@ChuckIsReady
2018-11-16T03:42:37.000000Z
字数 4898
阅读 556
BI期末
- 列表项
- 列表项
列表项
未分类
I. The Business Intelligence Perspective
A. Major characteristics and competitive advantages
B. Decision support systems(DSS)
C. Structure and components
Business Intelligence (BI) is an umbrella term that combines architectures, tools, databases, applications, and methodologies. Its major objective is to enable interactive access (sometimes in real time) to data, enable manipulation of these data, and to provide business managers and analysts the ability to conduct appropriate analysis. (it helps transform data, to information (and knowledge), to decisions and finally to action)
advantages
The ability to provide accurate information when needed, including a real-time view of the corporate performance and its partsBI Architecture
- Data Warehouse is a large repository of well-organized historical data
- Business analytics are the tools that allow transformation of data into information and knowledge
- Business performance management (BPM) allows monitoring, measuring, and comparing key performance indicators
- User interface (e.g., dashboards) allows access and easy manipulation of other BI components
DSS: A DSS is typically built to support the solution of a certain problem
The major DSS components are: data management, model management, user interface and knowledge base.
• Data management includes a database management system and one or more databases.
• Model management includes models and their management system.
• User interface includes bi-directional human-computer communication and its management.
• Knowledge base includes artificial intelligence enhancements to the other components.Decision making process
Intelligence consists of gathering information by examining reality, then identifying and defining the problem. In this phase problem ownership should also be established.
Design consists of determining alternatives and evaluating them. If the evaluation will
require construction of a model, that is done in this phase as well.The choice phase consists of selecting a tentative solution and testing its validity.
Implementation of the decision consists of putting the selected solution into effect.
II. The Data Warehouse
A. Characteristics
Data warehouse: A physical repository where relational data are specially organized to provide enterprise-wide, cleansed data in a standardized format
Characteristics of DW
- Subject oriented
- Integrated
- Time-variant (time series)
- Nonvolatile
- Summarized
- Not normalized
- Metadata
- Web based, relational/multi-dimensional
- Client/server
- Real-time and/or right-time (active)( Definitions
- Operational data stores (ODS)
A type of database often used as an interim area for a data warehouse
- Oper marts
An operational data mart.
- Enterprise data warehouse (EDW)
A data warehouse for the enterprise.
- Metadata
Data about data. In a data warehouse, metadata describe the contents of a data warehouse and the manner of its acquisition and use )
B. Architectures
• Three-tier architecture
1. Data acquisition software (back-end)
2. The data warehouse that contains the data & software
3. Client (front-end) software that allows users to access and analyze data from the warehouse
• Two-tier architecture
First 2 tiers in three-tier architecture is combined into one10 factors that potentially affect the architecture:就记5个短的好了
1. Technical issues
2. Social or political factors
3. Nature of end-user tasks
4. Upper management’s information needs
5. Urgency of need for a data warehouse
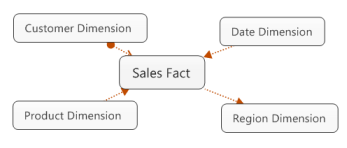
C. Star and snowflake schemas
Star Schema
Very asymmetric
Fact table is the only table that has multiple connections connecting it to other tables
All other tables have only a single connection attaching them to the central table
Snowflake Schema
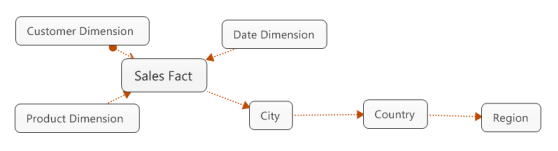
• A snowflake schema is a variation of the star schema in which dimension tables are in the third or in BCNF normal form
• By the normalization, each dimension attribute hierarchy is split into a number of relation schemas
• These relation schemas are associated by primary key / foreign key pairs
D. Data integration and the extraction, transformation, and load (ETL) process
Data Integration: 3 processes: data access, data federation and change capture,data can be accessed and made accessible to an array of ETL and analysis tools and data warehousing environments
Extraction -- reading data from a database
- Transformation -- converting the extracted data from its previous form into the form in which it needs to be so that it can be placed into a data warehouse or simply another database
- Load -- putting the data into the data warehouse
E. Development
III. Analytic Processing and Business Analytics
A. OLAP (Online Analytic Processing)
Types of OLAP Servers
Relational OLAP (ROLAP)
– Use relational or extended-relational DBMS to store and manage warehouse data and OLAP middle ware to support missing pieces
– Include optimization of DBMS backend, implementation of aggregation navigation logic, and additional tools and services
– greater scalabilityMultidimensional OLAP (MOLAP)
– Array-based multidimensional storage engine (sparse matrix techniques)
– fast indexing to pre-computed summarized data- Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP)
– User flexibility, e.g., low level: relational, high-level: array- Specialized SQL servers
– specialized support for SQL queries over star/snowflake schemas
B. Multi-dimensional analysis
C. Knowledge discovery and information mining
IV Case Studies and Applications, which may include one or more of the following:
A. Customer relationship management (CRM)
B. Supply chain management (SCM)
C. Business Performance Management (BPM)
D. Clinical Decision Support Systems
V Other
A. Entity Relationship Diagram ERD ER图
1 对 1 1-1 实体 -> 正方形
1 对多 1-M 操作 -> 棱形
多对多 M-N 属性 -> 椭圆, 主键 -> 下划线