@zifeng328573112
2020-05-10T06:55:55.000000Z
字数 10638
阅读 857
GreenDao源码解析
1. 简介
- [TOC]
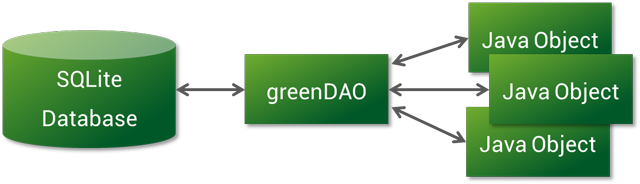
- greenDAO 是一个将对象映射到 SQLite 数据库中的轻量且快速的 ORM 解决方案。
2. 特点
- [TOC]
-
- 性能最大化,可能是Android平台上最快的ORM框架;
- 易于使用的API;
- 最小的内存开销;
- 依赖体积小;
- 支持数据库加密;
- 强大的社区支持。
3. 源码框架
[TOC]
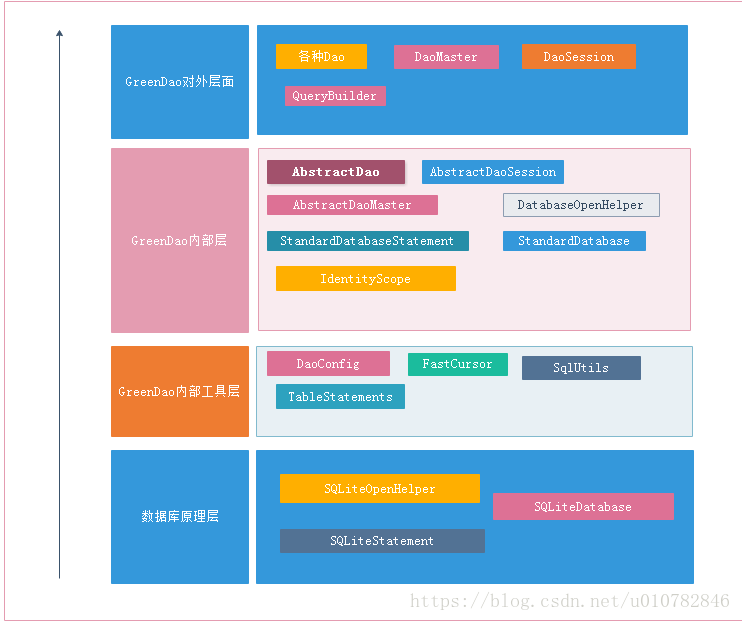
GreenDao可以划分为四层:
- 底层以Sqlite为基础;
- 工具层则是主要的对sql语句的处理和Dao配置与解析;
- 内部类则是提供对外层的一些基础类;
- 对外层则是针对对实体进行增删改查。
GreenDao的实现原理进行分析,如下图所示:
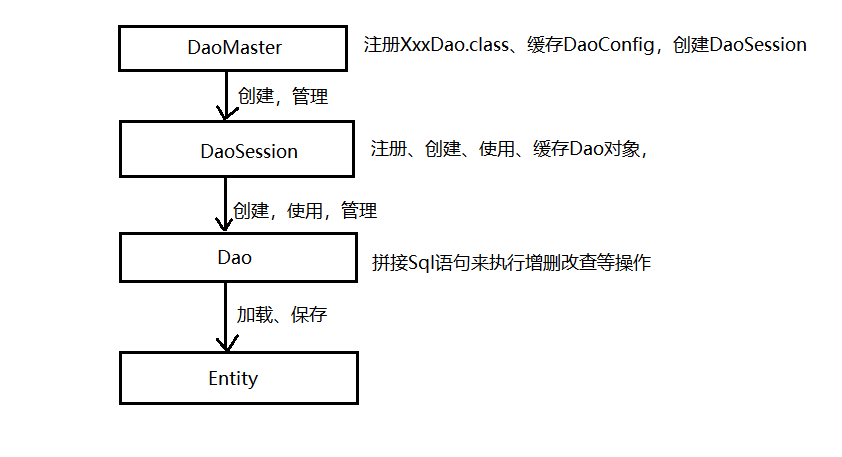
其中:
- DaoMaster:Dao中的管理者。它保存了sqlitedatebase对象以及操作DAO classes(注意:不是对象)。其提供了一些创建和删除table的静态方法,其内部类OpenHelper和DevOpenHelper实现了SQLiteOpenHelper,并创建数据库的框架。
- DaoSession:操作具体的DAO对象(注意:是对象),比如各种getter方法。
- Daos:实际生成的某某DAO类,通常对应具体的java类。
Entities:持久的实体对象。
4. DaoMaster
- [TOC]
- 4.1:首先从DaoMaster的构造函数进行,需要传入一个SQLiteDatabase的实例。
public DaoMaster(SQLiteDatabase db) {this(new StandardDatabase(db));}public DaoMaster(Database db) {super(db, SCHEMA_VERSION);registerDaoClass(BankInformationBeanDao.class);}
得到一个SQLiteDatabase的实例,则需要一个Helper类。在GreenDao中用到的
$ DevOpenHelper->OpenHelper->DatabaseOpenHelper->SQLiteOpenHelper
DevOpenHelper继承OpenHelper类,里面有一个方法,更新版本。
/** WARNING: Drops all table on Upgrade!* Use only during development.*/public static class DevOpenHelper extends OpenHelper {public DevOpenHelper(Context context, String name) {super(context, name);}public DevOpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory) {super(context, name, factory);}@Overridepublic void onUpgrade(Database db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {Log.i("greenDAO", "Upgrading schema from version " + oldVersion + " to " + newVersion + " by dropping all tables");dropAllTables(db, true);onCreate(db);}}
OpenHelper继承DatabaseOpenHelper类,里面也只有一个方法,创建一个表。
/*** Calls {@link #createAllTables(Database, boolean)} in {@link #onCreate(Database)} -*/public static abstract class OpenHelper extends DatabaseOpenHelper {public OpenHelper(Context context, String name) {super(context, name, SCHEMA_VERSION);}public OpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory) {super(context, name, factory, SCHEMA_VERSION);}@Overridepublic void onCreate(Database db) {Log.i("greenDAO", "Creating tables for schema version " + SCHEMA_VERSION);createAllTables(db, false);}}
DatabaseOpenHelper继承自Sqlite帮助类,通过代理模式的思想,SQLiteDatabase扩展成Database。
/*** Like {@link #getWritableDatabase()},* but returns a greenDAO abstraction of the database.* The backing DB is an standard {@link SQLiteDatabase}.*/public Database getWritableDb() {return wrap(getWritableDatabase());}/*** Like {@link #getReadableDatabase()},* but returns a greenDAO abstraction of the database.* The backing DB is an standard {@link SQLiteDatabase}.*/public Database getReadableDb() {return wrap(getReadableDatabase());}
StandardDatabase实现了Database接口,Database拥有SQLiteDatabase所有的功能方法,只是替换调用。相当于用代理的方式实现了SQLiteDatabase的所有方法。
DatabaseOpenHelper第二个功能是扩展了EncryptedHelper继承于net.sqlcipher.database.SQLiteOpenHelper,当我们需要加密的时候可以使用。
从构造函数中可以看出,在初始化时会将XXXDao类进行注册。DaoMaster继承AbstractDaoMaster,而真正的注册是在AbstractDaoMaster进行注册。
/*** The master of dao will guide you:* start dao sessions with the master.* @author Markus*/public abstract class AbstractDaoMaster {protected final Database db;protected final int schemaVersion;protected final Map<Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>>, DaoConfig> daoConfigMap;public AbstractDaoMaster(Database db, int schemaVersion) {this.db = db;this.schemaVersion = schemaVersion;daoConfigMap = new HashMap<Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>>, DaoConfig>();}protected void registerDaoClass(Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>> daoClass) {DaoConfig daoConfig = new DaoConfig(db, daoClass);daoConfigMap.put(daoClass, daoConfig);}public int getSchemaVersion() {return schemaVersion;}/** Gets the SQLiteDatabase for custom database access.* Not needed for greenDAO entities.*/public Database getDatabase() {return db;}public abstract AbstractDaoSession newSession();public abstract AbstractDaoSession newSession(IdentityScopeType type);}
以Class来作为key,对DaoConfig进行配置缓存绑定。DaoConfig将留在后面4.2说明。
DaoMaster还有一个作用是创建DaoSession。
public DaoSession newSession() {return new DaoSession(db, IdentityScopeType.Session, daoConfigMap);}public DaoSession newSession(IdentityScopeType type) {return new DaoSession(db, type, daoConfigMap);}
4.2:DaoConfig
DaoConfig就是用来存储XXXDao中的一些必要的数据。
$ public final class DaoConfig implements Cloneable {
public final Database db;public final String tablename;public final Property[] properties;public final String[] allColumns;public final String[] pkColumns;public final String[] nonPkColumns;/** Single property PK or null if there's no PK or a multi property PK. */public final Property pkProperty;public final boolean keyIsNumeric;public final TableStatements statements;private IdentityScope<?, ?> identityScope;
这些属性对象是通过xxxDao.class反射来得到。
private static Property[] reflectProperties(Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>> daoClass) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {Class<?> propertiesClass = Class.forName(daoClass.getName() + "$Properties");Field[] fields = propertiesClass.getDeclaredFields();ArrayList<Property> propertyList = new ArrayList<Property>();final int modifierMask = Modifier.STATIC | Modifier.PUBLIC;for (Field field : fields) {// There might be other fields introduced by some tools, just ignore them (see issue #28)if ((field.getModifiers() & modifierMask) == modifierMask) {Object fieldValue = field.get(null);if (fieldValue instanceof Property) {propertyList.add((Property) fieldValue);}}}Property[] properties = new Property[propertyList.size()];for (Property property : propertyList) {if (properties[property.ordinal] != null) {throw new DaoException("Duplicate property ordinals");}properties[property.ordinal] = property;}return properties;}
IdentityScope表示是否需要缓存策略。缓存策略有两种:Session, None。当为None,表示不进行缓存,而为Session,则根据主键是否是数字来赋予内存缓存的管理对象。
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")public void initIdentityScope(IdentityScopeType type) {if (type == IdentityScopeType.None) {identityScope = null;} else if (type == IdentityScopeType.Session) {if (keyIsNumeric) {identityScope = new IdentityScopeLong();} else {identityScope = new IdentityScopeObject();}} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported type: " + type);}}
其中在IdentityScopeObject类中,直接用HashMap,以主键为Key,一个存储实体的队列为值,而在IdentityScopeLong则用LongHashMap,里面也是以主键为Key,一个存储实体的队列为值。
LongHashMap拥有containsKey(long key)、get(long key)、put(long key, T value)、remove(long key)等方法,与HashMap不同的是,LongHashMap的阈值是默认容量的4/3倍。超过该阈值时进行两倍扩容;而HashMap则是有一个扩容因子为0.75,如果超过默认容量的0.75倍,也进行两倍扩容。
另一个重要的属性对象则是Property,放在3.2节进行讲解。
4.3:Property
该类的主要作用是将bean类中的成员变量封装成一个对象,然后可以直接将这些对象进行一些条件查询。封装成对象主要是在xxxDao内进行封装。
| 条件查询 | 符号 |
|---|---|
| eq | = |
| notEq | <> |
| like | |
| between | |
| in | |
| notIn | |
| gt | > |
| lt | < |
| ge | 》= |
| isNull | |
| le | <= |
| isNotNull |
4.4:TableStatements
GreenDao不管是做查询还是其他操作都是使用Statement来进行优化性能的,而且Statement是可以重用的。而TableStatements是Statement的管理类。
public DatabaseStatement getInsertStatement() {if (insertStatement == null) {String sql = SqlUtils.createSqlInsert("INSERT INTO ", tablename, allColumns);DatabaseStatement newInsertStatement = db.compileStatement(sql);synchronized (this) {if (insertStatement == null) {insertStatement = newInsertStatement;}}if (insertStatement != newInsertStatement) {newInsertStatement.close();}}return insertStatement;}
可以看出,TableStatements维护着一个insertStatement对象,当对象为null时,调用SqlUtils的createSqlInsert的方法将这些参数拼接成sql语句。如果不为null就直接返回,为null就拼接创建,以达到复用优化性能的作用。
/*** Insert an entity into the table associated with a concrete DAO.** @return row ID of newly inserted entity*/public long insertOrReplace(T entity) {return executeInsert(entity, statements.getInsertOrReplaceStatement(), true);}private long executeInsert(T entity, DatabaseStatement stmt, boolean setKeyAndAttach) {long rowId;if (db.isDbLockedByCurrentThread()) {rowId = insertInsideTx(entity, stmt);} else {// Do TX to acquire a connection before locking the stmt to avoid deadlocksdb.beginTransaction();try {rowId = insertInsideTx(entity, stmt);db.setTransactionSuccessful();} finally {db.endTransaction();}}if (setKeyAndAttach) {updateKeyAfterInsertAndAttach(entity, rowId, true);}return rowId;}private long insertInsideTx(T entity, DatabaseStatement stmt) {synchronized (stmt) {if (isStandardSQLite) {SQLiteStatement rawStmt = (SQLiteStatement) stmt.getRawStatement();bindValues(rawStmt, entity);return rawStmt.executeInsert();} else {bindValues(stmt, entity);return stmt.executeInsert();}}}protected void updateKeyAfterInsertAndAttach(T entity, long rowId, boolean lock) {if (rowId != -1) {K key = updateKeyAfterInsert(entity, rowId);attachEntity(key, entity, lock);} else {// TODO When does this actually happen? Should we throw instead?DaoLog.w("Could not insert row (executeInsert returned -1)");}}
/*** Attaches the entity to the identity scope.* Calls attachEntity(T entity).* @param key Needed only for identity scope,* pass null if there's none.* @param entity The entitiy to attach*/protected final void attachEntity(K key, T entity, boolean lock) {attachEntity(entity);if (identityScope != null && key != null) {if (lock) {identityScope.put(key, entity);} else {identityScope.putNoLock(key, entity);}}}
- 通过判断当前线程是否和数据库关联来决定是否需要开启事务。
- 最后都执行insertInsideTx,里面的操作很简单就是调用之前子类的bindValue方法进行绑定值后执行Sql操作。
插入后的善后处理,这里就是更新实体的ID为RowId和做内存缓存。
上面的操作是单个实体的插入,当使用多数据插入的时候,需要加锁,因为多数据插入需要耗时,所以加锁是为了防止多线程问题。
GreenDao是怎么优化和做缓存
a、通过Statement的复用,达到优化的效果,这是所有数据库都通用的。
b、通过Key映射保存到内存中,保存的值当前是软引用,要不很容易爆表。DaoSession和AbstractDaoSession
DaoSession 管理着所有的DAO对象主要用于提供获取DAOs的接口,每一个DaoMaster持有一个数据库连接,通过DaoMaster的newSession()方法可以实例化多个Session,这些Session对应同一个数据库连接,但是系统会为每一个Session分配内存,在这片内存中会为实体进行缓存。每一个Session对应一个Identity scope。一个新的Session就代表一个会话,通过同一个会话中的DAOs进行的数据库操作。
5. DaoSession
- [TOC]
- 主要是创建xxxDao对象,然后将xxxDao注册到映射表。
public DaoSession(Database db, IdentityScopeType type, Map<Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>>, DaoConfig> daoConfigMap) {super(db);bankInformationBeanDaoConfig = daoConfigMap.get(BankInformationBeanDao.class).clone();bankInformationBeanDaoConfig.initIdentityScope(type);bankInformationBeanDao = new BankInformationBeanDao(bankInformationBeanDaoConfig, this);registerDao(BankInformationBean.class, bankInformationBeanDao);}
并且我们可以通过DaoSession实例直接得到xxxDao。
5.1: AbstractDaoSession
AbstractDaoSession里面就是实现一个从映射表中取出AbstractDao对象来进行增删改查的操作。
6. BankInformationBeanDao和AbstractDao
- [TOC]
- DAOs是负责直接实现增删改查数据库的,直接映射着我们要操作的JeanBean,所以默认情况下命名为XxxDAO。简而言之,要想操作数据库,都得先通过DaoSession的getXxxDAO系方法获得对应的DAO,再调用对应的方法, DAOs里生成数据库语句, 将成员变量与表里的参数绑定对应起来, 并且在它的父类AbstractDao 里实现了相对DaoSession的操作数据的方法。
6.1:xxxDao
- 每个实体Dao都有一个Properties来管理对象实体属性对表各列的映射关系,对像为Property;
- 提供创建表和删除表的实现;
- 提供Statement绑定对应实例的方法;
- 获得主键;
- 为了查询告诉,把实体Id设置成RowId。
6.2:AbstractDao
AbstractDao 里实现了相对DaoSession的操作数据的方法。
【增】
插入单个实体:insert(T)
插入或代替单个实体:insertOrReplace(T)
插入没有设置主键的单个实体:insertWithoutSettingPK(T)
数组的插入:insertInTX(T... entities)
集合实体的插入:insertInTx(Iterable)
插入或更新数组:insertInReplaceInTx(T... entities)
插入或更新集合:insertInReplaceInTx(Iterable)
【删】
删除单个实体:delete(T entity)
删除全部:deleteAll()
通过主键进行删除:deleteByKey(K key)
删除一个数组:deleteInTx(T... entities)
删除一个集合:deleteInTx(Iterable entities)
通过key删除一个数组:deleteByKeyInTx(K... keys)
通过key删除一个集合:deleteByKeyInTx(Iterable keys)
【改】
更新一个实体:update(T entity)
更新一个数组:updateInTx(T... entities)
更新一个集合:updateInTx(Iterable entities)
【查】
通过queryBuilder对象进行查询:queryBuilder();
查询的规则有以下几种:
| 查询条件 | 注释 |
|---|---|
| where | 条件子句,相当于SQL中的Where |
| distinct | 去重查询,相当于是在SQL语句中加了distinct |
| whereOr | 或条件查询 |
| and | 且条件查询 |
| orderAsc | 升序或降序查询 |
| limit | 分页查询 |
| list | 执行Query并把返回集合,并且entity都会加载到内存中,返回的结果通常就是ArrayList |
| listLazy | Entity按需加载到内存中,在第一次访问list中的element时,它就会被加载并且缓存 |
| listLazyUncached | 每次访问结果集的时候都是从数据库中加载,而不使用缓存。 |
| listIterator() | 通过迭代器访问结果集,并且采用的时lazy-loading,结果不会缓存。 |
| like() | 模糊查询 |
