@kiraSally
2019-11-25T06:24:14.000000Z
字数 22526
阅读 6521
并发番@ThreadLocal一文通(1.7版)
JAVA 并发 源码 1.7版
- 读者请先阅读笔者的 并发番@Thread一文通(1.7版)
- 读者请先阅读笔者的 集合番@WeakHashMap一文通(1.7版)
- 笔者个人博客 kiraSally的掘金个人博客 感谢支持
1.ThreadLocal
1.1 ThreadLocal的定义
- ThreadLocal通过为每个线程提供一个独立的变量副本解决了变量并发访问的冲突问题
- 当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本
- 在ThreadLocal类中有一个Map,用于存储每一个线程的变量副本,Map中元素的键为线程对象,而值对应线程的变量副本
ThreadLocal
JDK1.5引入泛型后,ThreadLocal告别Object时代进入泛型时代
- 存储线程私有变量的一个容器
- ThreadLocal不是为了解决多线程访问共享变量,而是为每个线程创建一个单独的变量副本,提供了保持对象的方法和避免参数传递的复杂性
1.2 ThreadLocal的数据结构
1.2.1 类定义
public class ThreadLocal<T>
1.2.2 重要内部元素
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
1.2.3 构造器
/** ThreadLocal只提供了一个空的默认构造器,够纯粹 **/public ThreadLocal() {}
1.3 ThreadLocal的重要方法
1.3.1 set方法
/*** Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable to the specified value.* Most subclasses will have no need to override this method,relying solely on the* {@link #initialValue} method to set the values of thread-locals.* 设置当前线程在当前ThreadLocal中的线程局部变量的值* 其子类无须重写该方法,只要重写initialValue方法设置初始默认值即可* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of* this thread-local. 将当前值拷贝成当前线程的局部变量*/public void set(T value) {//获取当前线程Thread t = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程持有的MapThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);//createMap or set directlyif (map != null)//注意 key为this,指的就是当前调用set方法的ThreadLocal对象本身map.set(this, value);else//根据当前线程初始化它的ThreadLocalMap并设置值createMap(t, value);}
1.3.2 get方法
/*** Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable.* If the variable has no value for the current thread,it is first initialized to* the value returned by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.* 返回当前线程在当前ThreadLocak中所对应的线程局部变量* 若当前值不存在,则返回initialValue方法设置的初始默认值* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local*/public T get() {//获取当前线程Thread t = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程持有的MapThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null) {ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);if (e != null)return (T)e.value;}//Map为空或值为空,返回默认值return setInitialValue();}
1.3.3 remove方法
/*** Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local variable.* If this thread-local variable is subsequently {@linkplain #get read}* by the current thread, its value will be reinitialized by invoking its* {@link #initialValue} method, unless its value is {@linkplain #set set}* by the current thread in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations* of the {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.* 移除当前线程在当前ThreadLocal中对应的私有变量* 当该变量之后被当前线程读取(get),该值会重新被initialValue方法初始化除非这期间被set* 这将会导致initialValue方法会被当前线程多次调用* @since 1.5 该方法是JDK1.5新增方法*/public void remove() {//获取当前线程持有的ThreadLocalMap,由此可见get和set中的相关代码也应该合并为一行ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());if (m != null)//注意是从ThreadLocalMap移除的当前ThreadLocal对象(即ThreadLocalMap的key)m.remove(this);}
1.3.4 getMap方法
/*** Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in* InheritableThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @return the map*/ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {return t.threadLocals;}
1.3.5 createMap方法
/*** Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in* InheritableThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map* @param map the map to store.*/void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}
1.3.6 nextHashCode方法
/*** Returns the next hash code.*/private static int nextHashCode() {return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);}
1.3.7 initialValue方法
/*** Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this thread-local variable.* This method will be invoked the first time a thread accesses the variable* with the {@link #get} method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}* method, in which case the <tt>initialValue</tt> method will not be invoked for the thread.* Normally, this method is invoked at most once per thread, but it may be invoked again* in case of subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.* 返回当前线程在当前ThreadLocal中的初始默认值* 第一次get操作会调用该方法,除非之前已经调用了set方法(即已有值)* 一般情况下该方法只会被执行一次,但有可能出现多次,比如:* 调用remove方法之后调用了get方法* <p>This implementation simply returns <tt>null</tt>; if the programmer desires* thread-local variables to have an initial value other than <tt>null</tt>,* <tt>ThreadLocal</tt> must be subclassed, and this method overridden.* Typically, an anonymous inner class will be used.* 该方法默认返回null,可以重写该方法(比如继承或实现一个匿名类)* @return the initial value for this thread-local*/protected T initialValue() {return null;}---------------/** 比如 自定义一个String类型的匿名ThreadLocal**/ThreadLocal<String> stringThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>(){@Overrideprotected String initialValue() {return "I am kira";}};
2.ThreadLocalMap - 线程隔离的秘密
2.1 ThreadLocalMap的定义
- ThreadLocalMap是一个专门为线程本地变量设计的一个特殊的哈希表
- ThreadLocalMap的key为ThreadLocal,value即为要保存的变量的值
- 每个线程都有一个私有的ThreadLocalMap对象,其可以存放多个不同ThreadLocal作为key的键值对
- ThreadLocalMap采用的是开地址法而不是链表来解决冲突,并要求容量必须是2次幂
2.2 ThreadLocalMap的数据结构
2.2.1 类定义
static class ThreadLocalMap
2.2.2 Entry
/*** The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using* its main ref field as the key (which is always a* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.* 它使用主要的引用域作为自身的key(即ThreadLocal对象)* 由于Entry继承自WeakReference,而ThreadLocal被WeakReference封装* !!重点:因此Entry的Key才是弱引用(而不是Entry)!!(笔者在内存泄露会进一步阐述)* 当调用get方法返回null时,这意味着该key不再被引用,因此该entry将会从数组中移除* 弱引用:当JVM在GC时如果发现弱引用就会立即回收* 比较有意思的是Entry并没有使用HashMap.Entry的链表结构* 感兴趣的读者可先思考ThreadLocalMap是如何处理hash冲突的问题(后面就讲解)*/static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;//当ThreadLocal的外部强引用被回收时,ThreadLocalMap的key会变成null//注意key是个ThreaLocal对象,但因为key被WeakReference封装,因此才具有弱引用特性Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}
2.2.3 重要内部元素
/*** The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.* 容量必须2次幂,服务于Hash算法*/private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;/*** The table, resized as necessary. table.length MUST always be a power of two.* 底层实现还是一个Entry数组*/private Entry[] table;/*** The number of entries in the table.* 数组已有元素数量*/private int size = 0;/*** The next size value at which to resize.* 阈值,默认为0*/private int threshold; // Default to 0
2.2.4 构造器
/*** Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.* 默认构造器,包含一个键值对:一个ThreadLocal类型的key,一个任意类型的value* createMap方法会直接使用该构造器一次性完成ThreadLocalMap的实例化和键值对的存储*/ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];//计算数组下标 跟HashMap的 index = key.hashCode() & (cap -1) 保持一致(即取模运算优化版)int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);//在数组指定下标处填充数组table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);size = 1;setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);//默认阈值是 32/3 约等于 10.6667}/*** Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.* 取len的三分之二,而不是HashMap的0.75*/private void setThreshold(int len) {threshold = len * 2 / 3;}
2.3 ThreadLocalMap的重要方法
2.3.1 set方法
/*** Set the value associated with key.* 存储键值对,比较有趣的是Entry并不是链表,这意味着ThreadLocalMap底层只是数组* 其解决冲突(或者说散列优化)的关键在于神奇的0x61c88647* 若遇到过期槽,就占用该过期槽(会涉及位移和槽清除操作)* 当清理成功同时到达阈值,需要扩容* @param key the thread local object* @param value the value to be set*/private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//数组容量//计算数组下标 跟HashMap的 index = key.hashCode() & (cap -1) 保持一致(即取模运算优化版)int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal k = e.get();//若key已存在,替换值即可if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}//若当前槽为过期槽,就清除和占用该过期槽if (k == null) {replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}//否则继续往后 直到找到key相等或第一个过期槽为止}tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);int sz = ++size;//当清理成功同时到达阈值,需要扩容//cleanSomeSlots要处理的量是已有元素数量if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash();}/*** Increment i modulo len. 不超过长度就自增1*/private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);}
2.3.2 replaceStaleEntry方法
/*** Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation with an entry* for the specified key. The value passed in the value parameter is stored in* the entry, whether or not an entry already exists for the specified key.* 在set时用新元素替换掉一个过期元素(也就是占用过期元素的所在槽)* As a side effect, this method expunges all stale entries in the* "run" containing the stale entry. (A run is a sequence of entries* between two null slots.)* 该方法的副作用是将当前过期槽前后两个空槽之间的所有过期元素全部移除* @param key the key* @param value the value to be associated with key* @param staleSlot index of the first stale entry encountered while searching for key.* !!重点:过期槽:这里指的都是key为null的槽,由于key(ThreadLocal)是弱引用类型,* !!所以可能被GC自动回收,从而导致key为null,但槽对应的Entry并不一定被回收,value不一定被回收*/private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal key, Object value, int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;Entry e;int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;//先备份一个要处理的过期槽下标//1和2 的综合作用是将当前过期槽前后两个空槽之间的所有过期元素全部移除//1.从当前过期槽开始往前找,一旦找到一个空槽就停止,记录前一个空槽下标for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = prevIndex(i, len))//找到前一个空槽并记录其下标if (e.get() == null)slotToExpunge = i;//Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever occurs first//2.从当前过期槽开始往后找,一旦找到当前key 或 之后的第一个空槽 就停止for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal k = e.get();//一旦先找到key,就替换if (k == key) {e.value = value;tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];//原槽点对应entry移动到新的槽点上tab[staleSlot] = e;//当前entry占领原槽点// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists//当第一次扫描找到,slotToExpunge要变成i,作为后续清除操作的新的起始槽点if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);return;}// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the// first still present in the run.//当第一次扫描的时候就碰到过期槽点(或空槽点),slotToExpunge要变成i//作为后续清除操作的起始槽点if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;}// If key not found, put new entry in stale slot// 若key不存在,直接用新元素占据该过期槽点tab[staleSlot].value = null;//先把过期槽点的value清除,防止泄露tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);//占领// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them//若还有过期元素,清除他们if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);}
2.3.3 cleanSomeSlots方法
/*** Heuristically scan some cells looking for stale entries.* This is invoked when either a new element is added, or* another stale one has been expunged. It performs a* logarithmic number of scans, as a balance between no* scanning (fast but retains garbage) and a number of scans* proportional to number of elements, that would find all* garbage but would cause some insertions to take O(n) time.* 当添加一个新元素或一个过期元素被移除时,该方法会被调用,用来扫描一些槽的过期元素并清洗* 为了取得无扫描和全扫描之间的一个平衡,该方法使用对数扫描(也就是log)* 它将发现需要回收的元素同时可能导致插入操作的性能降低为O(n)* @param i a position known NOT to hold a stale entry. The* scan starts at the element after i. 从该槽点之后开始扫描(已知该槽点没有存储过期元素)* @param n scan control: <tt>log2(n)</tt> cells are scanned,* unless a stale entry is found, in which case <tt>log2(table.length)-1</tt>* additional cells are scanned.When called from insertions,this parameter is the number* of elements, but when from replaceStaleEntry, it is the table length.* log2(n)个槽点将被扫描,当插入时被调用,这指的是已有元素数量,当替换时被调用,指的是数组容量* But this version is simple, fast, and seems to work well.* 官方说这种写法简单、快速同时工作良好,读者可自行测试一番(主要跟n的权重有关)* @return true if any stale entries have been removed.* 一旦有过期元素被移除,就返回true,表示至少有一个过期元素被清除成功*/private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {boolean removed = false;Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//这里跟skipList的跳跃思想有点类似,区别是跳跃表是空间换时间,这是就是简单的跳跃do {i = nextIndex(i, len);Entry e = tab[i];//找到一个过期槽点(可能也是空槽点)if (e != null && e.get() == null) {n = len;removed = true;//找到一个过期槽点就标志成功//但有个疑问就是此时并没有完成清洗操作,但文档描述称 have been removedi = expungeStaleEntry(i);}} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);//2进制往右移动一位:即log2(n)//简单回顾一下数学知识:2^n 的逆运算就是 log2(n),不理解的读者请心中愧对中学数学老师3秒钟return removed;}
2.3.4 expungeStaleEntry方法
/*** Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null.* 在当前过期槽点和下一个空槽点之间,移除过期元素* 该方法主要干了两个事情:* 1.清理当前过期槽* 2.从下一个槽开始遍历数组,移除过期槽,一旦遇到空槽就停止:* 2.1 当key为空时,移除过期槽* 2.2 当key非空但rehash之后rehash之后下标变化则移除原槽,元素搬迁新空槽* @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot 返回过期槽后面第一个空槽下标* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked for expunging).* 在当前过期槽点和下一个空槽点之间所有过期元素都会被移除*/private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//注意是数组容量// expunge entry at staleSlot 移除过期槽中的过期元素 加速GCtab[staleSlot].value = null;//1.value help gctab[staleSlot] = null;//2.slot help gcsize--;// Rehash until we encounter null 遍历数组并Rehash,直到遇到null时停止Entry e;int i;//从当前过期槽的下一个槽开始遍历数组for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);//根据(e = tab[i]) != null可知,一旦遇到空槽就停止(e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal k = e.get();//key是空就清除元素,防止内存泄露,help gcif (k == null) {//为了防止内存泄露,当ThreadLocal已过期失效时,通过主动移除value和slot帮助加速GC//同时还可以空出一个空槽供后面使用,不浪费空间e.value = null;tab[i] = null;size--;} else {//当key已存在,则需要重新计算下标(为什么不叫index而叫h?)int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);//当前后坐标不一致时(可能是扩容导致的 - 总之就是len变动导致下标变化)if (h != i) {//清空原槽,元素搬迁到新的空槽,原槽提供给新元素使用tab[i] = null;// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until// null because multiple entries could have been stale.// 一直往后找,直到找到一个空槽位置while (tab[h] != null)h = nextIndex(h, len);tab[h] = e;}}}return i;}
2.3.5 getEntry方法
/*** Get the entry associated with key. This method itself handles* only the fast path: a direct hit of existing key.* It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part* by making this method readily inlinable.* 该方法自身只处理直接匹配到的情况,主要是最大化直接匹配的性能* 匹配不到的话就依赖getEntryAfterMiss方法* @param key the thread local object* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);Entry e = table[i];//直接匹配,主要是为了最大化性能,能不开启循环就不循环if (e != null && e.get() == key)return e;else//找不到就依赖getEntryAfterMiss方法return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);}
2.3.6 getEntryAfterMiss方法
/*** Version of getEntry method for use when key* is not found in its direct hash slot.* 该方法用于根据下标不能直接找到的情况*/private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//不能直接匹配到的话,就只能循环遍历while (e != null) {ThreadLocal k = e.get();//找到立即返回if (k == key)return e;//遇到过期槽,移除过期槽if (k == null)expungeStaleEntry(i);else//否则继续往后遍历i = nextIndex(i, len);e = tab[i];}return null;}
2.3.7 remove方法
/*** Remove the entry for key.* 当找到该元素的时候,主要做了两个清洗操作* 1.将key(ThreadLocal)设置为null* 2.当前槽变成过期槽,因此要清除当前槽所存储的Entry元素(主要是避免内存泄露)*/private void remove(ThreadLocal key) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {if (e.get() == key) {e.clear();//会将key设为null -> this.referent = nullexpungeStaleEntry(i);//清除过期元素return;}}}
2.4 碰撞解决与神奇的0x61c88647
- 机智的读者肯定发现ThreadLocalMap并没有使用链表或红黑树去解决hash冲突的问题,而仅仅只是使用了数组来维护整个哈希表,那么重中之重的散列性要如何保证就是一个很大的考验
- ThreadLocalMap通过结合三个巧妙的设计去解决这个问题:
- 1.Entry的key设计成弱引用,因此key随时可能被GC(也就是失效快),尽量多的面对空槽
- 2.(单个ThreadLocal时)当遇到碰撞时,通过线性探测的开放地址法解决冲突问题
- 3.(多个ThreadLocal时)引入了神奇的
0x61c88647,增强其的散列性,大大减少碰撞几率- 之所以不用累加而用该值,笔者认为可能跟其找最近的空槽有关(跳跃查找比自增1查找用来找空槽可能更有效一些,因为有了更多可选择的空间
spreading out),同时也跟其良好的散列性有关- 0x61c88647与黄金比例、Fibonacci 数有关,读者可参见What is the meaning of 0x61C88647 constant in ThreadLocal.java
/*** The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.* 为了让哈希码能均匀的分布在2的N次方的数组里*/private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;/*** Returns the next hash code.* 每个ThreadLocal的hashCode每次累加HASH_INCREMENT*/private static int nextHashCode() {//the previous id + our magic numberreturn nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);}
3.ThreadLocal的实现机制
- 每个线程都拥有一个ThreadLocalMap对象,即
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null- 每一个ThreadLocal对象有一个创建时生成唯一的HashCode,即
nextHashCode(),通过取模确定所在槽下标位置- 访问一个ThreadLocal变量的值,即是查找ThreadLocalMap中对应键值对,即key为该ThreadLocal的键值对
- 由于一个ThreadLocalMap可以拥有很多个ThreadLocal,推导可得一个线程可拥有多个ThreadLocal(或者说拥有多个不同ThreadLocal作为key的键值对)
//可以定义多个ThreadLocal,每个线程都拥有自己私有的各种泛型的ThreadLocal//比如线程A可同时拥有以下三个ThreadLocal对象作为keyThreadLocal<String> stringThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>();ThreadLocal<Object> objectThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Object>();ThreadLocal<Integer> intThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>();
4.ThreadLocal与内存泄露
4.1 JVM的堆栈
4.1.1 Java堆(Heap)
- 堆是所有线程共享的一块内存区域(硬件表现为内存条)
- 唯一作用是存放所有对象实例,即所有的对象实例以及数组都要在堆上分配内存
4.1.2 JVM栈(JVM Stack)
- 栈为线程私有,生命周期与栈保持一致
- 主要用来描述的是Java方法执行的内存模型:每个方法在执行的同时都会创建一个栈帧,用来存放局部变量表、操作数栈、动态链接、方法出口等信息
- 每个方法从调用到执行结束的就是栈帧入栈、出栈的过程
- 局部变量表存放所有基本数据类型、对象引用 和returnAddress类型
- 若线程请求的栈深度大于JVM许可深度,将抛出 StackOverflowError异常,即栈溢出
- 若栈支持动态拓展,但拓展时无法申请到足够的内存,将抛出OutOfMemoryError异常,即堆(内存)溢出
4.2 内存泄露
- 内存泄露指的是已动态分配的堆中对象由于种种原因无法被释放,造成内存浪费,最终导致程序运行速度下降甚至程序崩溃
- 在Java中的具体表现是堆中的 无用对象因为种种原因没有被及时(或无法)GC,导致一直滞留在内存中无法被销毁,造成内存浪费,当内存不足无法分配更多内存时,最终将抛出OutOfMemoryError异常,即内存溢出
- 有兴趣的读者可以进一步研究GC的引用可达性机制(有机会笔者将在GC番中进一步介绍)
4.3 ThreadLocal与内存泄露
4.3.1 ThreadLocal实现原理图
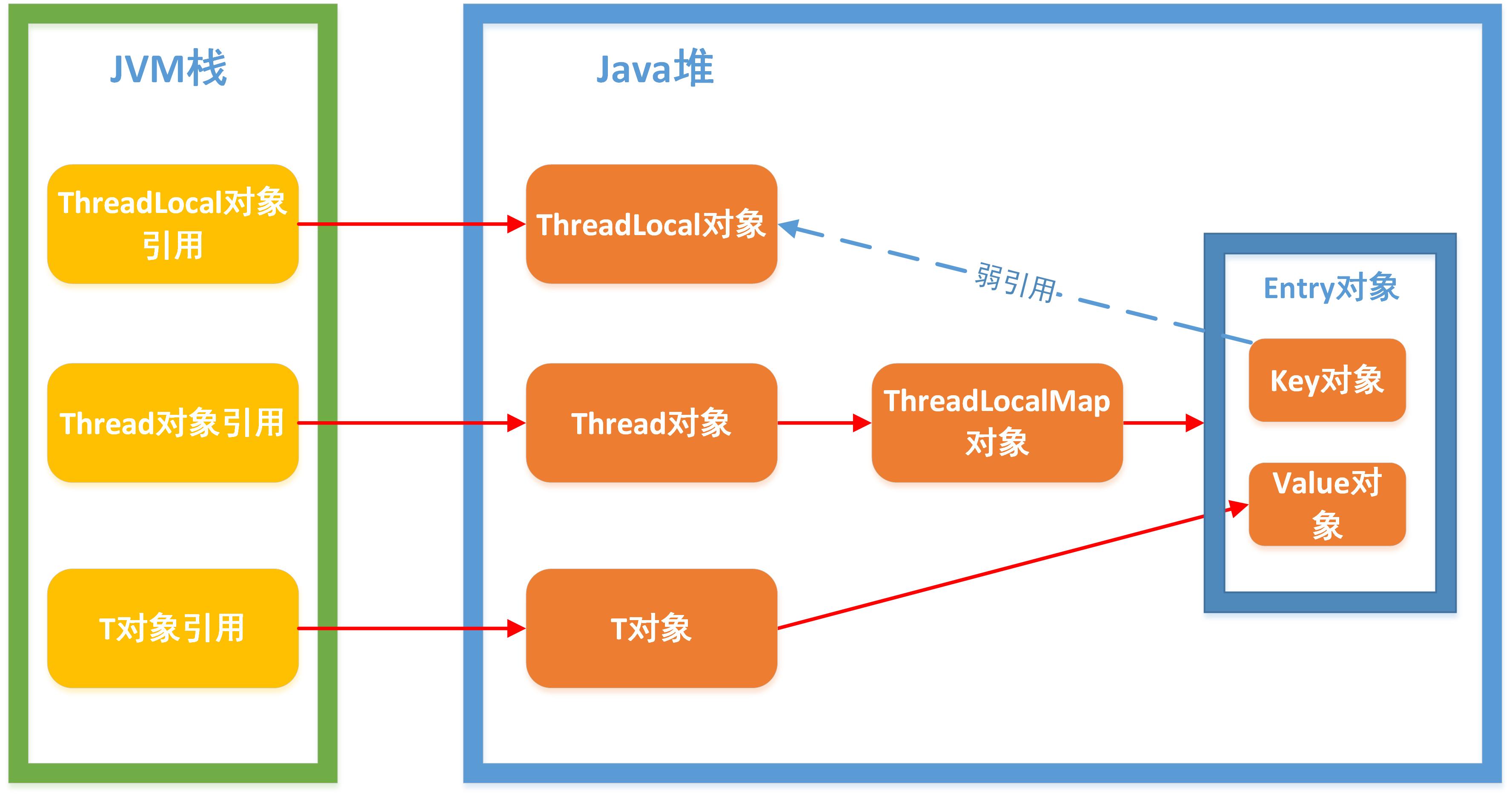
4.3.2 ThreadLocal导致内存泄露的错误行为
- 1.使用static的ThreadLocal,延长了ThreadLocal的生命周期,可能导致内存泄漏
- 2.分配使用了ThreadLocal又不再调用
get(),set(),remove()方法就会导致内存泄漏- 3.当使用线程池时,即当前线程不一定会退出(比如固定大小的线程池),这样将一些大对象设置到ThreadLocal中,可能会导致系统出现内存泄露(当对象不再使用时,因为引用存在,无法被回收)
4.3.3 ThreadLocal导致内存泄露的根源
- 首先需要明确一点:ThreadLocal本身的设计是不会导致内存泄露的,原因更多是使用不当导致的!
- ThreadLocalMap对象被Thread对象所持有,当线程退出时,Thread类执行清理操作,比如清理ThreadLocalMap;否则该ThreadLocalMap对象的引用并不会被回收。
//先回顾一下:Thread的exit方法/*** This method is called by the system to give a Thread* a chance to clean up before it actually exits.*/private void exit() {if (group != null) {group.threadTerminated(this);group = null;}/* Aggressively null out all reference fields: see bug 4006245 */target = null;/* Speed the release of some of these resources */threadLocals = null;//清空threadLocalMap的引用inheritableThreadLocals = null;inheritedAccessControlContext = null;blocker = null;uncaughtExceptionHandler = null;}
- 根源:由于Entry的key弱引用特性(见注意),当每次GC时JVM会主动将无用的弱引用回收掉,因此当ThreadLocal外部没有强引用依赖时,就会被自动回收,这样就可能造成当ThreadLocal被回收时,相当于将Map中的key设置为null,但问题是该key对应的entry和value并不会主动被GC回收,
- 当Entry和value未被主动回收时,除非当前线程死亡,否则线程对于Entry的强引用会一直存在,从而导致内存泄露
- 建议: 当希望回收对象,最好使用
ThreadLocal.remove()方法将该变量主动移除,告知JVM执行GC回收- 注意: ThreadLocal本身不是弱引用的,Entry继承了WeakReference,同时Entry又将自身的key封装成弱引用,所有真正的弱引用是Entry的key,只不过恰好Entry的key是ThreadLocal!!
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {//这里才是真正的弱引用!!super(k);//将key变成了弱引用!而key恰好又是ThreadLocal!value = v;}}public class WeakReference<T> extends Reference<T> {public WeakReference(T referent) {super(referent);}public WeakReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue<? super T> q) {super(referent, q);}}
!!! 为了更理性地验证这个问题,我给出了如下实验代码:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap map = new HashMap();Obj o1 = new Obj();Obj o2 = new Obj();map.put(o1, "o1");map.put(o2, "o2");o1 = null;System.gc();System.out.println("first gc:" + map);o2 = null;System.gc();System.out.println("second gc:" + map);map.clear();System.gc();System.out.println("GC after map clear" + map);}}class Obj {private final String DESC = "obj exists";@Overridepublic String toString() {return DESC;}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {System.out.println("gc over");}}
打印结果:o1 gc:{obj exists=o1}GC after map clear{}gc over------------------------------------------------------------GC日志结果:0.197: [Full GC (System.gc()) 0.197: [CMS: 0K->465K(5120K), 0.0023683 secs] 2046K->465K(9728K), [Metaspace: 3087K->3087K(1056768K)], 0.0024750 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]0.201: [Full GC (System.gc()) 0.201: [CMS: 465K->386K(5120K), 0.0015944 secs] 710K->386K(9728K), [Metaspace: 3100K->3100K(1056768K)], 0.0016526 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]------------------------------------------------------------根据试验结果表明,当map 的key被设置为null时,实际上GC时并没有被回收,而当clear(即将value设置为null时),GC回收有效因此实际上内存泄漏的问题本质上还是GC的可达性分析认为map中的value非null时具有强依赖性!因此map想真正实现gc,除了自身为null(具体可以参见4.3.1 和4.3.3)这种途径外,第二种就是将value设置为null!因此ThreadLocal本身没问题而是需要注意如何使用,原因在于其被Weak修饰,虽然gc后key会被回收,但value并没有,value需要满足一定条件才能被设置为null,具体可以参见4.3.3 - 2 (我们会发现这几个方法调用时会讲key=null的value也设置为null!)!!!我们总结一下内存泄漏的根本原因:当key变成null后却没有清除null导致。(弱引用只是导致key自动变成null的原因,不是根本原因,参见HashMap);也验证了我们上面提到的"根源"
留个小问题:为什么要用weak?为什么不是value 使用weak ?
5.ThreadLocal的正确使用实例
5.1 SimpleDateFormat的线程不安全
- SimpleDateFormat(下面简称sdf)类内部有一个Calendar对象引用,因此该cal对象会被所有线程共享
- sdf调用parse()和format()方法时会调用该对象,而多线程环境cal对象的date是不确定的,可能随时会被后面的线程覆盖,因此线程不安全
5.2 SimpleDateFormat结合ThreadLocal实现线程安全
public class ThreadLocalDemo {//SimpleDateFormat缓存private static Map<String, ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>> sdfMap =new HashMap<String, ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>>();//对象锁private static ReentrantLock sdfLock = new ReentrantLock();/*** @Description: 推荐直接使用该方法 获取 DateFormat对象* 推荐理由:SimpleDateFormat非线程安全且生成开销大* @param pattern 格式规则* @return DateFormat*/public static SimpleDateFormat getDateFormat(final String pattern) {ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> tl = sdfMap.get(pattern);if (tl == null) {try {//最多10毫秒if (!sdfLock.tryLock(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {return new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);}tl = sdfMap.get(pattern);if (tl == null) {tl = new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>() {//这里重写initialValue,第一次get就获取该初始化,省去了set操作@Overrideprotected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() {return new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);}};sdfMap.put(pattern, tl);}} catch (Exception exception) {} finally {sdfLock.unlock();}}return tl.get();}//测试用例 笔者让100个线程同时开启服务,主要查看一下GC情况public static void main(String[] args) {//让100个线程同时干活CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(100, new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("100个线程全部准备完毕");}});//让100个线程活都干完了再GCCountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(100);Random random = new Random();//时间随机Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"准备中");cyclicBarrier.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}Date date = new Date(random.nextLong());SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = getDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + simpleDateFormat.format(date));countDownLatch.countDown();}};for (int i = 0 ; i<100;i++){new Thread(runnable).start();}try {//让100个线程活都干完了再GCcountDownLatch.await();System.gc();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}--------------------//输出:......Thread-98准备中Thread-99准备中100个线程全部准备完毕Thread-10:189499633-16-20 20:16:37Thread-61:63942764-13-30 06:13:03Thread-42:236537261-53-07 05:53:07......[GC (System.gc()) 38408K->1288K(251392K), 0.0033599 secs][Full GC (System.gc()) 1288K->986K(251392K), 0.0152343 secs]//分析:通过打印GC发现GC效果还是很不错的,清理了很大一个空间出来//补充:为了打印GC,在VM options中要加入-verbose:gc
6.ThreadLocal vs 同步机制
同步机制(如
synchronized)其通过控制对共享变量的访问顺序来解决多线程安全问题,但正因为同步导致共享变量在同一时刻内只能被一个线程访问,线程间必须通过竞争获取同步锁(耗时)进而才能访问变量,因此这是一种以延长访问时间来换取线程安全性的策略ThreadLocal通过为每一个线程都备份一份变量拷贝从而彻底消除竞争条件,变量间不需要共享,自然也就没有了并发问题。但由于变量私有而不是共享,因此ThreadLocal并不能真正的解决共享变量的并发安全问题,对比同步机制,这是一种以空间来换取线程安全性的策略
7.常见面试题
- 先谈谈ThreadLocal的实现原理?它是如何解决并发问题的?(这是个陷阱)
- 再说说TheadLocal如何处理冲突?
- 那么我们谈谈ThreadLocal的内存泄漏问题?
- 最后你说说ThreadLocal的适用场景?工作中有用到吗?如何正确使用?
- 终极问题:为什么一定要用weak?value用weak行不行?
- 额外问题:了解过netty的FastThreadLocal吗?
并发番@ThreadLocal一文通(1.7版) 由 黄志鹏kira 创作,采用 知识共享 署名-非商业性使用 4.0 国际 许可协议 进行许可。
本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。
