@kiraSally
2018-03-12T10:39:46.000000Z
字数 9932
阅读 3480
集合番@LinkedList一文通(1.7版)
JAVA COLLECTIONS 源码 1.7版本
- 笔者个人博客 kiraSally的掘金个人博客 感谢支持
1.LinkedList的定义
- 继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表,可以被当作
堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作 - 有序,非线程安全的双向链表,默认使用尾部插入法
- 适用于频繁新增或删除场景,频繁访问场景请选用
ArrayList - 插入和删除时间复杂为O(1),其余最差O(n)
- 由于实现Deque接口,双端队列相关方法众多,会专门来讲,这里不多加详述
- 此版本基于JDK1.7
2.LinkedList的数据结构
2.1 类定义
public class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- 继承
AbstractSequentialList,能被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作- 实现
List接口,能进行队列操作- 实现
Deque接口,能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用- 实现
Cloneable接口,重写clone(),能克隆(浅拷贝)- 实现
java.io.Serializable接口,支持序列化
2.2 重要全局变量
/*** 当前链表元素数量*/transient int size = 0;/*** Pointer to first node.* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || (first.prev == null && first.item != null)* 链表头部节点*/transient Node<E> first;/*** Pointer to last node.* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || (last.next == null && last.item != null)* 链表尾部节点*/transient Node<E> last;
2.3 构造器
/*** Constructs an empty list.* 默认空构造器 -- 注意LinkedList并不提供指定容量的构造器*/public LinkedList() {}/*** Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's iterator.* 支持将一个Collection转换成LinkedList** @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}
2.4 Node
/*** 存储对象的结构:* 每个Node节点包含了上一个节点和下一个节点的引用,从而构成了双向的链表*/private static class Node<E> {E item;//存储元素Node<E> next;// 指向下一个节点Node<E> prev;// 指向上一个节点//注意第一个元素是prev,第二个元素才是存储元素即可Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}
3.LinkedList的存储
3.1 add方法
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list.* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.* 插入一个新元素到链表尾部* @param e element to be appended to this list* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 返回插入结果*/public boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;}/*** Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).* 插入一个新元素到指定下标位置,大于该下标的所有元素统一向右移动一位* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public void add(int index, E element) {checkPositionIndex(index);//下标边界校验if (index == size) //当下标==链表长度时,尾部插入linkLast(element);elselinkBefore(element, node(index));//否则,前部插入(起始位置为index)}
3.2 checkPositionIndex方法
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {if (!isPositionIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}/*** Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an iterator or an add operation.* 当迭代或插入操作时,需要判断下标的边界*/private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index <= size;}
3.3 linkLast方法
/*** Links e as last element.* 将e变为链表的最后一个元素*/void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);//注意:新建node的next为nulllast = newNode;//将新建node作为链表尾部节点//当原队尾为null时,即链表为空时if (l == null)first = newNode;//将新建node同时作为链表头部节点elsel.next = newNode;//将原链表尾部节点的next引用指向新建node,形成链表结构size++;//当前链表长度+1modCount++;//新增操作属于结构性变动,modCount计数+1}
3.4 linkBefore方法
/*** Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.* 插入一个新的元素到指定非空节点之前*/void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// assert succ != null;//逻辑与linkLast基本一致,区别在于将last变成prev,将新节点插入到succ节点之前final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);succ.prev = newNode;//唯一的区别,将新节点插入到succ节点之前if (pred == null)first = newNode;elsepred.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;//插入属于结构性变动,modCount计数+1}
3.5 linkBefore与空指针
- 如果读者有心的话会发现
linkBefore()并没有做空指针判断,而只是提供注释提示,原因在于两点
- 1.调用该方法前会调用 checkPositionIndex(index) 会先校验边界问题,当出现index > size时会抛出
IndexOutOfBoundsException,从而终止方法 - 2.接着succ=node(index),而succ一定非空,理由是node对象非空,空的只是元素而已(允许null值)
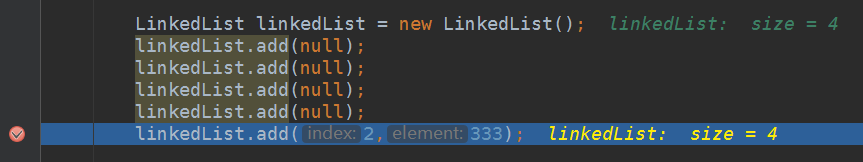
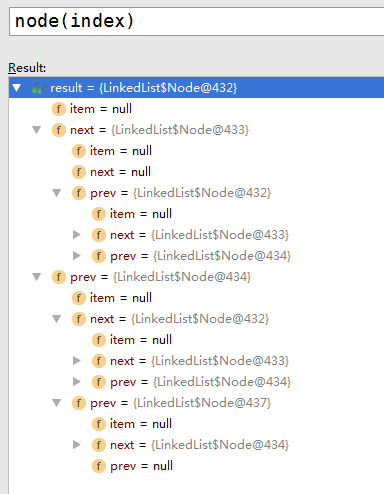
- 1.调用该方法前会调用 checkPositionIndex(index) 会先校验边界问题,当出现index > size时会抛出
4.LinkedList的读取
4.1 get方法
/*** Returns the element at the specified position in this list.* 获取指定下标元素* @param index index of the element to return* @return the element at the specified position in this list* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E get(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return node(index).item; //注意返回不是node,而是item;同时node一定不为null,而item允许为null}
4.2 checkElementIndex方法
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {if (!isElementIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}/*** Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.* 判断当前下标是否存在元素,原理参见`linkBefore`* 有心的读者可能发现了:* (get)isElementIndex = index >= 0 && index < size;* (add)isPositionIndex = index >= 0 && index <= size;* 两个方法几乎一致,但有一个很明显的区别: isPositionIndex 多了个index=size的判断!!* 由此(从方法名也可知-论方法名的严谨性)可知 :* get时下标必须小于size,否则下标越界;* add(指定元素)时 :* 当index = size时,采用尾部插入,因为要占据下标为size的位置;* 当index < size时,采用前部插入,因为要占据下标为index的位置,同时原位置元素后移;*/private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index < size;}
4.3 node方法
/*** Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.* 返回指定下标的非空node* 这里笔者有个疑问:node本身没有动词形式,为何不是getNode?* 顺便提一句:nodeJs真的不错!*/Node<E> node(int index) {// assert isElementIndex(index);//值得一提的是,为了提高查询效率,node查询选择使用二分查找法//个人观点:但可能因为Josh Bloch大神认为LinkedList并不适合查找,因此只是简单进行了一次二分而已if (index < (size >> 1)) {Node<E> x = first; //若在前半边,就从前往后找for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)x = x.next;return x;} else {Node<E> x = last; //若在后半边,就从后往前找for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)x = x.prev;return x;}}
5.LinkedList的移除
5.1 remove方法
/*** Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.* 默认删除头部节点* @return the head of this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty* @since 1.5*/public E remove() {return removeFirst();}/*** Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).* Returns the element that was removed from the list.* 根据下标删除元素* @param index the index of the element to be removed* @return the element previously at the specified position* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E remove(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);//边界校验 index >= 0 && index < sizereturn unlink(node(index));//解绑操作}/*** Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,if it is present.* If this list does not contain the element, it is unchanged.* More formally, removes the element with the lowest index {@code i} such that* <tt>(o==null?get(i)==null:;o.equals(get(i)))</tt> (if such an element exists).* Returns {@code true} if this list contained the specified element (or equivalently,* if this list changed as a result of the call).* 直接移除某个元素:* 当该元素不存在,不会发生任何变化* 当该元素存在且成功移除时,返回true,否则false* 当有重复元素时,只删除第一次出现的同名元素 :* 例如只移除第一次出现的null(即下标最小时出现的null)* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element*/public boolean remove(Object o) {//虽然跟ArrayList一样需要遍历,但由于不需要调用耗时的`System.arraycopy`,效率更高if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null) {unlink(x);return true;}}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item)) {unlink(x);return true;}}}return false;}
5.2 unlink方法
/*** Unlinks non-null node x.* 解除node链接,主要干了三件事情:* 1.解绑当前元素的前后节点链接,前后节点重新绑定关系* 2.当前元素的所有属性清空,help gc* 3.链表长度-1,modCount计数+1(help fail-fast)* @return 返回元素本身 注意是item,而不是node*/E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null;final E element = x.item;final Node<E> next = x.next;//后一位节点final Node<E> prev = x.prev;//前一位节点//解绑前一位节点if (prev == null) {//当前节点位于链表头部first = next;//后一位节点放链表头部} else {//非链表头部prev.next = next;//将前一位节点的next指向下一位节点x.prev = null;//当前节点的前一位节点清空 ,help gc}//解绑后一位节点if (next == null) {//当前节点位于链表尾部last = prev;//前一位节点放链表尾部} else {//非链表尾部next.prev = prev;//将后一位节点的prev指向前一位节点x.next = null;//当前节点的后一位节点清空 ,help gc}x.item = null;//当前节点元素清空size--;//链表长度-1modCount++;//删除操作属于结构性变动,modCount计数+1return element;//返回元素本身}
5.3 unlinkFirst方法
/*** Unlinks non-null first node f.* 解绑头部*/private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {// assert f == first && f != null;final E element = f.item;final Node<E> next = f.next;f.item = null;f.next = null; // help GCfirst = next; //下一个节点作为新的头部节点if (next == null) //头部已经为null,那么尾部也是nulllast = null;elsenext.prev = null;//新头部节点的prev需要清空,非闭环size--;modCount++;return element;}
5.4 unlinkLast方法
/*** Unlinks non-null last node l.* 解绑尾部*/private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {// assert l == last && l != null;final E element = l.item;final Node<E> prev = l.prev;l.item = null;l.prev = null; // help GClast = prev; //上一个节点作为新的尾部节点if (prev == null) //尾部已经为null,那么头部也是nullfirst = null;elseprev.next = null;//新尾部节点的next需要清空,非闭环size--;modCount++;return element;}
6.LinkedList的其他主要API整理
6.1 查找
- 获取头部节点:
getFirst(),peekFirst(),peek(),element()- 获取尾部节点:
getLast(),peekLast()
NoSuchElementException:getFirst()和getLast()
null:peekFirst()和peekLast()
peek()等同于peekFirst(),element()内部调用的getFirst()
6.2 插入
- 头部插入:
addFirst(E e),offerFirst(E e)- 尾部插入:
addLast(E e),offerLast(E e)
void:addFirst(E e)、addLast(E e),push(E e)
boolean:add(E e)、offer(E e)、offerFirst(E e),offerLast(E e)
linkLast(E e)等同于add(E e),大部分方法底层实现为linkFirst(E e)和linkLast(E e)
6.3 删除
- 头部删除:
removeFirst(),poll(),pollFirst(),pop()- 尾部删除:
removeLast(),pollLast()
NoSuchElementException:remove()、removeFirst(),removeLast(),removeLast()
null:poll()、pollFirst()、pollLast()
remove()等同于removeFirst(),大部分方法底层实现为unlinkFirst(Node<E> n)和unlinkLast(Node<E> n)
removeLastOccurrence(Object o)与remove(Object o)的实现几乎相同,区别前者是倒序查找,后者是正序查找
7.LinkedList的栈实现
- 栈(Stack)是限定仅在一端进行插入和删除运算的线性表
- 根据后进先出(LIFO)原则,顶部称为栈顶(top),底部称为栈底(bottom)
/*** 队列的LinkedList版本简单实现* 这里使用first(使用last原理也一样,保证只在一端操作即可)*/class Stack<T> {LinkedList<T> linkedList = new LinkedList<T>();/*** 入栈*/public void push(T v) {linkedList.addFirst(v);}/*** 出栈,不删除栈顶元素*/public T peek() {return storage.getFirst();}/*** 出栈 ,删除栈顶元素*/public T pop() {return storage.removeFirst();}}
8.LinkedList的队列实现
- 队列(Queue)是限定插入和删除各在一端进行的线性表
- 根据先进先出(FIFO)原则,表中允许插入的一端称为队尾(Rear),允许删除的一端称为队头(Front)
/*** 队列的LinkedList版本简单实现* 这里使用队尾插入,对头删除的写法(反过来原理一致,只要保证插入和删除各占一端即可)*/class Queue<T> {LinkedList<T> linkedList = new LinkedList<T>();/*** 入队,将指定的元素插入队尾*/public void offer(T v) {linkedList.offer(v);}/*** 出队,获取头部元素,但不删除,如果此队列为空,则返回 null*/public T peek() {return linkedList.peek();}/*** 出队,获取头部元素,但不删除,如果此队列为空,则抛异常*/public T element() {return linkedList.element();}/*** 出队,获取头部元素并删除,如果队列为空,则返回 null*/public T poll() {return linkedList.poll();}/*** 出队,获取头部元素并删除,如果队列为空,则抛异常*/public T remove() {return linkedList.remove();}}
集合番@LinkedList一文通(1.7版) 由 黄志鹏kira 创作,采用 知识共享 署名-非商业性使用 4.0 国际 许可协议 进行许可。
本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。
