@Yano
2017-08-06T08:43:06.000000Z
字数 3088
阅读 2683
Java 八大排序实现
Java
参考链接
本文只给出算法的Java实现版本,具体原理参考:八大排序算法。
公用代码
下面的swap()函数,是排序算法中经常用到的,单独贴出来。
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {int tmp = a[i];a[i] = a[j];a[j] = tmp;}
冒泡排序
/*** 冒泡排序:每次循环,将最后一个位置排序好* 算法改进:加一个标志位,记录每趟排序最后一个进行交换的位置,下一次只需扫描到pos* @param a*/public void bubbleSort(int[] a) {if (a == null) {return;}int right = a.length - 1;while (right > 0) {int pos = 0;for (int start = 0; start < right; start++) {if (a[start] > a[start + 1]) {swap(a, start, start + 1);pos = start;}}right = pos;}}
直接插入排序
将一个记录插入到已排序好的有序表中,从而得到一个新,记录数增1的有序表。即:先将序列的第1个记录看成是一个有序的子序列,然后从第2个记录逐个进行插入,直至整个序列有序为止。
public void insertSort(int[] a) {for (int right = 1; right < a.length; right++) {if (a[right] < a[right - 1]) {int tmp = a[right]; // 保存临时变量int left = right - 1;a[right] = a[right - 1]; // 先后移一个位置for (; left >= 0 && tmp < a[left]; left--) {a[left + 1] = a[left];}a[left + 1] = tmp;// 插入到正确位置}}}
简单选择排序
- 选出最小的元素,与数组第一个位置交换
- 选出第i小的元素,与数组第i个位置交换
- 直到第n-1个元素,与第n个元素比较为止
/*** 选择排序-简单选择排序* 基本思想:在一组要排序的数中,选取最小的与第一个位置交换*/public void selectSort(int[] a) {for(int start = 0; start < a.length; start++) {int key = selectMinKey(a, start);swap(a, key, start);}}private int selectMinKey(int[] a, int start) {int key = start;for(int i = start; i < a.length; i++) {key = a[key] > a[i] ? i : key;}return key;}
快速排序
public void quickSort(int[] a) {quickSort0(a, 0, a.length - 1);}private void quickSort0(int[] a, int low, int high) {if (low < high) {int pos = partition(a, low, high);quickSort0(a, low, pos - 1);quickSort0(a, pos + 1, high);}}private int partition(int[] a, int low, int high) {int privotKey = a[low];while (low < high) {while (low < high && a[high] >= privotKey) {high--;}swap(a, low, high);while (low < high && a[low] <= privotKey) {low++;}swap(a, low, high);}return low;}
归并排序
public void mergeSort(int[] a) {mergeSort0(a, 0, a.length - 1);}private void mergeSort0(int[] a, int left, int right) {if (left < right) {int mid = (left + right) / 2;mergeSort0(a, left, mid);mergeSort0(a, mid + 1, right);merge(a, left, mid, right);}}private void merge(int[] a, int start1, int mid, int right) {int[] tmp = new int[a.length];int k = start1; // tmp的初始下标int start = start1; // 记录初始位置int start2 = mid + 1; // 第2个数组的起始位置for(; start1 <= mid && start2 <= right; k++) {tmp[k] = a[start1] < a[start2] ? a[start1++] : a[start2++];}// 左边剩余的合并while (start1 <= mid) {tmp[k++] = a[start1++];}// 右边剩余的合并while (start2 <= right) {tmp[k++] = a[start2++];}// 复制数组while (start <= right) {a[start] = tmp[start];start++;}}
堆排序
public void heapSort(int[] a) {buildingHeap(a, a.length);for (int i = a.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {swap(a, i, 0);adjustHeap(a, 0, i);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}}/*** 选择排序-堆排序** 若以一维数组存储一个堆,则堆对应一个完全二叉树,且所有非叶结点的值,不大于其子女的值* 堆顶元素是最小的(小顶堆)*** 已知a[s...m]除了a[s]外均满足堆的定义 调整a[s],使之成为大顶堆,将第s个结点为根的子树筛选** a:待调整的堆数组 s:待调整的数组元素的位置 length:数组长度*/private void adjustHeap(int[] a, int s, int length) {int tmp = a[s];int child = 2 * s + 1; // 左孩子结点位置while (child < length) {// 如果有右孩子,同时右孩子值 > 左孩子值if (child + 1 < length && a[child] < a[child + 1])child++;if (a[s] < a[child]) { // 较大的子结点>父节点a[s] = a[child]; // 替换父节点s = child; // 重新设置,待调整的下一个结点位置child = 2 * s + 1;} elsebreak;a[s] = tmp; // 交换}}/*** 初始堆进行调整 将a[0...length-1]建成堆* 调整完后,第一个元素是序列最小的元素*/private void buildingHeap(int[] a, int length) {// 最有一个有孩子结点的位置是 i = (length - 1) / 2for (int i = (length - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {adjustHeap(a, i, length);}}
测试用例
@Testpublic void testHeapSort() {int[] a = new int[] { 4, 11, 5, 8, 1, 9, 2 };heapSort(a);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}
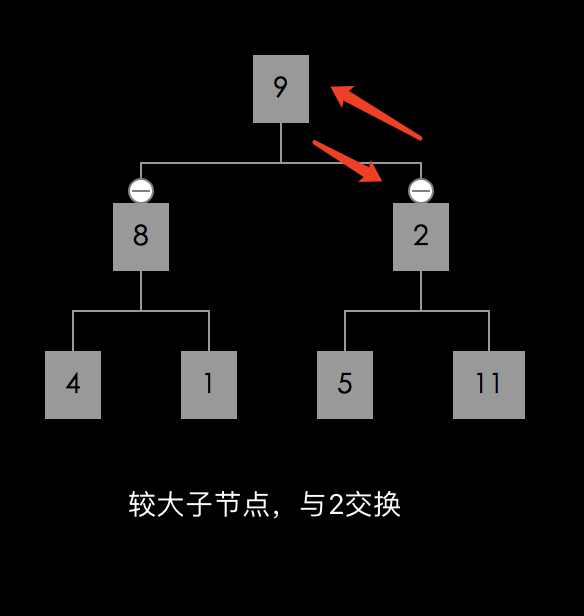
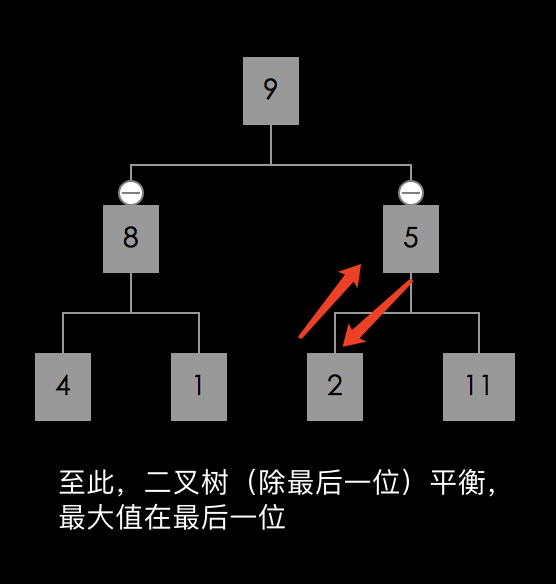
图解
buildingHeap 后,形成了大顶堆。
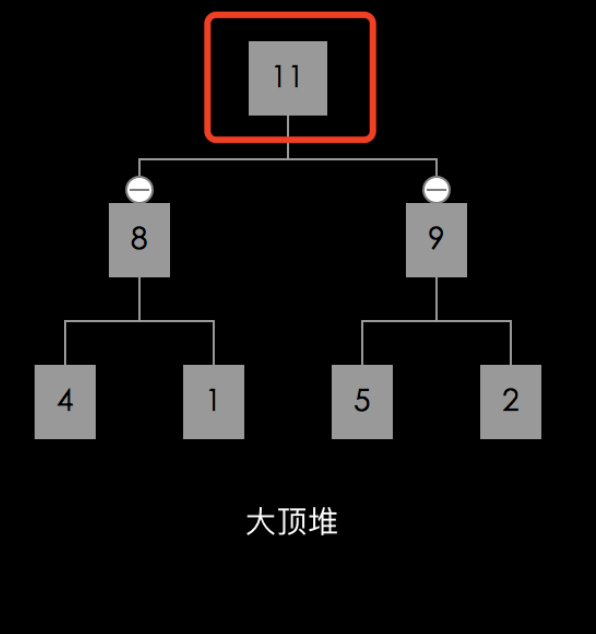
已经找到最大元素,与数组最后一个位置交换。
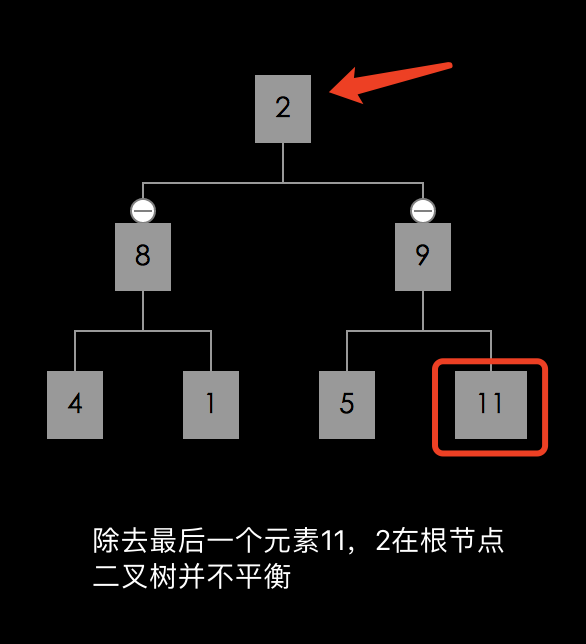
交换之后的二叉树并不平衡,需要调整。