@mShuaiZhao
2018-03-14T10:11:37.000000Z
字数 2058
阅读 563
Statistics with R Part01Week01
Coursera 2018.01
Designing Studies
1. Introduction
- populations and samples
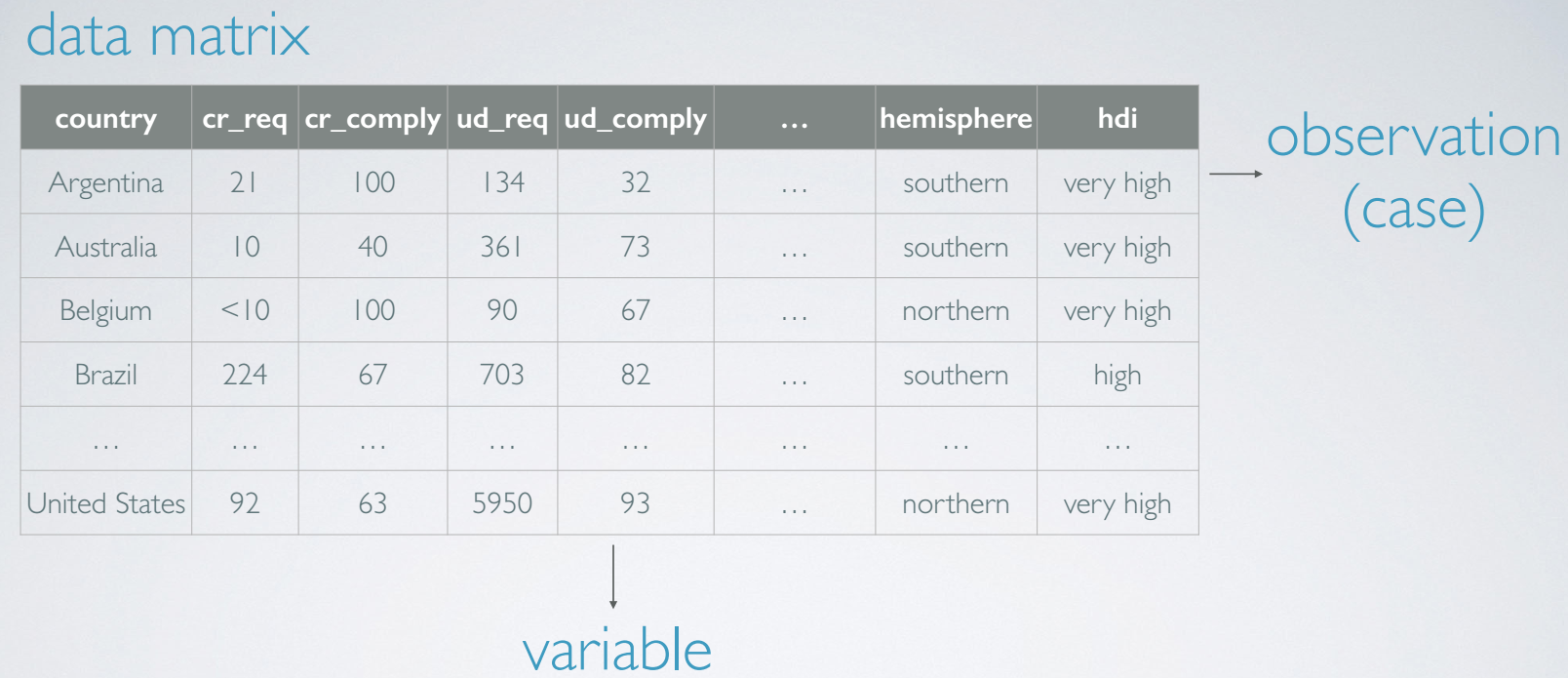
2. Data Basics
data matrix
observation(case)
variable
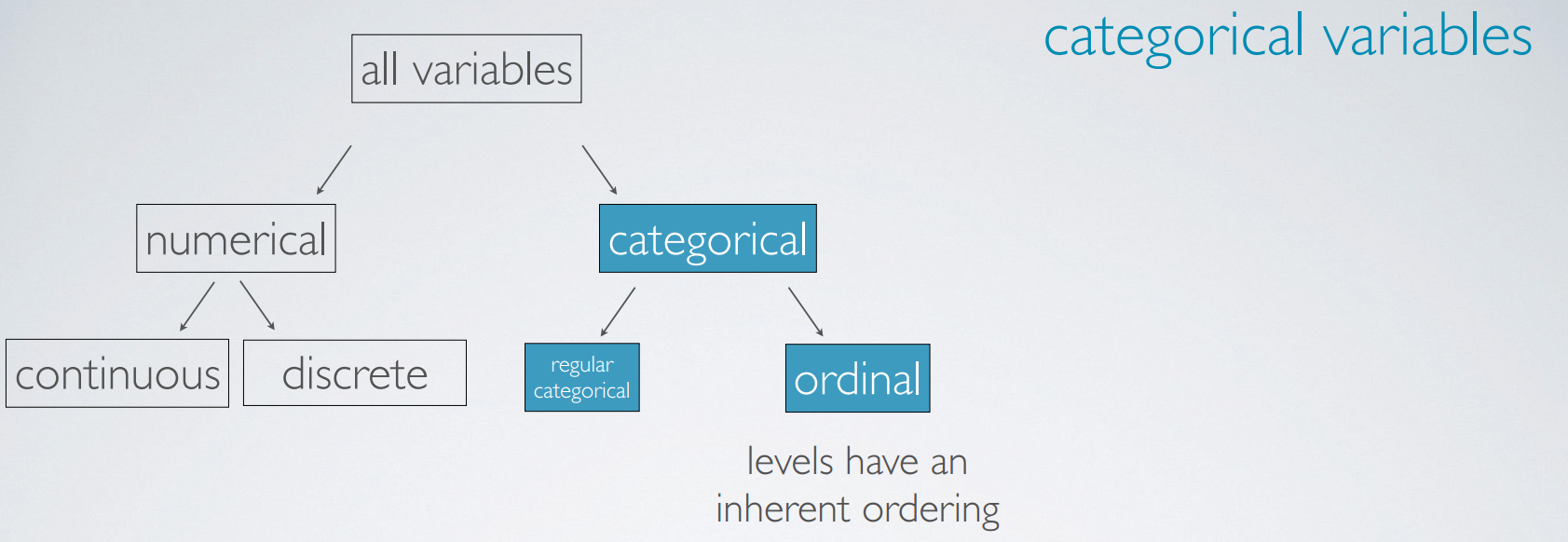
types of variables
relationships between variables
Two variables that show some connection with one another are called associated (dependent).
Association can be further described as positive or negative.
If two variables are not associated, they are said to be independent.
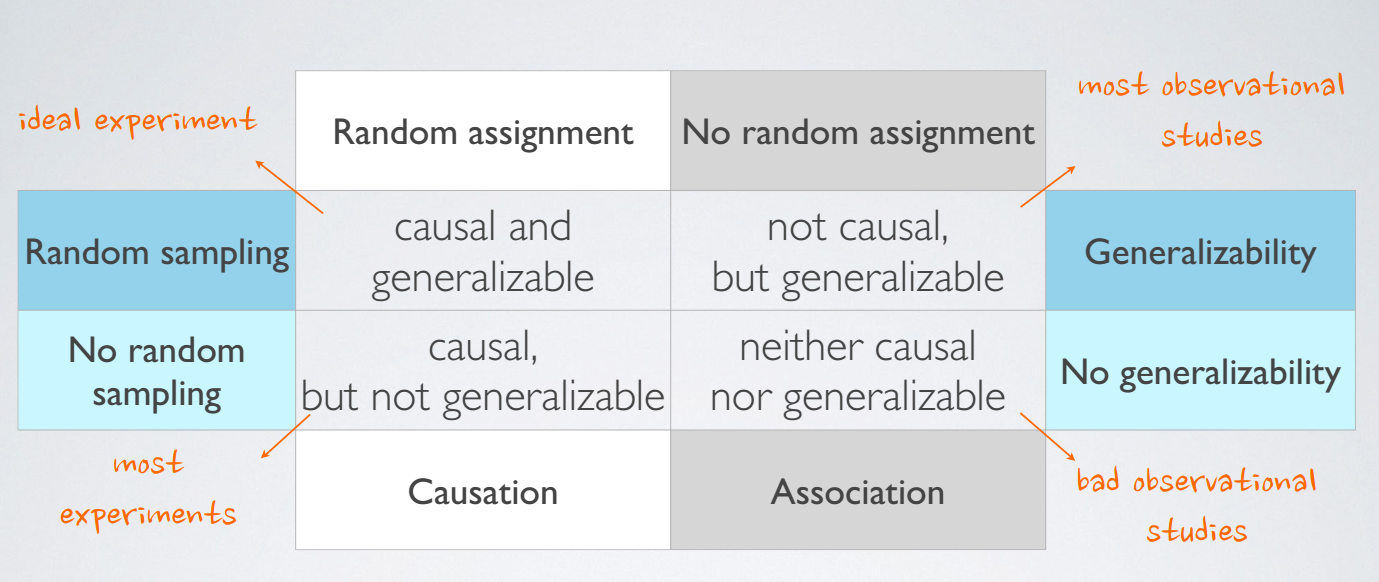
3. observational studies & experiments
define observational studies and experiments
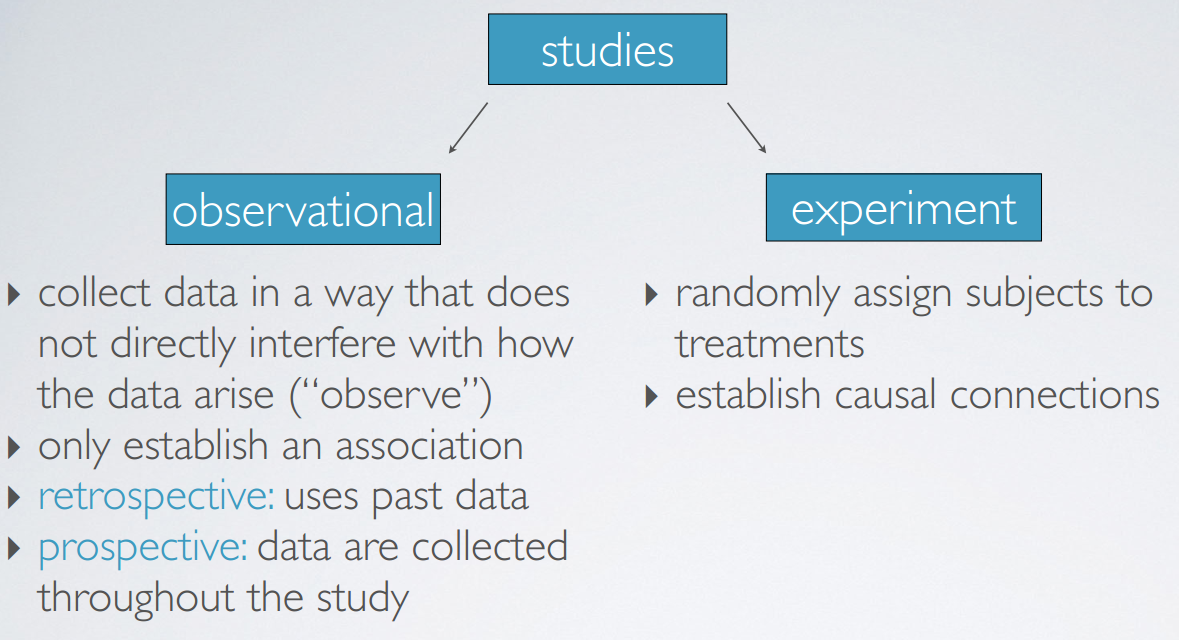
最主要的区别是experiments利用了random assignment
observational study就是只是观察,得到observationconfounding variables
extraneous variables that affect both the explanatory and the response variable,
and that make it seem like there is a relationship between themcorrelation does not imply causation
两个事件或变量相关并意味着,他们之间一定存在着因果(causation)关系。
4. sampling & sources of bias
Why sampling?
我们为什么要采样呢?
考虑人口普查。第一很难,非法移民之类;第二人口总数(总体)并不是stand still。
a few sources of sampling bias
Convenience sample
Individuals who are easily accessible are more likely to be included in the sample
Non-response
If only a (non-random) fraction of the randomly sampled people respond to a survey such that the sample is no longer representative of the population
随机采样对的样本中一部分不给于回应。
Voluntary response
Occurs when the sample consists of people who volunteer to respond because they have strong opinions on the issue
这些都导致样本并不具有代表性,并不能代表总的样本
sampling methods
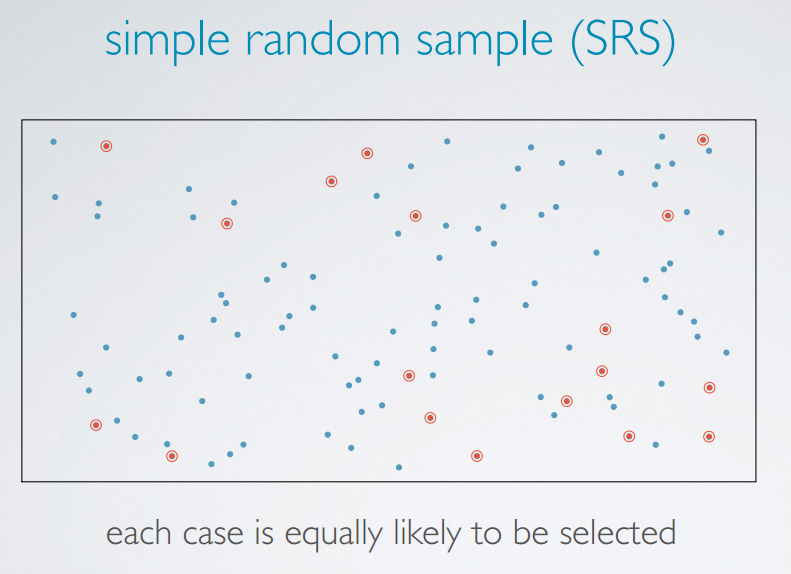
simple random sample (SRS)
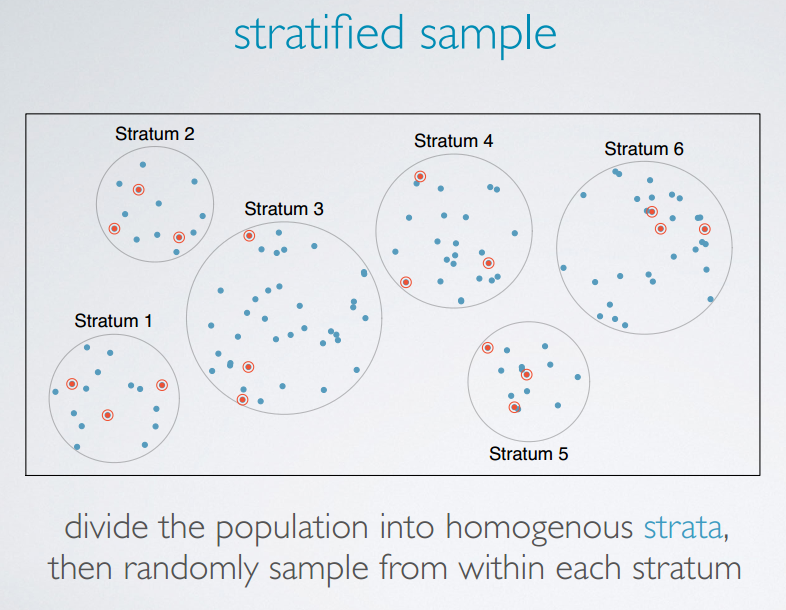
stratified sample
分层采样
例如把受采样的人群分为男\女分别采样。
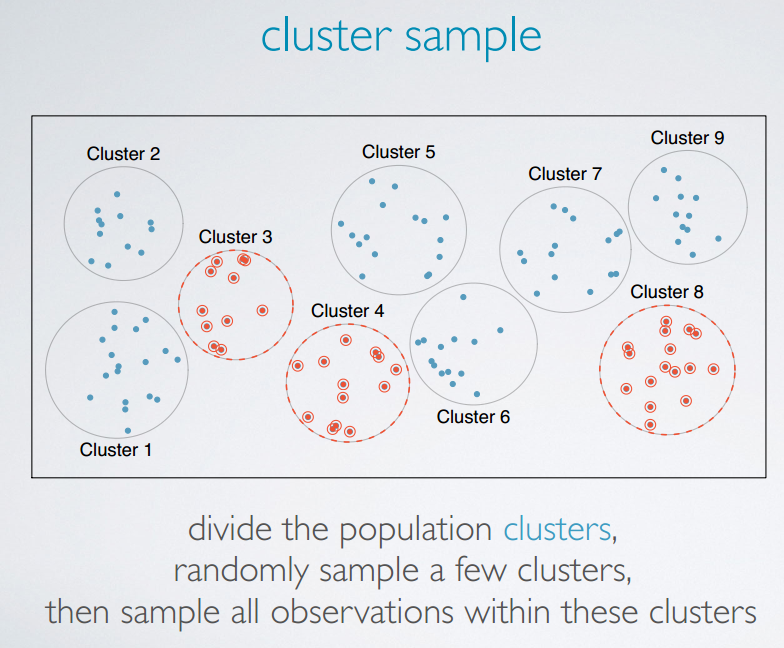
cluster sample
heterogeneous
The clusters, unlike strata and stratified sampling, are heterogeneous within themselves, and each cluster is similar to another, such that we can get away with just sampling from a few of the clusters.
multistage sample
基于cluster sample的基础之上,每个cluster中随机选择一些样本。
例如:将城市划分为多个区域,在每个区域中随机选择一些样本。

5. experimental design
principles of experimental design
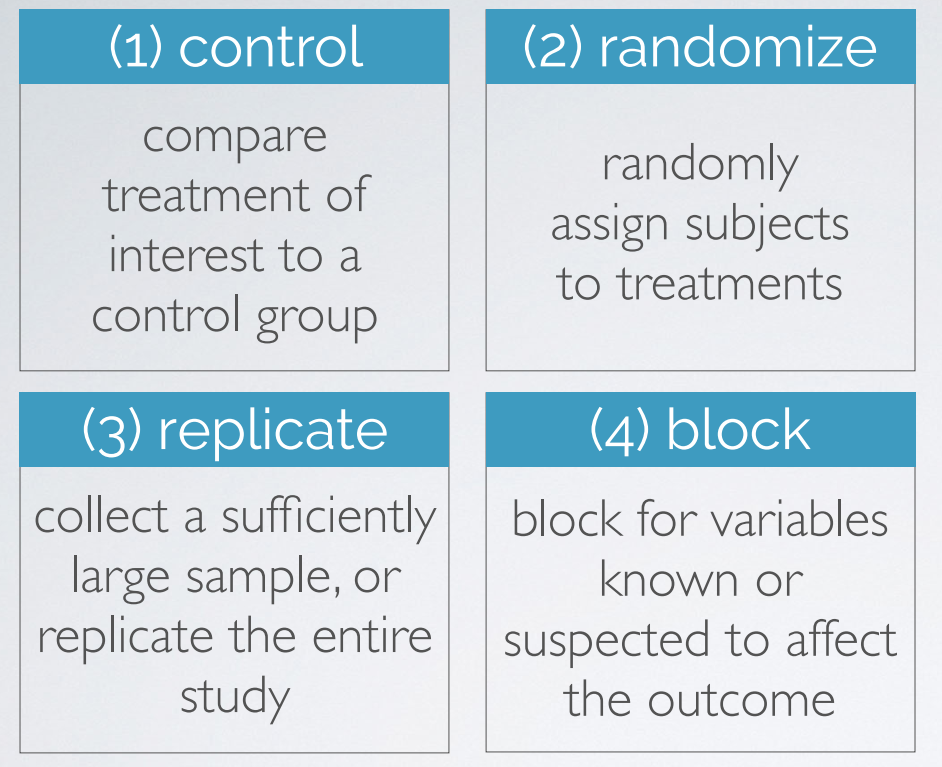
blocking vs. explanatory variables
explanatory variables (factors) - conditions we can impose on experimental units
blocking variables - characteristics that the experimental units come with, that we would like to control for

experimental terminology
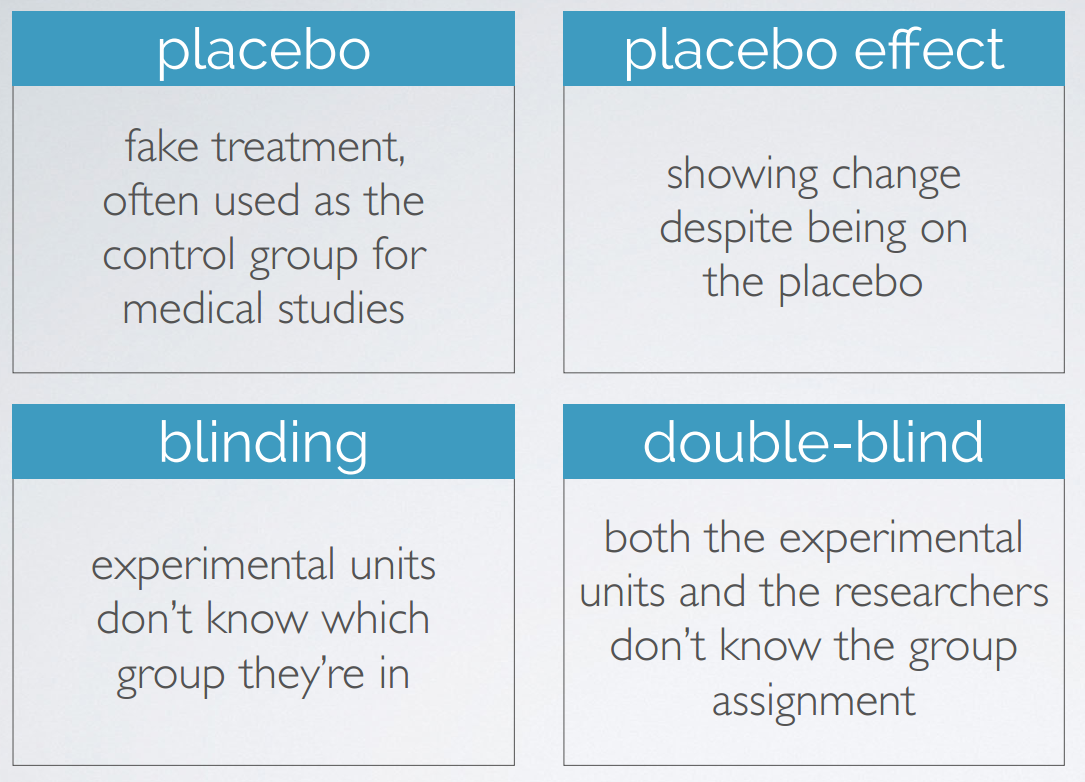
6. random sampling vs. assignment