@Guozhongzhi
2016-10-23T15:02:29.000000Z
字数 3873
阅读 891
第六次作业
计算物理 郭忠智
一、摘要
本次作业完成了计算物理课本上第二章problem2.10炮弹发射抛物线运动轨迹的近似计算,加入了风阻,以及海拔对空气浓度的影响,对炮弹运行轨迹做了估计,观察目标海拔对炮弹发射速度的影响等。
二、背景
2.10 Generalize the program developed for the previous priblem so that it can deal with situations in which the target is at different altitude than the cannon.Consider cases in which the target is highter and lower than the cannon.Also investigate how the minimum firing velocity required to hit the target varies as the altitude of the target is varied.
三、正文
(一)没有阻力时,运动的方程为:
引入速度有:
(二)引入迎面风阻:
考虑空气浓度随海拔变化,用代替,得到
为空气浓度比,由气体的绝热模型可以得到:
所以
阻力在水平和竖直方向上的分量为:
所以(3)式变为:
用欧拉方法,得到:
(二)用Python编写代码,计算欧拉方法给出的结果
代码如下:
import numpyimport mathimport pylab as plclass cannon_shell:def __init__(self, x_0, y_0, initial_velocity, theta_0, \time_step, total_time, target_altitude):self.theta = theta_0self.v = [initial_velocity]self.v_0 = initial_velocityself.x = [x_0]self.y = [y_0]self.v_x = [math.cos(theta_0 * math.pi / 180) * initial_velocity]self.v_y = [math.sin(theta_0 * math.pi / 180) * initial_velocity]self.g = 9.8self.dt = time_stepself.time = total_timeself.a= 65e-4self.alpha = 2.5self.T_0 = 300self.B_2_m = 4e-5self.fm = []self.fy = []self.target_altitude = target_altitudedef run(self):for i in range(self.time):self.v.append(math.sqrt(self.v_x[-1] ** 2 + self.v_y[-1] ** 2))self.v_x.append(self.v_x[-1] - ((1 - self.a * self.y[-1] / \self.T_0) ** self.alpha) * self.B_2_m * self.v_x[-1] * \self.dt * self.v[-1])self.x.append(self.x[-1] + self.dt * self.v_x[-1])self.v_y.append(self.v_y[-1] - self.g * self.dt - ((1 - \self.a * self.y[-1] / self.T_0) ** self.alpha) * \self.B_2_m *self.v_y[-1] * self.dt * self.v[-1])self.y.append(self.y[-1] + self.dt * self.v_y[-1])if self.y[-1] <= self.target_altitude and self.y[-2] >= \self.target_altitude:breakself.x[-1] = (self.target_altitude -self.y[-2]) * \(self.x[-1] - self.x[-2]) / (self.y[-1] - self.y[-2]) +self.x[-2]for j in range(len(self.x)):self.x[j] = self.x[j] / 1000for j in range(len(self.y)):self.y[j] = self.y[j] / 1000for j in range(100):self.fm.append(max(self.y))self.fy.append(self.y[-1])def show_results(self):font1 = {'family': 'serif','color': 'darkred','weight': 'normal','size': 16,}font2 = {'family': 'serif','color': 'darkred','weight': 'normal','size': 6,}pl.plot(self.x, self.y)pl.plot(numpy.linspace(0, self.x[len(self.x) / 2], 100), \self.fm, ':')pl.plot(numpy.linspace(0, self.x[-1], 100), self.fy, ':')pl.title('Trajectory of cannon shell', fontdict = font1)pl.xlim(0, 35)pl.ylim(0, 16)pl.legend(loc="best")pl.xlabel('x ($km$)')pl.ylabel('y ($km$)')pl.text(22, max(self.y),\\str(self.theta) +'$\degree$, ' + str(self.v_0) + '$m/s$,'\+ str(max(self.y)) + '$km$', fontdict = font2)pl.figure(1)for i in numpy.linspace(100, 700, 12):a = cannon_shell(0 , 0, i, 50, 0.1, 1500, 2000)a.run()pl.figure(1)a.show_results()pl.show()pl.figure(2)for j in numpy.linspace(0, 45, 11):a = cannon_shell(0 , 0, 700, 30 + j, 0.1, 1500, 5000)a.run()pl.figure(2)a.show_results()pl.show()
上述算法计算了在同一发射角度、不同发射速度给出的轨迹,以及同一发射速度、不同发射角度的轨迹。给出的结果如下:
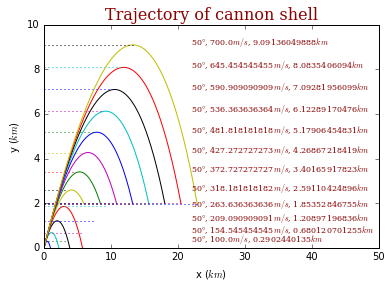
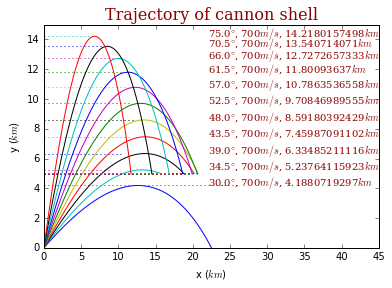
四、结论
从运行结果可以看到,当考虑空气浓度随海拔的变化后。炮弹运动轨迹与抛物线相似,观察图线,可以发现固定发射角度时,炮弹达到目标高度随发射速度成正相关。当固定发射速度,改变发射角度,炮弹达到目标高度时的前进距离会发生变化。
