后。
但是存在一个问题:
this.state = {count: 0}this.setState({count: 0});// 组件 state 并未被改变,但仍会触发 render 方法
shouldComponentUpdate
shouldComponentUpdate: function(nextProps, nextState) {return true;}
频繁执行此函数,默认返回true, 若返回true则执行render方法
尽量保证shouldComponentUpdate实现简单,执行快速
// typeof value === 'string'shouldComponentUpdate: function(nextProps, nextState) {return this.props.value !== nextProps.value;}
PureRenderMixin && ShallowCompare
var PureRenderMixin = require('react-addons-pure-render-mixin');React.createClass({mixins: [PureRenderMixin],render: function() {return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>;}});// ORimport PureRenderMixin from 'react-addons-pure-render-mixin';class FooComponent extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.shouldComponentUpdate = PureRenderMixin.shouldComponentUpdate.bind(this);}render() {return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>;}}
// Shallow Comparevar shallowCompare = require('react-addons-shallow-compare');export class SampleComponent extends React.Component {shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {return shallowCompare(this, nextProps, nextState);}render() {return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>;}}
两者都是浅比较,如果更深层次的值发生了变化就会失效
如果深层的值发生变化,例如点击下列链接JS BIN 1中的 SetToSameCount ,会发现 render times 没有变化(预期效果),再点 SetToSameSchool ,render times 增加了(非预期效果,因为任何的state都没有改变)
这是由于js中两个object比较,比较的是引用,而string比较,则比较的是值
var a = 'a'var b = 'a'a === b // truevar c = {c: 1}var d = {c: 1}c === d // false
解决这个问题,就需要深层比较, 但是深层比较比较费时,效率低,违背了之前保证scu函数简单的原则,因此引入Immutable.js
Immutable.js
局部更新
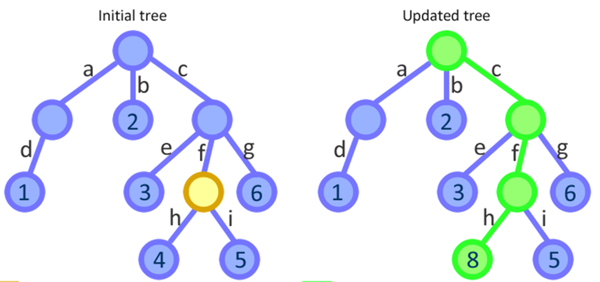
假如我们要修改左图中黄色节点的子节点4,那么Immutable.js只需要更新右图中的绿色节点,其余节点不需拷贝,继续复用。也就是说,Immutable.js会更新从根节点到所修改节点路径上的所有节点,由于修改了根节点,所以返回一个新对象。
内部采用类似链表的实现方式,避免了局部更新造成的深拷贝的消耗
用immutablejs 改造上述例子JS BIN 2
点击中SetToSameCount和SetToSameSchool,会发现 render times都没有发生变化
不可变变量
Javascript中对象都是参考类型,可变的好处是节省内存或是利用可变性做一些事情,但是,在复杂的开发中它的副作用远比好处大的多
a = {a:1}b = ab.a = 2a.a === 2 // true//-----option = {a:1}function a(opt){opt.a = 2}a(option)option.a === 2 // true
例如,在JS BIN 1中,在输入框中high school name,会覆盖掉middle school name, 而在JS BIN 2中,由于每次改变之后,都是生成的新变量,就不会出现上述问题
优点
1. Immutable 降低了 Mutable 带来的复杂度
function touchAndLog(touchFn) {let data = { key: 'value' };touchFn(data);console.log(data.key); // 猜猜会打印什么?}
在不知touchFn代码的情况下,不敢随意使用data,因为它有可能被修改
2. 节省内存
Immutable.js 使用了 Structure Sharing 会尽量复用内存。
import { Map} from 'immutable';let a = Map({select: 'users',filter: Map({ name: 'Cam' })})let b = a.set('select', 'people');a === b; // falsea.get('filter') === b.get('filter'); // true
3. 拥抱函数式编程
Immutable 本身就是函数式编程中的概念,纯函数式编程比面向对象更适用于前端开发。因为只要输入一致,输出必然一致,这样开发的组件更易于调试和组装。
其他
1. ===比较的是内存地址
let map1 = Immutable.Map({a:1, b:1, c:1});let map2 = Immutable.Map({a:1, b:1, c:1});map1 === map2; // falseImmutable.is(map1, map2); // truemap1.equals(map2); // true
Immutable.is比较的是两个对象的hashCode或valueOf(对于 JavaScript 对象)。由于 immutable 内部使用了 Trie 数据结构来存储,只要两个对象的hashCode相等,值就是一样的。这样的算法避免了深度遍历比较,性能非常好。
