@codejan
2018-11-13T12:44:33.000000Z
字数 5014
阅读 1702
实验报告_生产者消费者问题
操作系统
一. 题目
利用信号量机制, 实现生产者与消费者问题.
二. 方案设计
1)背景知识
- IPC
在linux下的多个进程间的通信机制叫做IPC(Inter-Process Communication), 它是多个进程之间相互沟通的一种方法, 在linux下有多种进程间通信的方法: 半双工管道、命名管道、消息队列、信号、信号量、共享内存、内存映射文件,套接字等等.
利用命令ipcs可以查看目前系统的共享内存、信号量, 队列信息.
利用linux的IPC机制, 可以实现记录型信号量, P操作, V操作和共享数据结构.
关于IPC的详细内容, 可以参考这篇文档:
Beej's Guide to Unix IPC - 信号量
一个整形(sem), 两个原子操作
P():sem减一, 如果sem<0, 等待, 否则继续.
V():sem加一, 如果sem<=0, 唤醒一个等待的P.
可以用停车场来类比: 显示灯可以看做信号量, 停车场内部可以看成临界区. 当内部的车停满时, 如果又有车想要进来, 执行P操作, 显示灯变为-1小于0, 必须有车出去才能够让等待的车进去
信号量是整数, 也是被保护的量
初始化完成后, 唯一能够改变一个信号量的值的办法是通过P()和V()
操作必须是原子
P()能够阻塞, V()不会阻塞.
通过P/V操作, 可以控制程序的挂起/唤醒, 达到一个线程等待另一个线程处理事情的目的.
2)解题思路
通过设置fullBuffer, emptyBuffer信号量解决生产者-消费着问题. 如果把fullBuffer和mutex的P操作顺序互换, 可能会引起死锁.
伪代码如下:
Class BoundedBudder {mutex = new Semaphore(1);fullBuffer = new Semaphore(0);emptyBuffer = new Semphore(n);}BoundedBudder::Producer(c) {emptyBuffer->P();mutex->P();add c to the buffer;mutex->V();fullBuffer->V();}BoundedBudder::Consumer(c) {fullBuffer->P();mutex->P();remove c from the buffer;mutex->V();emptyBuffer->V();}
3)具体实现
源代码pv.h和pv.c实现P,V操作, 其他程序使用#include<pv.h>调用.
源代码producter.c先获取信号量和共享内存, 设置共享缓冲区. 然后模拟生产者的行为, 每次生产一个随机数存放在缓冲区, 总共打印 20 次, 每次延迟一秒.
源代码 consumer.c 先获取信号量和共享内存, 设置共享缓冲区. 然后模拟消费者的行为, 每次从缓冲区中取出一个数打印, 总共取 20 次, 每次延迟一秒.
空文件 file_for_key 被用于产生、获取信号量和共享内存.
利用makefile指定编译顺序
三. 运行结果与分析
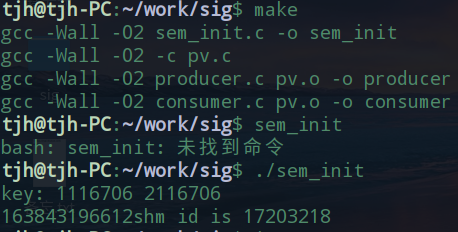
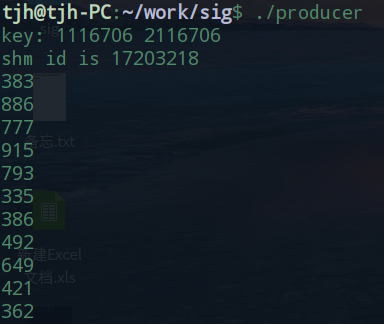
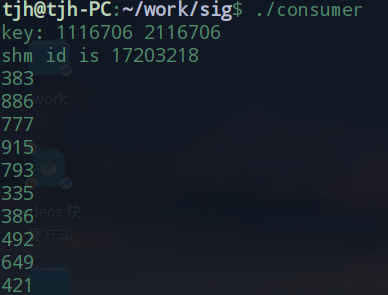
运行 make 之后, 得到三个可执行文件 sem_init, producter, consumer. 运行make clean可以清除这三个文件
在终端中先运行 sem_init, 然后在新开的终端上运行 producter 和 consumer, 通过观察各个终端上的输
出, 可以判断是否符合预期.
四. 源代码
pv.h
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/ipc.h>#include <sys/sem.h>#include <sys/shm.h>#define BUFFER_SIZE 10#define SHM_SIZE 102#define PRODUCT_NUM 25voidP (int sem_id);voidV (int sem_id);
pv.c
#include "pv.h"voidP (int sem_id){struct sembuf semop_buf;semop_buf.sem_num = 0;semop_buf.sem_op = -1;semop_buf.sem_flg = 0;if (semop (sem_id, &semop_buf, 1) == -1){perror ("PP"); //perror - print a system error messageexit (0);}}voidV (int sem_id){struct sembuf semop_buf;semop_buf.sem_num = 0;semop_buf.sem_op = 1;semop_buf.sem_flg = 0;if (semop (sem_id, &semop_buf, 1) == -1){perror ("VV");exit (0);}}voidshowval (int sem_a, int sem_b){int val_a, val_b;val_a = semctl (sem_a, 0, GETVAL);val_b = semctl (sem_b, 0, GETVAL);printf ("process %d: %d %d\n", getpid (), val_a, val_b);if (val_a == 1 && val_b == 1)exit (0);}
producer.c
#include "pv.h"intmain (){int sem_empty, sem_full;key_t key[2];//ftok - convert a pathname and a project identifier to a System V IPC keykey[0] = ftok ("file_for_key", 1);key[1] = ftok ("file_for_key", 2);printf ("key: %x %x\n", key[0], key[1]);/*semget - get a System V semaphore set identifierRETURN VALUEIf successful, the return value will be the semaphore set identifier (a non‐negative integer), otherwise, -1 is returned, with errno indicating theerror.*/sem_empty = semget (key[0], 0, 0);sem_full = semget (key[1], 0, 0);if (sem_empty < 0 || sem_full < 0){printf ("There are not sem_empty or sem_full!\n");exit(1);}int shm_id = shmget (key[0], 0, 0);if (shm_id)printf ("shm id is %d\n", shm_id);else{printf ("Key %d have not SHARE MEMORY!\n", key[0]);exit(1);}int *buffer;int *in;int *out;/*shmat, shmdt - System V shared memory operationsRETURN VALUEOn success, shmat() returns the address of the attached shared memory seg‐ment; on error, (void *) -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate thecause of the error.*/in = (int *) shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0);out = in + 1;buffer = out + 1;int i = 0;/*producer的过程:1. 对信号量sem_empty执行P操作2. 向缓冲区中in指针的位置放入一个随机数并打印3. 把in指针向前移动一个单位4. 对信号量sem_full执行V操作5. 计数器加16. 如此往复, 直到生产完成指定数量为止*/while (1){P(sem_empty);buffer[*in] = random() % 1000;printf ("%d\n", buffer[*in]);*in = (*in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;V(sem_full);i++;if (i > PRODUCT_NUM)break;}return 0;}
consumer.c
#include "pv.h"intmain (){int sem_empty, sem_full;key_t key[2];//ftok - convert a pathname and a project identifier to a System V IPC keykey[0] = ftok ("file_for_key", 1);key[1] = ftok ("file_for_key", 2);printf ("key: %x %x\n", key[0], key[1]);/*semget - get a System V semaphore set identifierRETURN VALUEIf successful, the return value will be the semaphore set identifier (a non‐negative integer), otherwise, -1 is returned, with errno indicating theerror.*/sem_empty = semget (key[0], 0, 0);sem_full = semget (key[1], 0, 0);if (sem_empty < 0 || sem_full < 0){printf ("There are not sem_empty or sem_full!\n");exit(1);}int shm_id = shmget (key[0], 0, 0);if (shm_id)printf ("shm id is %d\n", shm_id);else{printf ("Key %d have not SHARE MEMORY!\n", key[0]);exit(1);}int *buffer;int *in;int *out;/*shmat, shmdt - System V shared memory operationsRETURN VALUEOn success, shmat() returns the address of the attached shared memory seg‐ment; on error, (void *) -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate thecause of the error.*/in = (int *) shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0);out = in + 1;buffer = out + 1;int i = 0;/*producer的过程:1. 对信号量sem_empty执行P操作2. 向缓冲区中in指针的位置放入一个随机数并打印3. 把in指针向前移动一个单位4. 对信号量sem_full执行V操作5. 计数器加16. 如此往复, 直到生产完成指定数量为止*/while (1){P(sem_empty);buffer[*in] = random() % 1000;printf ("%d\n", buffer[*in]);*in = (*in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;V(sem_full);i++;if (i > PRODUCT_NUM)break;}return 0;}
makefile
all: sem_init producer consumerpv.o: pv.cgcc -Wall -O2 -c pv.csem_init: sem_init.cgcc -Wall -O2 sem_init.c -o sem_initproducer: producer.c pv.ogcc -Wall -O2 producer.c pv.o -o producerconsumer: consumer.c pv.ogcc -Wall -O2 consumer.c pv.o -o consumerclean:rm -f pv.o sem_init producer consumer \sem_init.c~ producer.c~ consumer.c~ pv.c~ pv.h~
