@flyboy1995
2016-11-07T02:52:01.000000Z
字数 2927
阅读 38
第七次作业
作业3.13
摘要
计算混沌系统中两个单摆的运动差别,并得出Lyapunov指数.
背景
题目原文:
3.13:Write a program to calculate and compare the behavior of two,nearly identical pendulums.Use it to calculate the divergence of two nearby trajectories in the chaotic regime,as in Figure 3.7,and and make a qualitative estimate of the corresponding Lyapunov exponent from the slope of a plot of log(Δθ) as a function of t.
正文
关系式:
代码如下:
import pylab as plimport numpy as npimport mathclass chaotic_pendulums:def __init__(self,length=9.8,q=0.5,initial_theta=0.2,initial_theta1=(0.2-0.001),initial_omega=0,initial_omega1=0,F_d=1.2,Omega_d=2.0/3,step_time=0.04,total_time=120):self.theta=[initial_theta]self.omega=[initial_omega]self.theta1=[initial_theta1]self.omega1=[initial_omega1]self.d_theta=[math.log(0.001)]self.dt=step_timeself.l=lengthself.q=qself.total_time=total_timeself.fd=F_dself.omegad=Omega_dself.t=[0]self.n=int(total_time/step_time)def pendulum(self):while self.t[-1]<=self.total_time:temp_omega=self.omega[-1]+(-9.8/self.l*math.sin(self.theta[-1])-self.q*self.omega[-1]+self.fd*math.sin(self.omegad*self.t[-1]))*self.dtself.omega.append(temp_omega)temp_theta=self.theta[-1]+temp_omega*self.dtself.theta.append(temp_theta)temp_t=self.t[-1]+self.dtself.t.append(temp_t)def pendulum1(self):self.t=[0]while self.t[-1]<=self.total_time:temp_omega1=self.omega1[-1]+(-9.8/self.l*math.sin(self.theta1[-1])-self.q*self.omega1[-1]+self.fd*math.sin(self.omegad*self.t[-1]))*self.dtself.omega1.append(temp_omega1)temp_theta1=self.theta1[-1]+temp_omega1*self.dtself.theta1.append(temp_theta1)temp_t=self.t[-1]+self.dtself.t.append(temp_t)def cal_d_theta(self):while self.t[-1]<=self.total_time:temp_omega=self.omega[-1]+(-9.8/self.l*math.sin(self.theta[-1])-self.q*self.omega[-1]+self.fd*math.sin(self.omegad*self.t[-1]))*self.dtself.omega.append(temp_omega)temp_theta=self.theta[-1]+temp_omega*self.dtself.theta.append(temp_theta)temp_omega1=self.omega1[-1]+(-9.8/self.l*math.sin(self.theta1[-1])-self.q*self.omega1[-1]+self.fd*math.sin(self.omegad*self.t[-1]))*self.dtself.omega1.append(temp_omega1)temp_theta1=self.theta1[-1]+temp_omega1*self.dtself.theta1.append(temp_theta1)self.d_theta.append(math.log(math.fabs(temp_theta-temp_theta1)))temp_t=self.t[-1]+self.dtself.t.append(temp_t)def show_result(self):pl.plot(self.t,self.theta)pl.xlabel("time($s$)")pl.ylabel("angle($radians$)")def show_result1(self):_plot,=pl.plot(self.t,self.theta1)pl.xlabel("time($s$)")pl.ylabel("angle($radians$)")pl.legend([_plot],["initial_theta=0.2-0.001"])def show_result2(self):pl.plot(self.t,self.d_theta)pl.xlabel("time($s$)")pl.ylabel("log(d_theta)($radians$)")a=chaotic_pendulums()a.pendulum()a.show_result()b=chaotic_pendulums()b.pendulum1()b.show_result1()c=chaotic_pendulums()c.cal_d_theta()c.show_result2()z=np.polyfit(c.t,c.d_theta,1)p=np.poly1d(z)print(z)print(p)
结论
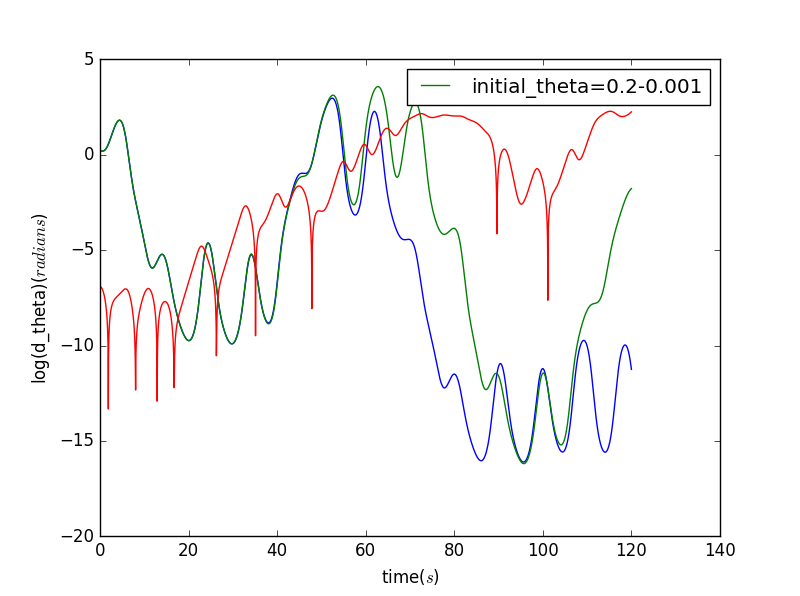
Lyapunov指数为0.08508
致谢
感谢秦大粤同学的分享!
