@yangfch3
2017-01-18T08:23:49.000000Z
字数 5042
阅读 4240
Shell 编程 - 02
shell
接前文:Shell 编程 - 01
01 篇介绍的是基础知识:
- 变量
- 运算符
- 数据类型
本章介绍其他语法与流程结构
echo - 回显
echo 用于在屏幕上打印出指定的字符串。
最好的理解 echo 的方法就是:
mouth=8echo "${mouth}-1-2009"echo "OK!\n"echo "It is a test" > myfileecho '$name\"' # 注意单引号echo `date`
在 "" 内可以使用 $()(推荐) 或 `` 包裹命令
echo "There are $(ls | wc -l) items here."
printf - 格式化输出
printf 命令用于格式化输出,是 echo 命令的增强版。它是 C 语言 printf() 库函数的一个有限的变形
# format-string为双引号$ printf "%d %s\n" 1 "abc"1 abc# 单引号与双引号效果一样$ printf '%d %s\n' 1 "abc"1 abc# 没有引号也可以输出$ printf %s abcdefabcdef# 格式只指定了一个参数,但多出的参数仍然会按照该格式输出,format-string 被重用$ printf %s abc defabcdef$ printf "%s\n" abc defabcdef$ printf "%s %s %s\n" a b c d e f g h i ja b cd e fg h ij# 如果没有 arguments,那么 %s 用NULL代替,%d 用 0 代替$ printf "%s and %d \n"and 0# 如果以 %d 的格式来显示字符串,那么会有警告,提示无效的数字,此时默认置为 0$ printf "The first program always prints'%s,%d\n'" Hello Shell-bash: printf: Shell: invalid numberThe first program always prints 'Hello,0'
if - 条件分支
三种 if :
- if ... fi 语句;
- if ... else ... fi 语句;
- if ... elif ... else ... fi 语句。
if ... else 语句的语法:
if [ expression ]thenStatement(s) to be executed if expression is truefi
if ... else ... fi 语句的语法:
if [ expression ]thenStatement(s) to be executed if expression is trueelseStatement(s) to be executed if expression is not truefi
if ... elif ... fi 语句可以对多个条件进行判断,语法为:
if [ expression 1 ]thenStatement(s) to be executed if expression 1 is trueelif [ expression 2 ]thenStatement(s) to be executed if expression 2 is trueelif [ expression 3 ]thenStatement(s) to be executed if expression 3 is trueelseStatement(s) to be executed if no expression is truefi
单行书写,使用 ; 分隔
if test $[2*3] -eq $[1+5]; then echo 'The two numbers are equal!'; fi;
凡是使用分行的情况都可以使用
;连为一行
if ... else 语句也经常与 test 命令结合使用,如下所示:
num1=$[2*3]num2=$[1+5]if test $[num1] -eq $[num2]thenecho 'The two numbers are equal!'elseecho 'The two numbers are not equal!'fi
case - 分支简写
case...esac 用于简写分支(不需要那么多 if)
case 值 in模式1)command1command2command3;;模式2)command1command2command3;;*)command1command2command3;;esac
option="${1}"case ${option} in-f) FILE="${2}"echo "File name is $FILE";;-d) DIR="${2}"echo "Dir name is $DIR";;*)echo "`basename ${0}`:usage: [-f file] | [-d directory]"exit 1 # Command to come out of the program with status 1;;esac
运行输出:
$./test.shtest.sh: usage: [ -f filename ] | [ -d directory ]$ ./test.sh -f index.htm$ vi test.sh$ ./test.sh -f index.htmFile name is index.htm$ ./test.sh -d unixDir name is unix
for - 循环
遍历参数序列
for 变量 in 参数序列docommand1command2...commandNdone
其中参数序列的写法:
{m..n}:表示从 m 到 n 的数值区间x y z:表示 x y z 三个值做为遍历时的参数
区间循环
for ((a=1; a <= 3; a++))docommand1command2done
例如:
for loop in 1 2 3 4 5doecho "The value is: $loop"donefor str in 'This is a string'doecho $strdonefor FILE in $HOME/.bash*doecho $FILEdone
while - 条件循环
语法格式:
while [command] # 这里的 command 与 if 哪里的条件语句一样doStatement(s) to be executed if command is truedone
例如:条件递增
COUNTER=0while [ $COUNTER -lt 5 ]doCOUNTER='expr $COUNTER+1'echo $COUNTERdone
例如:读取键盘信息。下面的例子中,输入信息被设置为变量FILM,按 Ctrl-D 结束循环
echo 'type <CTRL-D> to terminate'echo -n 'enter your most liked film: 'while read FILMdoecho "Yeah! great film the $FILM"done
until - 寻真循环
until 循环执行一系列命令直至条件为 true 时停止。until 循环与 while 循环在处理方式上刚好相反。
until commanddoStatement(s) to be executed until command is truedone
break continue - 调出循环
用在循环内,break, continue 用于跳出循环。break 是完全的跳出并结束循环,continue 是跳出当前,后面还没完成的循环还会继续。
不像 JS 中的 lable,break 后面可以接数值,用于表示调出循环的层级。如果没有接数值则表示跳出当前层循环。continue 后同样可以接数值。
for var1 in 1 2 3dofor var2 in 0 5doif [ $var1 -eq 2 -a $var2 -eq 0 ]thenbreak 2elseecho "$var1 $var2"fidonedone
while :doecho -n "Input a number between 1 to 5: "read aNumcase $aNum in1|2|3|4|5) echo "Your number is $aNum!";;*) echo "You do not select a number between 1 to 5!"continueecho "Game is over!";;esacdone
function - 函数
其实 bash 许多命令的本质就是一个函数,利用函数我们能拆解一个复杂功能为小模块,达到原子代码的复用。
# 形式1:直接函数名,无关键字function_name () {list of commands[ return value ]}# 形式2:function 关键字function function_name () {list of commands[ return value ]}
Shell 函数必须先定义后使用。
函数的返回值:可以显式增加 return 语句;如果不加,会将最后一条命令运行结果作为返回值。
Shell 函数返回值只能是整数,一般用来表示函数执行成功与否,0表示成功,其他值表示失败。
如果 return 其他数据,比如一个字符串,往往会得到错误提示:“numeric argument required”。
函数调用
只需要给出函数名,不需要加括号。在调用函数时可以在函数名后面添加任意数量的参数,以空格间隔
function_namefunction_name var1 var2 var3
函数的嵌套
number_one () {echo "Url_1 is http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/shell/"number_two}number_two () {echo "Url_2 is http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/u/xitong/"}number_one
删除函数
unset .f function_name
函数的参数
- 不像其他语言,Shell 函数定义时,括号内不可以有任何参数
- 函数调用不会用到括号
函数调用时的传参:
funWithParam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 34 73
函数内部使用参数:$(n) 与特殊变量
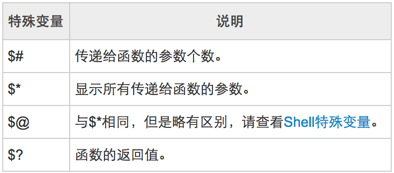
funWithParam(){echo "The value of the first parameter is ${1} !"echo "The value of the second parameter is ${2} !"echo "The value of the tenth parameter is $10 !" # 观察 $10 与 $(10) 的输出区别echo "The value of the tenth parameter is ${10} !"echo "The value of the eleventh parameter is ${11} !"echo "The amount of the parameters is $# !" # 参数个数echo "The string of the parameters is $* !" # 传递给函数的所有参数}
特殊变量:
输入输出重定向
输出重定向
>:暴力重定向>>:追加输出到文件尾
命令的输出不仅可以是显示器(标准输出回显),还可以很容易的转移向到文件,这被称为输出重定向。
which zsh > location.txtwhich bash >> location.txt
输入重定向
<:和输出重定向一样,Unix 命令也可以从文件获取输入。
echo < location.txt
高级重定向
(n, m 可以为 0, 1, 2,分别表示标准输入,标准输出,标准错误输出)
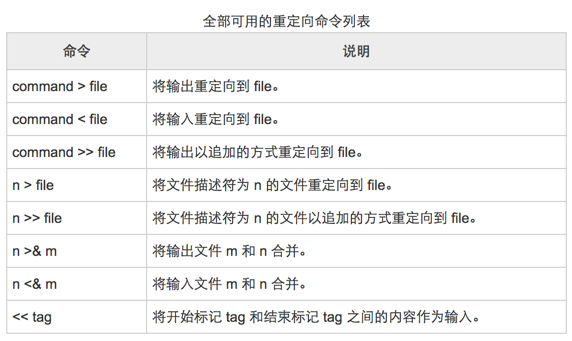
(这里的标准输入文件,标准输出文件,标准错误文件即上面的 0, 1, 2)
重定向高级一点的写法:
# 希望将 stdout 和 stderr 合并后重定向到 filecommand > file 2>&1# 对 stdin 和 stdout 都重定向command < file1 >file2
嵌入文档
<<delimiter:自定义的标志,常见EOF
command << delimiterdocumentdelimiter
它的作用是将两个 delimiter 之间的内容(document) 作为输入传递给 command。
例如:
$wc -l << EOFThis is a simple lookup programfor good (and bad) restaurantsin Cape Town.EOF3
文件包含
Shell 也可以包含外部脚本,将外部脚本的内容在当前脚本执行
#### subscript.shurl="http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/view/2738.html"#### main.sh. ./subscript.sh # subscript.sh 表示的是另外一个 shecho $url
