@flyboy1995
2016-10-09T13:42:26.000000Z
字数 2541
阅读 45
第四次作业
作业1.5
摘要
本次作业研究的是两种放射性原子核A和B之间进行的衰变,原子核A会衰变成原子核B,而原子核B也会衰变成原子核A。题目要求我们研究A和B原子核的数量随时间的变换。并改变不同的初始条件后证实当系统稳定时,A和B原子核的数量是常量。
背景
题目原文:
1.5. Consider again a decay problem with two types of nuclei A and B, but now suppose that nuclei of type A decay into type B, while nuclei of type B decay into type A. Strictly speaking, this is not a "decay" process, since it is possible for the type B nuclei to turn back into type A. A better analogy would be a resonance in which a system can tunnel or move back and forth between two states A and B which have equal energies. The corresponding rate equations are
where for simplicity we have assumed that the two types of decay are characterized by the same time constant . Solve the system of equations for the numbers of nuclei, and , as functions of time. Consider different initial confitions, such as =100, =0, etc., and take =1 s. Show that your numerical results are consistent with the idea that the system reaches a steady state in which and are constant. In such a steady state, the time derivatives and should vanish.
正文
编程思路与课堂上所讲大同小异,由题目所给条件及泰勒展开可得:
按课上所讲思路,代码如下:
import pylab as plclass uranium_decay:def __init__(self, number_of_nuclei_A = 100, number_of_nuclei_B = 0 , time_constant = 1, time_of_duration = 5, time_step = 0.05):self.n_uranium_A = [number_of_nuclei_A]self.n_uranium_B = [number_of_nuclei_B]self.t = [0]self.tau = time_constantself.dt = time_stepself.time = time_of_durationself.nsteps = int(time_of_duration // time_step + 1)print("Initial number of nuclei A ->", number_of_nuclei_A)print("Initial number of nuclei B ->", number_of_nuclei_B)print("Time constant ->", time_constant)print("time step -> ", time_step)print("total time -> ", time_of_duration)def calculate(self):for i in range(self.nsteps):tmp_A = self.n_uranium_A[i] - self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau * self.dt+self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau * self.dttmp_B = self.n_uranium_B[i] - self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau * self.dt+self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau * self.dtself.n_uranium_A.append(tmp_A)self.n_uranium_B.append(tmp_B)self.t.append(self.t[i] + self.dt)def show_results(self):pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_A)pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_B)pl.xlabel('time ($s$)')pl.ylabel('Number of Nuclei A and B')pl.show()def store_results(self):myfile = open('nuclei_decay_data.txt', 'w')for i in range(len(self.t)):print'self.t[i], self.n_uranium_A[i], self.n_uranium_B[i], file = myfile'myfile.close()a = uranium_decay()a.calculate()a.show_results()
结论
当t=0时,原子核A的数量为100,原子核B的数量为0,时间常量设置为1。模拟结果如图所示: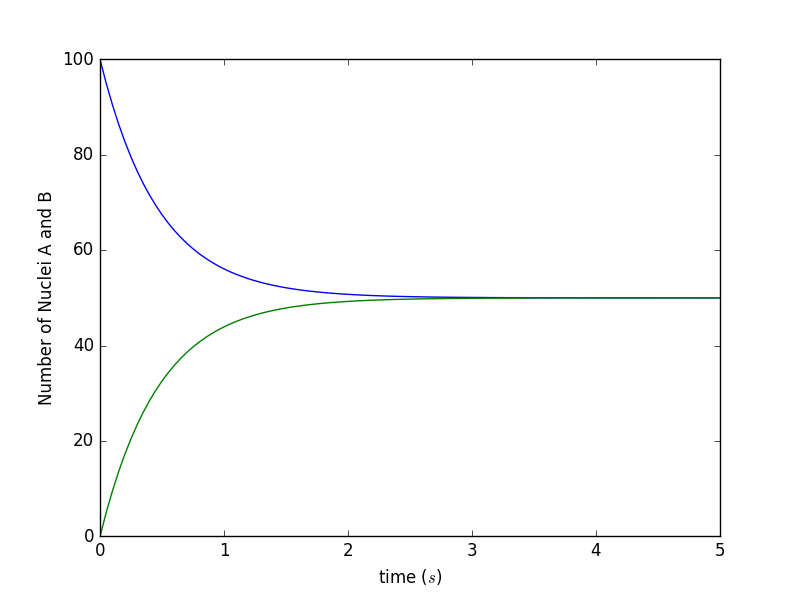
当t=0时,原子核A的数量为100,原子核B的数量为20,时间常量设置为1。模拟结果如图所示: 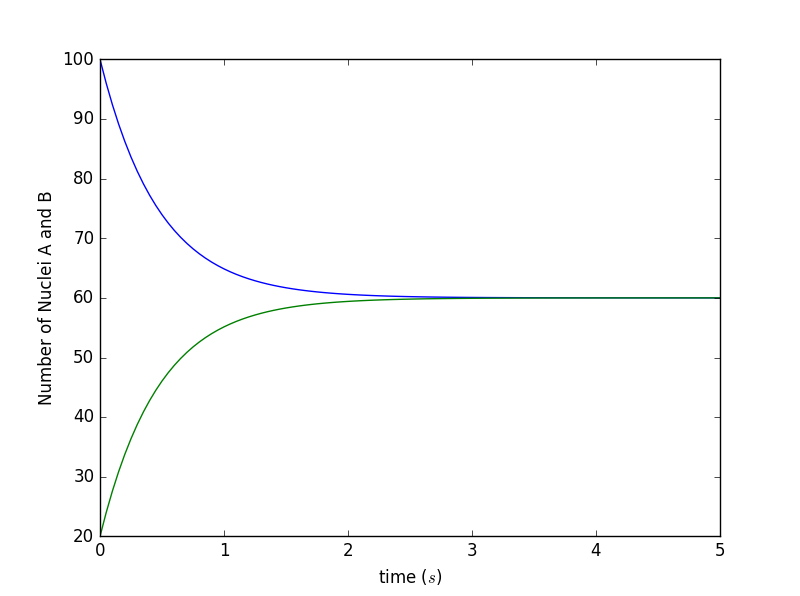
由实验结果所得:原子核A和原子核B的数量会逐渐趋于一致,且两种原子核数量的变化率变为0。
致谢
感谢蔡浩老师将课堂ppt及代码传到网上给我们参考。
