@okokme
2018-07-24T13:25:23.000000Z
字数 2293
阅读 790
简化版chmod命令
Linux
---使用系统调用实例
在实现之前首先说一下#include<xxx.h>与#include<sys/xxx.h>的区别:
一般的头文件#include< xxxx.h>在/usr/include下面,这里是标准C程序头文件。
如果你的头文件前加了,#include< sys/xxx.h>那说明这是系统调用函数头文件,其在/usr/include/sys下面。 注:/usr/include是gcc的默认头文件目录。
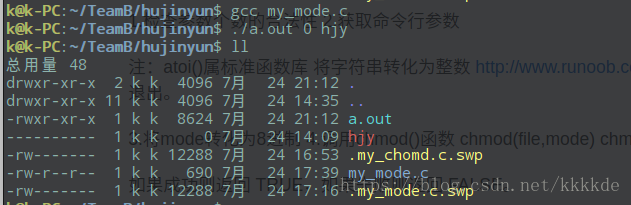
一个简单的系统编程:
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<sys/types.h>#include<sys/stat.h>int main(int argc, char **argv){int mode;//权限int mode_u;int mode_g;int mode_o;char *path;//检查参数个数的合理性if(argc < 3){printf("%s <mode num> <target file>");exit(0);}//获取命令行参数mode = atoi(argv[1]);if(mode>777 && mode<0){printf("wrong mode");exit(1);}//mode转换为8进制mode_u = mode / 100;mode_g = (mode - mode_u*100)/10;mode_o = mode - mode_u*100 - mode*10;mode = mode_u*8*8 + mode_g*8 + mode_o;//调用chmod()函数path = argv[2];if(chmod(path,mode)==-1){perror("chmod error");exit(1);}return 0;}
简化版chomd指令实施步骤:
1.检查参数个数的合法性
2.获取命令行参数
注:atoi()属标准函数库 将字符串转化为整数
http://www.runoob.com/cprogramming/c-function-atoi.html
exit(0) 表示程序正常退出,exit⑴/exit(-1)表示程序异常退出。
3.将mode转化为8进制
4.系统调用调用chmod()函数
chmod(file,mode)
chmod() 函数改变指定文件的权限。
如果成功则返回 TRUE,如果失败则返回 FALSE。
mode模式位:
mode 表示新目录的权限,可以取以下值:
S_IRUSR
S_IREAD
S_IWUSR
S_IWRITE
S_IXUSR
S_IEXEC
S_IRWXU
This is equivalent to (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IXUSR).
S_IRGRP
Read permission bit for the group owner of the file. Usually 040.
S_IWGRP
Write permission bit for the group owner of the file. Usually 020.
S_IXGRP
Execute or search permission bit for the group owner of the file. Usually 010.
S_IRWXG
This is equivalent to (S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IXGRP).
S_IROTH
Read permission bit for other users. Usually 04.
S_IWOTH
Write permission bit for other users. Usually 02.
S_IXOTH
Execute or search permission bit for other users. Usually 01.
S_IRWXO
This is equivalent to (S_IROTH | S_IWOTH | S_IXOTH).
S_ISUID
This is the set-user-ID on execute bit, usually 04000. See How Change Persona.
S_ISGID
This is the set-group-ID on execute bit, usually 02000. See How Change Persona.
S_ISVTX
This is the sticky bit, usually 01000.
S_IRWXU 00700权限,代表该文件所有者拥有读,写和执行操作的权限
S_IRUSR(S_IREAD) 00400权限,代表该文件所有者拥有可读的权限
S_IWUSR(S_IWRITE) 00200权限,代表该文件所有者拥有可写的权限
S_IXUSR(S_IEXEC) 00100权限,代表该文件所有者拥有执行的权限
S_IRWXG 00070权限,代表该文件用户组拥有读,写和执行操作的权限
S_IRGRP 00040权限,代表该文件用户组拥有可读的权限
S_IWGRP 00020权限,代表该文件用户组拥有可写的权限
S_IXGRP 00010权限,代表该文件用户组拥有执行的权限
S_IRWXO 00007权限,代表其他用户拥有读,写和执行操作的权限
S_IROTH 00004权限,代表其他用户拥有可读的权限
S_IWOTH 00002权限,代表其他用户拥有可写的权限
S_IXOTH 00001权限,代表其他用户拥有执行的权限
例子:
#include #include
int status;
status = mkdir("/home/newdir", S_IRWXU | S_IRWXG | S_IROTH | S_IXOTH);
这样就创建了一个newdir目录,权限通过ls -al 查看为
drwxr-xr-x
跟用linux命令mkdir创建的目录权限位一致。