@double-C
2016-05-03T09:31:11.000000Z
字数 1743
阅读 839
第五次作业 chapter1 exercise1.6
朱楚楚 材料物理 2013301510058
computationalphysics chapter1
摘要
用欧拉法解决以人口增长问题为背景的模型,比较参数b在不同取值下的情况。
背景介绍
Population growth problems often give rise to rate equations that are first-order. For example,the equation
might describe hoe the number of individuals in a population,N,varies with time. Here the first term aN corresponds to the birth of new members, while the second term - corresponds to deaths. The death term is proportional to to allow for the fact that food will become harder to find when the population becomes larger. Begin by solving (1.13) with using the Euler method, and compare your numerical result with the exact solution. Then solve (1.13) with nonzero values . Given an intuitive explanation of your results. Interesting values of and depend on the initial population . For small , and is a good choice, while for a good choice is and .
正文
-
人口增长不受食物、空间等外界条件限制,死亡率为0。则人口随时间变化的方程可化为:
可以解出此时人口增长模式为:
令 .
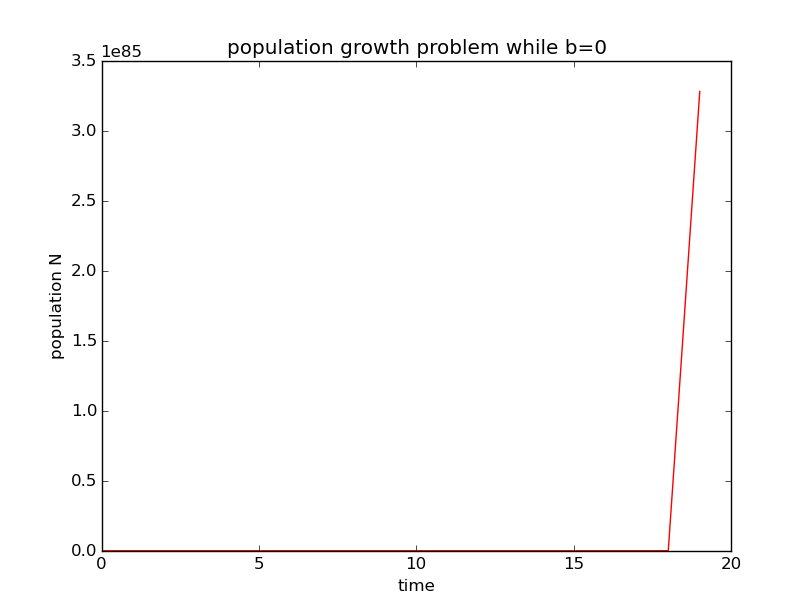
此为未用欧拉法所得 的精确解。
未用欧拉法所得所得人口增长图像如下:
代码在此
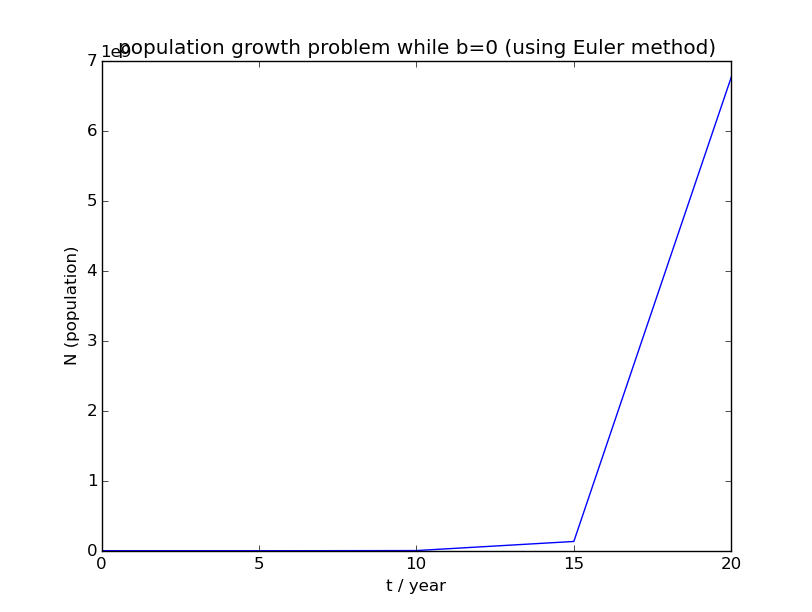
运用欧拉法所得人口增长图像如下:
代码在此
-
人口增长受食物、空间等外界条件限制,死亡率不为0。此时与的关系如下:
运用欧拉法如下
对在点进行泰勒展开有:
据此编写python代码,根据题意令并选择不同的 和时间 进行比较.
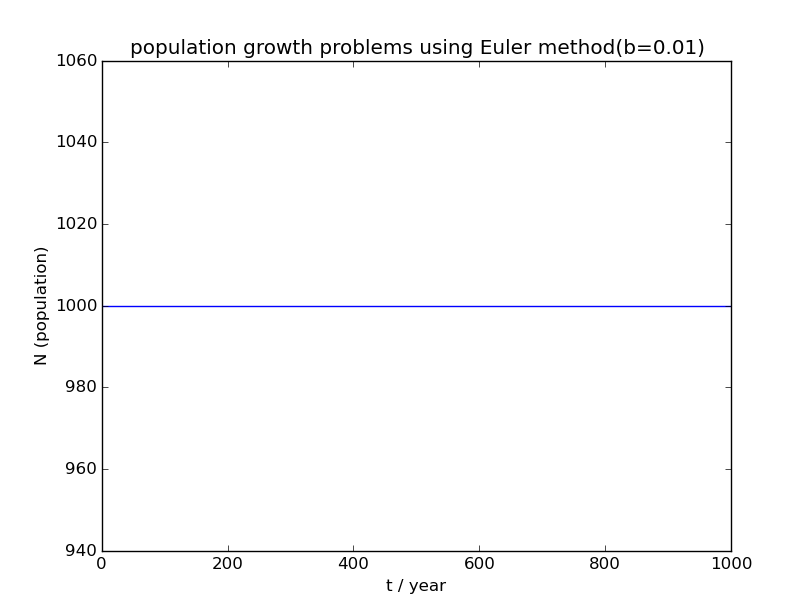
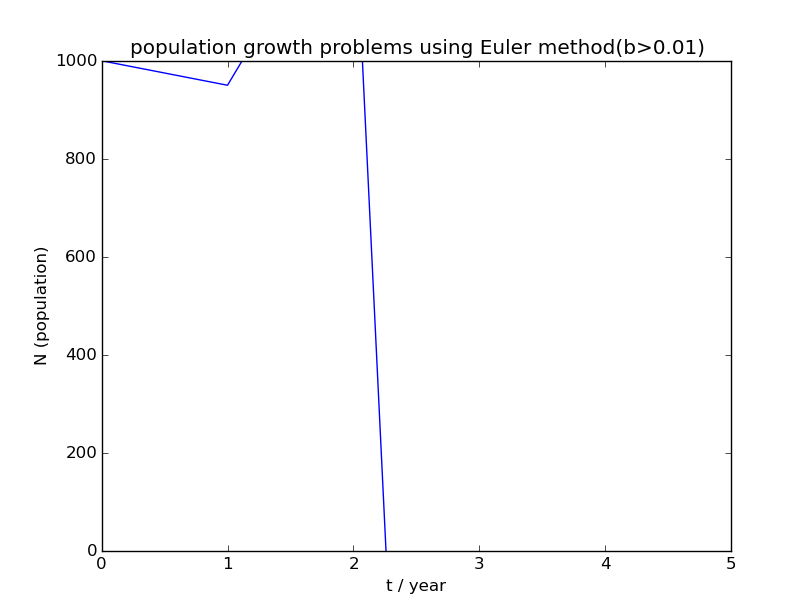
运行程序所得人口增长图像如下:
1)
2)
3)
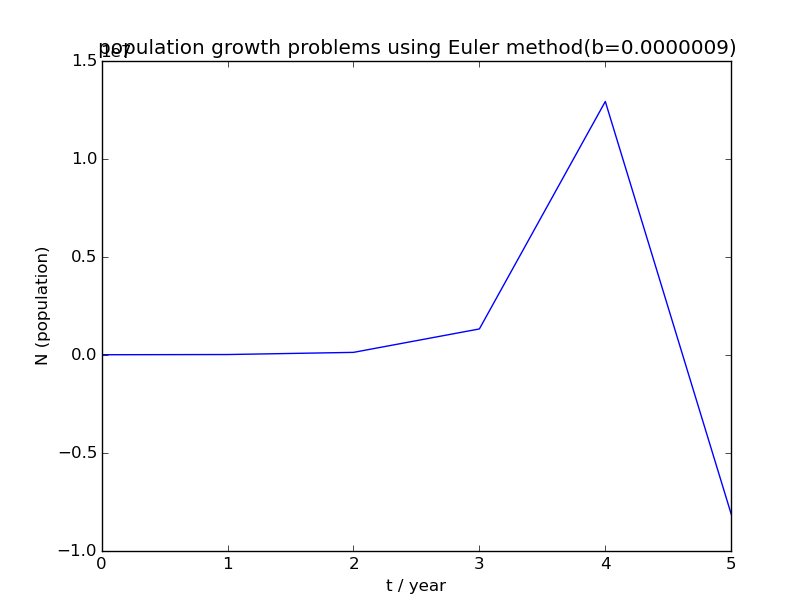
4)
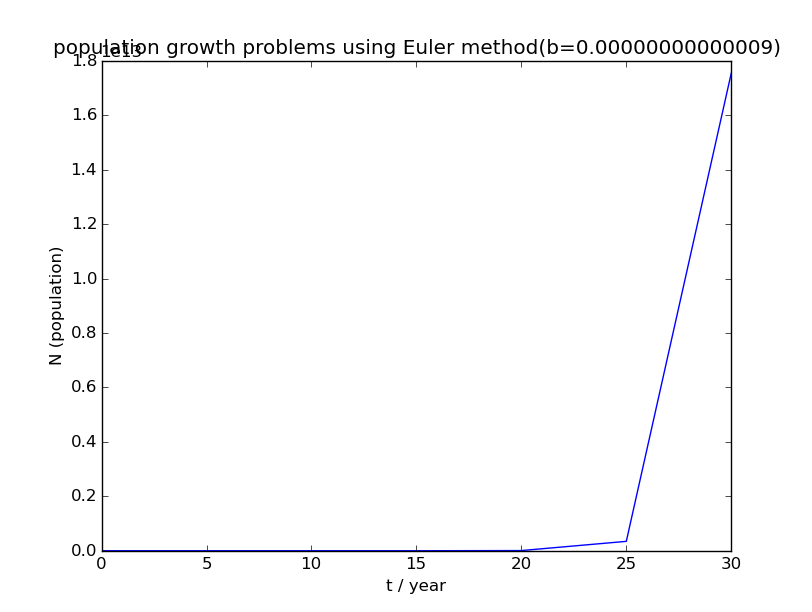
代码在此
结论
1)与本章1.1题不同,b=0时欧拉法所得数值解与精确解所有差别。从图像可以看出,运用欧拉法所得数值解的人口数量更快地变为非0值;
2)b=0.01时人口增长率为0,也就是说此时人口出生率=人口死亡率,人口将长期维持初始人口数量不变,这是一种稳定情况;
3)b>0.01时,人口无法维持长期稳定。人口数量经历一段时间的波动后必将迅速降至0;
4)b<0.01时,人口数量会在缓慢增长一段时间后开始激增,然后又迅速下降。人口数量可能骤降至0也可能下降一段时间后维持稳定。
致谢
这次作业依然参考了[蔡老师的代码]及同班同学的作业,除此之外还参考了matplotlib教程、python教程。结果如有不对请多多指正。
