@kiraSally
2018-03-12T10:48:28.000000Z
字数 11451
阅读 2334
集合番@ArrayList一文通(1.8版)
JAVA COLLECTIONS 源码 1.8版
- 笔者个人博客 kiraSally的掘金个人博客 感谢支持
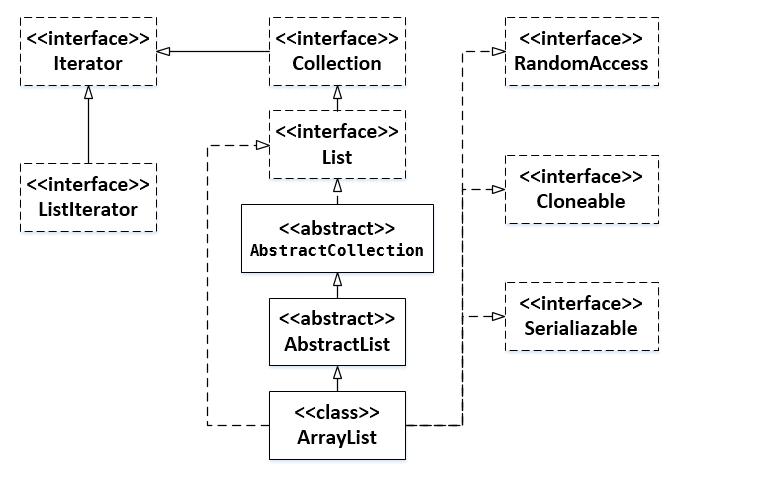
1.ArrayList上级接口的变化
- 先回顾一下ArrayList的类定义
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- 接口/类新增方法
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {.....//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,返回分片迭代器@Overridedefault Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);}//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,返回串行流对象default Stream<E> stream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,返回并行流对象default Stream<E> parallelStream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);}/*** Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given* predicate. Errors or runtime exceptions thrown during iteration or by* the predicate are relayed to the caller.* 1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,移除集合内所有匹配规则的元素,支持Lambda表达式*/default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {//空指针校验Objects.requireNonNull(filter);//注意:JDK官方推荐的遍历方式还是Iterator,虽然forEach是直接用for循环boolean removed = false;final Iterator<E> each = iterator();while (each.hasNext()) {if (filter.test(each.next())) {each.remove();//移除元素必须选用Iterator.remove()方法removed = true;//一旦有一个移除成功,就返回true}}//这里补充一下:由于一旦出现移除失败将抛出异常,因此返回false指的仅仅是没有匹配到任何元素而不是运行异常return removed;}}public interface Iterable<T>{.....//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,用于遍历集合default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (T t : this) {action.accept(t);}}//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,返回分片迭代器default Spliterator<T> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);}}public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,用于对集合进行排序,主要是方便Lambda表达式default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {Object[] a = this.toArray();Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);ListIterator<E> i = this.listIterator();for (Object e : a) {i.next();i.set((E) e);}}//1.8新增方法:提供了接口默认实现,支持批量删除,主要是方便Lambda表达式default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {Objects.requireNonNull(operator);final ListIterator<E> li = this.listIterator();while (li.hasNext()) {li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));}}/*** 1.8新增方法:返回ListIterator实例对象* 1.8专门为List提供了专门的ListIterator,相比于Iterator主要有以下增强:* 1.ListIterator新增hasPrevious()和previous()方法,从而可以实现逆向遍历* 2.ListIterator新增nextIndex()和previousIndex()方法,增强了其索引定位的能力* 3.ListIterator新增set()方法,可以实现对象的修改* 4.ListIterator新增add()方法,可以向List中添加对象*/ListIterator<E> listIterator();}
2.ArrayList的变化
- 1.8的
ArrayList只是在1.7的基础上做了很少的改动,主要集中于初始化以及实现接口新增方法方面- 1.7版本请参见笔者的 集合番@ArrayList一文通(1.7版)
3.ArrayList的属性变化
- 全局变量的变更
/*** The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer.* Any empty ArrayList with elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to* DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.* 数组缓存,跟1.7版本相比,主要有两个变化:* 1.去掉private属性,使用默认的friendly作用域,开放给同包类使用* 2.一个空数组的elementData将设置为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA直到第一个元素新增时* 使用DEFAULT_CAPACITY(10)完成有容量的初始化 -- 优化:这里选择将内存分配后置,而从尽可能节省空间*/transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access/*** Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.* 当时用空构造时,给予数组(elementData)默认值*/private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
- 构造器的变更
/*** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.* 1.8版的默认构造器,只会初始化一个空数组*/public ArrayList() {super();this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;//初始化一个空数组}/*** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.* 1.7版的默认构造器,会直接初始化一个10容量的数组*/public ArrayList() {this(10);}
4.ArrayList的方法变化
- trimToSize方法变更
/*** 1.8版的trimToSize,跟1.7版相比:* 可以明显的看到去掉了oldCapacity这一临时变量* 笔者认为这进一步强调了HashMap是非线程安全的,因此直接用length即可*/public void trimToSize() {modCount++;if (size < elementData.length) {elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}}/*** 1.7版的trimToSize*/public void trimToSize() {modCount++;int oldCapacity = elementData.length;if (size < oldCapacity) {elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}}
5.ArrayList的新增方法
5.1 forEach方法
/*** Performs the given action for each element of the {@code Iterable}* until all elements have been processed or the action throws an* exception. Unless otherwise specified by the implementing class,* actions are performed in the order of iteration (if an iteration order* is specified). Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the* caller.* 1.8新增方法,重写Iterable接口的forEach方法* 提供对数组的遍历操作,由于支持Consumer因此在遍历时将执行传入的方法*/@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);final int expectedModCount = modCount;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;final int size = this.size;for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {action.accept(elementData[i]);//执行传入的自定义方法}if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}--------------List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("有村架纯");list.add("桥本环奈");list.add("斋藤飞鸟");list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + "!!")); //输出:有村架纯!!桥本环奈!!斋藤飞鸟!!
5.2 removeIf方法
/*** Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given* predicate. Errors or runtime exceptions thrown during iteration or by* the predicate are relayed to the caller.* 1.8新增方法,重写Collection接口的removeIf方法* 移除集合内所有复合匹配条件的元素,迭代时报错会抛出异常 或 把断言传递给调用者(即断言中断)* 该方法主要干了两件事情:* 1.根据匹配规则找到所有符合要求的元素* 2.移除元素并转移剩余元素位置* 补充:为了安全和快速,removeIf分成两步走,而不是直接找到就执行删除和转移操作,写法值得借鉴*/@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {Objects.requireNonNull(filter);// figure out which elements are to be removed any exception thrown from// the filter predicate at this stage will leave the collection unmodifiedint removeCount = 0;//BitSet用于按位存储,这里用作存储待移除元素(即符合匹配规则的元素)//BitSet能够通过位图算法大幅减少数据占用存储空间和内存,尤其适合在海量数据方面,这里是个很明显的优化//有机会会在基础番中解析一下BitSet的奇妙之处final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);final int expectedModCount = modCount;final int size = this.size;//每次循环都要判断modCount == expectedModCount!for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")final E element = (E) elementData[i];if (filter.test(element)) {removeSet.set(i);removeCount++;}}if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}// shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements// 当有元素被移除,需要对剩余元素进行位移final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;if (anyToRemove) {final int newSize = size - removeCount;for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);elementData[j] = elementData[i];}for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work}this.size = newSize;if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}modCount++;}//正常情况下,一旦匹配到元素,应该删除成功,否则将抛出异常,当没有匹配到任何元素时,返回falsereturn anyToRemove;}--------------List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("有村架纯");list.add("桥本环奈");list.add("斋藤飞鸟");list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + "!!")); //输出:有村架纯!!桥本环奈!!斋藤飞鸟!!System.out.println(list.removeIf(s -> s.startsWith("斋藤")));//输出:truelist.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + ",")); //输出:有村架纯!!桥本环奈!!--------------//这里补充一点,使用Arrays.asList()生成的ArrayList是Arrays自己的私有静态内部类//强行使用removeIf的话会抛出java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException的异常(因为它没实现这个方法)
5.3 replaceAll方法
/*** Replaces each element of this list with the result of applying the operator to that element.* Errors or runtime exceptions thrown by the operator are relayed to the caller.* 1.8新增方法,重写List接口的replaceAll方法* 提供支持一元操作的批量替换功能*/@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {Objects.requireNonNull(operator);final int expectedModCount = modCount;final int size = this.size;for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {elementData[i] = operator.apply((E) elementData[i]);}if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}modCount++;}--------------List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("有村架纯");list.add("桥本环奈");list.add("斋藤飞鸟");list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + "!!")); //输出:有村架纯!!桥本环奈!!斋藤飞鸟!!list.replaceAll(t -> {if(t.equals("桥本环奈")) t = "逢泽莉娜";//这里我们将"桥本环奈"替换成"逢泽莉娜"return t;//注意如果是语句块的话一定要返回});list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + "!!")); //输出:有村架纯!!逢泽莉娜!!斋藤飞鸟!!
5.4 sort方法
/*** Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified* 1.8新增方法,重写List接口的sort方法* 支持对数组进行排序,主要方便于Lambda表达式*/@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {final int expectedModCount = modCount;//Arrays.sort底层是结合归并排序和插入排序的混合排序算法,有不错的性能//有机会在基础番对Timsort(1.8版)和ComparableTimSort(1.7版)进行解析Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}modCount++;}--------------List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("有村架纯");list.add("桥本环奈");list.add("斋藤飞鸟");list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + "!!")); //输出:有村架纯!!桥本环奈!!斋藤飞鸟!!list.sort((prev, next) -> prev.compareTo(next));//这里我们选用自然排序list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + "!!"));//输出:斋藤飞鸟!!有村架纯!!桥本环奈!!
6.ArrayList的新增并行分片迭代器
- 什么是并行分片迭代器
- 并行分片迭代器是Java为了并行遍历数据源中的元素而专门设计的迭代器
- 并行分片迭代器借鉴了Fork/Join框架的核心思想:用递归的方式把并行的任务拆分成更小的子任务,然后把每个子任务的结果合并起来生成整体结果
- 并行分片迭代器主要是提供给Stream,准确说是提供给并行流使用,使用时推荐直接用Stream即可
- ArrayListSpliterator类解析
default Stream<E> parallelStream() {//并行流return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);//true表示使用并行处理}static final class ArrayListSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {private final ArrayList<E> list;//起始位置(包含),advance/split操作时会修改private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split//结束位置(不包含),-1 表示到最后一个元素private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last indexprivate int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set/** Create new spliterator covering the given range */ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList<E> list, int origin, int fence,int expectedModCount) {this.list = list; // OK if null unless traversedthis.index = origin;this.fence = fence;this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;}/*** 获取结束位置,主要用于第一次使用时对fence的初始化赋值*/private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first useint hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)ArrayList<E> lst;if ((hi = fence) < 0) {//当list为空,fence=0if ((lst = list) == null)hi = fence = 0;else {//否则,fence = list的长度expectedModCount = lst.modCount;hi = fence = lst.size;}}return hi;}/*** 对任务(list)分割,返回一个新的Spliterator迭代器*/public ArrayListSpliterator<E> trySplit() {//二分法int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small 分成两部分,除非不够分new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(list, lo, index = mid,expectedModCount);}/*** 对单个元素执行给定的执行方法* 若没有元素需要执行,返回false;若可能还有元素尚未执行,返回true*/public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {if (action == null)throw new NullPointerException();int hi = getFence(), i = index;if (i < hi) {//起始位置 < 终止位置 -> 说明还有元素尚未执行index = i + 1; //起始位置后移一位@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)list.elementData[i];action.accept(e);//执行给定的方法if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();return true;}return false;}/*** 对每个元素执行给定的方法,依次处理,直到所有元素已被处理或被异常终止* 默认方法调用tryAdvance方法*/public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loopArrayList<E> lst; Object[] a;if (action == null)throw new NullPointerException();if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null) {if ((hi = fence) < 0) {mc = lst.modCount;hi = lst.size;}elsemc = expectedModCount;if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {for (; i < hi; ++i) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];action.accept(e);}if (lst.modCount == mc)return;}}throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}/*** 计算尚未执行的任务个数*/public long estimateSize() {return (long) (getFence() - index);}/*** 返回当前对象的特征量*/public int characteristics() {return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;}}--------------List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("有村架纯");list.add("桥本环奈");list.add("斋藤飞鸟");Spliterator<String> spliterator = list.spliterator();spliterator.forEachRemaining(s -> System.out.print(s += "妹子!!"));//输出:有村架纯妹子!!桥本环奈妹子!!斋藤飞鸟妹子!!//因为这个类是提供给Stream使用的,因此可以直接用Stream,下面的代码作用等同上面,但进行了并发优化Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();parallelStream.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s += "妹子!!"));//输出:桥本环奈妹子!!有村架纯妹子!!斋藤飞鸟妹子!! --> 因为引入并发,所有执行顺序会有些不同
集合番@ArrayList一文通(1.8版) 由 黄志鹏kira 创作,采用 知识共享 署名-非商业性使用 4.0 国际 许可协议 进行许可。
本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。
