@ljt12138
2017-03-25T15:34:43.000000Z
字数 4284
阅读 984
计算几何学习笔记
计算几何是什么东西?能吃吗?
一、平面最近点对
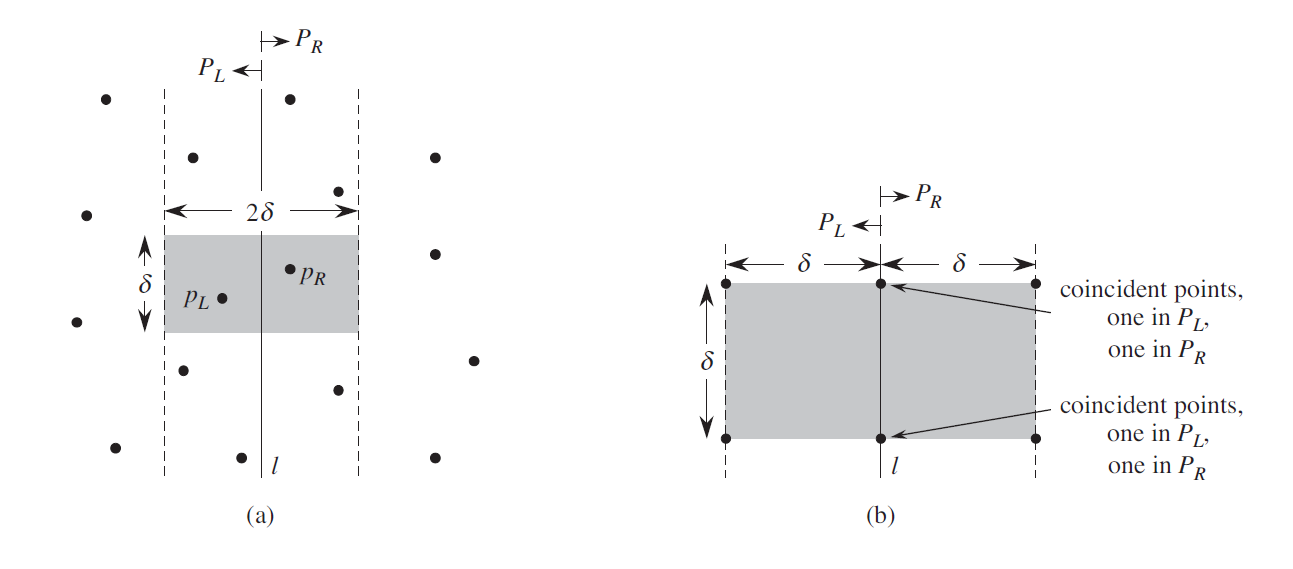
给定
如果用朴素的两两枚举,需要
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int MAXN = 200005;const double eps = 1e-9, inf = 1e100;struct p {double x, y;p(){}p(double x, double y):x(x),y(y){}friend bool operator < (const p &a, const p &b){ return abs(a.x-b.x)<=eps?a.y<b.y:a.x<b.x; }} v[MAXN];int n;double len(p a, p b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); }double dis(int l, int r){if (l >= r) return inf;int mid = (l+r)>>1;double a = dis(l, mid), b = dis(mid+1, r);double x = (v[mid].x+v[mid+1].x)/2.0, d = min(a, b);for (int i = mid; i >= l && x-v[i].x <= d; i--)for (int j = mid+1; j <= r && v[j].x-x <= d && abs(v[j].y-v[i].y) <= d; j++)if (len(v[i], v[j]) < d)d = len(v[i], v[j]);return d;}int main(){scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%lf%lf", &v[i].x, &v[i].y);sort(v+1, v+n+1);printf("%.4f", dis(1, n));return 0;}
二、凸包
凸包就是给定平面上若干个点和一个巨大的包含所有点的细理想轻橡皮筋,当你一松手
具体步骤是选取最左侧的一个点作为基准,对所有点按照极角排序,然后按照极角序丢进一个凸壳的栈,如果违反凸性就删除顶点元素。最后形成的就是一个凸包。
hdu1392代码。
(数据有误,两个点的时候要直接视作线段长)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int MAXN = 10005;const double eps = 1e-9, inf = 1e100;struct p {double x, y;p(){}p(double x, double y):x(x),y(y){}friend bool operator < (const p &a, const p &b){ return abs(a.x-b.x)<=eps?a.y<b.y:a.x<b.x; }friend bool operator == (const p &a, const p &b){ return abs(a.x-b.x)<=eps && abs(a.y-b.y)<=eps; }} v[MAXN];int n;double len(p a, p b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); }double det(p a, p b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; }double dot(p a, p b){ return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y; }p line(const p &s, const p &t){ return p(t.x-s.x, t.y-s.y); }p k;bool cmp(const p &a, const p &b){if (a == k || b == k) return a == k;return det(line(k, b), line(k, a)) >= 0;}stack<p> stk;double work(){k = v[1];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (v[i].x < k.x)k = v[i];sort(v+1, v+n+1, cmp);v[++n] = v[1];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {if (stk.size() <= 1) stk.push(v[i]);else {while (stk.size() > 1) {p tp = stk.top(); stk.pop();p t2 = stk.top(); stk.pop();if (det(line(tp, v[i]), line(tp, t2)) <= eps) {stk.push(t2), stk.push(tp);break;} elsestk.push(t2);}stk.push(v[i]);}}double ans = 0;while (stk.size() > 1) {p a = stk.top(); stk.pop();ans += len(a, stk.top());}while (!stk.empty()) stk.pop();return ans;}int main(){while (scanf("%d", &n), n != 0) {for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%lf%lf", &v[i].x, &v[i].y);if (n == 2) {printf("%.2f\n", len(v[1], v[2]));continue;}printf("%.2f\n", work());}return 0;}
三、旋转卡壳
考虑如何求解平面上的最远点对?
首先最远点对一定在凸包上,如果直接枚举凸包上的点,最坏情况下会退化至
一种巧妙的方法是用一组平行线“卡”这个凸包:
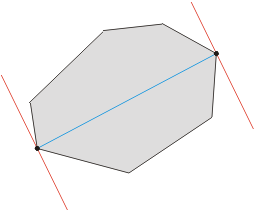
枚举一个点,运用叉积判断远近,直接暴力搞就好,可以证明是
然而坑多如狗...
比如重点,算凸包的时候要删去;
比如退化成线,要选一个第二关键字,即当极角一样时,要按照距离初始点远近排序。
poj2187
#include <cmath>#include <cstdio>#include <algorithm>#include <cstring>#include <iostream>#include <stack>#include <vector>using namespace std;struct p {long long x, y;p():x(0),y(0){}p(long long x, long long y):x(x), y(y) {}long long operator * (const p &a){ return x*a.y-y*a.x; }friend bool operator == (const p &a, const p &b){ return b.x == a.x && b.y == a.y; }void print(){ printf("(%lld, %lld) ", x, y); }} v[50005];int n;p k;long long ans = 0;p line(const p &a, const p &b){ return p(b.x-a.x, b.y-a.y); }long long len_power(const p &a){ return a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y; }bool cmp(const p &a, const p &b){if (a == k || b == k) return a == k;if (line(k, b)*line(k, a) == 0)return len_power(line(k, a)) < len_power(line(k, b));return line(k, b)*line(k, a) > 0;}stack<p> stk;void work(vector<p> &vec){k = v[1];for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)if (k.x > v[i].x || (k.x == v[i].x && k.y > v[i].y)) k = v[i];sort(v+1, v+n+1, cmp);n = unique(v+1, v+n+1)-v-1;v[++n] = k;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {if (stk.size() <= 1) stk.push(v[i]);else {while (stk.size() >= 2) {p tp = stk.top(); stk.pop();p t2 = stk.top(); stk.pop();if (line(tp, v[i])*line(tp, t2) <= 0) {stk.push(t2), stk.push(tp);break;} else stk.push(t2);}stk.push(v[i]);}}while (!stk.empty()) vec.push_back(stk.top()), stk.pop();for (int i = 0, j = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) {while (line(vec[i], vec[i+1])*line(vec[i], vec[j]) < line(vec[i], vec[i+1])*line(vec[i], vec[j+1]))(++j) %= vec.size();ans = max(ans, len_power(line(vec[i], vec[j])));}cout << ans << endl;}vector<p> vec;int main(){scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%lld%lld", &v[i].x, &v[i].y);work(vec);return 0;}
四、数值积分
用的最多的貌似是辛普森积分。
就是当距离很小时,用二次函数拟合。
NOI2005,月下柠檬树,待做
五、半平面交
玄学,待做。
