@zhuanxu
2018-02-23T09:42:56.000000Z
字数 4768
阅读 2655
深度学习实战第四课
fast-ai
上来先是前3课学生做的一些优秀笔记:
- Improving the way we work with learning rate
- The Cyclical Learning Rate technique
- Exploring Stochastic Gradient Descent with Restarts (SGDR)
- Transfer Learning using differential learning rates
- Getting Computers To See Better Than Humans
课程覆盖内容概览,当前在第4课。

Dropout [04:59]
learn = ConvLearner.pretrained(arch, data, ps=0.5, precompute=True)
- precompute=True:提前计算最后一个卷基层的激活输出,并将其做cache,显著加快训练速度。
learn
Sequential(
(0): BatchNorm1d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(1): Dropout(p=0.5)
(2): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=512)
(3): ReLU()
(4): BatchNorm1d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5)
(6): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=120)
(7): LogSoftmax()
)
- learn:输出我们在卷基层后加入的网络,上面显示的是precompute=True时,我们需要训练的网络层
(0), (4):BatchNorm将会在最后一课讲述
(1), (5): Dropout
(2):Linear 全连接层
(3):ReLU 去除负值
(6): Linear 第二个全连接层,输出为类别数
7): LogSoftmax 通过log提高运算精度
什么是 Dropout 和 p? [08:17]
Dropout(p=0.5)
p代表我们需要随机丢弃的激活层输出,p=0.5 表示我们随机丢弃50%的输出,Dropout是一种防止过拟合的正则化方法。
注意
- 默认情况下第一层的p=0.25,第二层是0.5[17:54],如果我们训练中发现过拟合,尝试增大p到0.5,如果还是过拟合则到0.7。
- ResNet34 相对来说网络层数少,还不是很复杂,我们可以使用默认的dropout,但是像ResNet50,如果出现过拟合,我们将调大dropout。
为什么我们在实际训练中经常发现val-loss小于train-loss的情况,特别是在训练刚开始的时候?因为我们在做 inference 的时候,dropout=0,即利用了所有信息。
在fast.ai中我们通过参数ps来设置新增网络的层的dropout,我们不会去改变pre-trained网络的dropout,因为这些都是已经训练好的了。
learn = ConvLearner.pretrained(arch, data, ps=0.5, precompute=True)
我们可以设置ps=0,但是会发现训练几个epoch后就会出现过拟合现象(training loss ≪ validation loss):
[2. 0.3521 0.55247 0.84189]
当ps=0.的时候,Dropout都不会加进模型中:
Sequential(
(0): BatchNorm1d(4096, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=512)
(2): ReLU()
(3): BatchNorm1d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(4): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=120)
(5): LogSoftmax()
)
我们可以发现上面我们默认添加了2个全连接层,我们可以通过参数xtra_fc来控制。
learn = ConvLearner.pretrained(arch, data, ps=0., precompute=True,
xtra_fc=[]); learn
Sequential(
(0): BatchNorm1d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=120)
(2): LogSoftmax()
)
learn = ConvLearner.pretrained(arch, data, ps=0., precompute=True,
xtra_fc=[700, 300]); learn
Sequential(
(0): BatchNorm1d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=700)
(2): ReLU()
(3): BatchNorm1d(700, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(4): Linear(in_features=700, out_features=300)
(5): ReLU()
(6): BatchNorm1d(300, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(7): Linear(in_features=300, out_features=120)
(8): LogSoftmax()
)
问题:我们是否可以设置不同的dropout,当时可以,通过参数ps来控制。
learn = ConvLearner.pretrained(arch, data, ps=[0., 0.2],
precompute=True, xtra_fc=[512]); learn
Sequential(
(0): BatchNorm1d(4096, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=512)
(2): ReLU()
(3): BatchNorm1d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True)
(4): Dropout(p=0.2)
(5): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=120)
(6): LogSoftmax()
)
- 我们没有什么理论来指导我们是前面的层dropout大还是后面的层大
- 当我们不确定的时候,我们最好使用相同的dropout
- 一般只在最后一层设置Dropout
结构化、时序数据学习[25:03]
有两种类别的列数据:
- 类别(Categorical):一般有不同的level
- 连续(continuous):一般是浮点数
- 像 Year , Month 这种整数,我们可以将其看做连续也可以是类别,如果是类别,那就是告诉神经网络Year的不同值是完全不同的,而如果是连续,则是找到一个函数进行fit,更具体的解释可以看到之前的文章为什么要做one-hot
- 选择Categorical和continuous是需要在建模阶段做出的决策,一般来说如果数据是Categorical的,那就是Categorical,如果数据是continuous的,我们需要决定是continuous还是Categorical
- 一般来说,如果值是浮点型,我们很难将其转换为Categorical(我们将类别的数目称为 Cardinality)
Categorical 变量 [50:49]
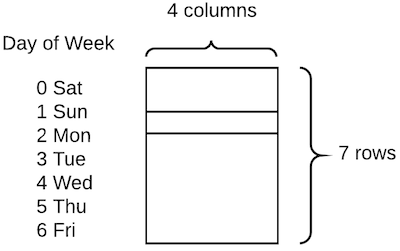
通过embed方式,我们将DayOfWeek由一个number转换为了一个4维向量。
问题:我们怎么去选择embed size?
cat_sz = [(c, len(joined_samp[c].cat.categories)+1)for c in cat_vars]cat_sz[('Store', 1116),('DayOfWeek', 8),('Year', 4),('Month', 13),('Day', 32),('StateHoliday', 3),('CompetitionMonthsOpen', 26),('Promo2Weeks', 27),('StoreType', 5),('Assortment', 4),('PromoInterval', 4),('CompetitionOpenSinceYear', 24),('Promo2SinceYear', 9),('State', 13),('Week', 53),('Events', 22),('Promo_fw', 7),('Promo_bw', 7),('StateHoliday_fw', 4),('StateHoliday_bw', 4),('SchoolHoliday_fw', 9),('SchoolHoliday_bw', 9)]
- 上面我们列举出了所有的categorical variable 和它的 cardinality
- 我们每个类别都加了一个1,目的是如果该列出现空值,可以用0表示
- 选择 embed size 的经验是:将 cardinality / 2,最大不超过50
emb_szs = [(c, min(50, (c+1)//2)) for _,c in cat_sz]
问题:embeddings 适合所有的 categorical variable 嘛?
假设我们有 600,000 行数据,并且某列特征有 600,000 个不同值,此时是非常不好的 categorical variable。
问题:我们如何处理dates and times类型的数据?
add_datepart(weather, "Date", drop=False)add_datepart(googletrend, "Date", drop=False)add_datepart(train, "Date", drop=False)add_datepart(test, "Date", drop=False)
fastai中有个add_datepart函数,能够将一个时间列转换为多个列。
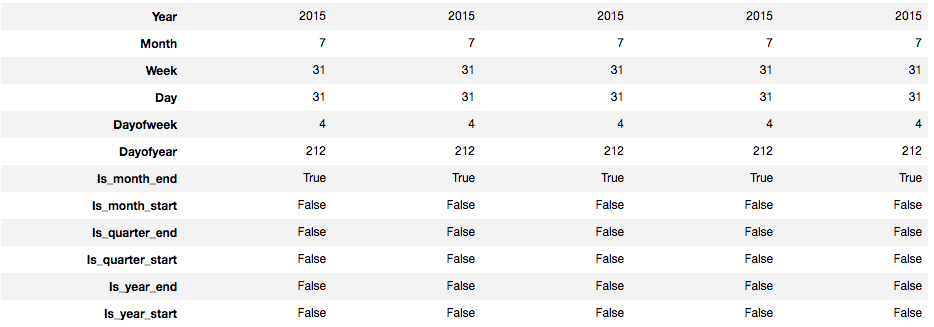
举个例子来说明这么处理的好处,假设我们发现数据有周期性的特征,在Mondays上升,Wednesdays下降,如果没有dayOfWeek特征,我们很难让网络自己去根据2018-02-23去学习出来,但是有了dayOfWeek就容易很多。
下面总结下整个处理过程:
1.列举出所有 categorical variable 和 continuous variable 的名字,将其放入 Pandas data frame
2.创建 validation set 的 indexes
3.调用如下代码:
md = ColumnarModelData.from_data_frame(PATH, val_idx, df,yl.astype(np.float32), cat_flds=cat_vars, bs=128,test_df=df_test)
4.计算出每个 categorical variable 的 Embed size
5.调用 get_learner
m = md.get_learner(emb_szs, len(df.columns)-len(cat_vars), 0.04, 1,[1000,500], [0.001,0.01], y_range=y_range)
6.调用m.fit
本文是 fastai 课程的第四课结构化处理部分,欢迎持续关注。
你的鼓励是我继续写下去的动力,期待我们共同进步。

